Related Research Articles

The Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad (CMStP&P), better known as the Milwaukee Road, was a Class I railroad that operated in the Midwest and Northwest of the United States from 1847 until 1986.

The Northern Pacific Railway was a transcontinental railroad that operated across the northern tier of the western United States, from Minnesota to the Pacific Northwest. It was approved by Congress in 1864 and given nearly 40 million acres of land grants, which it used to raise money in Europe for construction.

The Dakota, Minnesota and Eastern Railroad is a wholly owned U.S. subsidiary of the Canadian Pacific Kansas City. Before its purchase, it was the largest Class II railroad in the United States, operating across South Dakota and southern Minnesota in the Northern Plains of the United States. Portions of the railroad also extended into Wyoming, Nebraska, Iowa, and Illinois. It interchanged with all seven U.S. Class I railroads.

The Minneapolis, Northfield and Southern Railway was an 87-mile (140 km) long American shortline railroad connecting Minneapolis and Northfield, Minnesota. It was incorporated in 1918 to take over the trackage of the former Minneapolis, St. Paul, Rochester and Dubuque Electric Traction Company, also known as the Dan Patch Lines. On June 2, 1982, it was acquired by the Soo Line Railroad, which operated it as a separate railroad until merging it on January 1, 1986, along with the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad.

Cedar Lake Trail is a 4.3-mile (6.9 km), shared-use path in the U.S. state of Minnesota, from downtown Minneapolis to the neighboring suburb of St. Louis Park. The trail begins at its eastern trailhead in downtown Minneapolis (44°59′11″N93°16′01″W) and continues west to Minnesota State Highway 100 in St. Louis Park (44°57′43″N93°20′36″W). At the trail's west end, a paved path continues for another 4.2 miles (6.8 km) through St. Louis Park to Hopkins under the former name of Hutchinson Spur Trail, but known as North Cedar Lake Regional Trail since 2009. In 2019, large portions of the Cedar Lake Trail were closed due to construction of the Southwest LRT extension with expected reopening in 2021 or 2022.

The Minneapolis and St. Louis Railway (M&StL) was an American Class I railroad that built and operated lines radiating south and west from Minneapolis, Minnesota for 90 years from 1870 to 1960. The railway never reached St. Louis but its North Star Limited passenger train ran to that city via the Wabash Railroad.
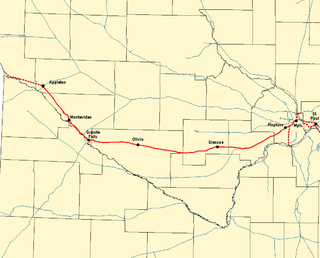
The Twin Cities and Western Railroad is a railroad operating in the U.S. state of Minnesota which started operations on July 27, 1991. Trackage includes the former Soo Line Railroad "Ortonville Line", originally built as the first part of the Pacific extension of the Milwaukee Road. This main line extends from Hopkins, Minnesota ,to Appleton, Minnesota. The line was originally built between Hopkins and Cologne, Minnesota, in 1876 by Hastings and Dakota Railroad. In 1913, the Milwaukee Road rerouted it, reducing the curves. The line was eventually extended to the Pacific.

The Minnesota Northern Railroad is a Class III shortline railroad that operates over 224 miles (360 km) of track in northwestern Minnesota. The railroad is co-owned by KBN Incorporated and Independent Locomotive Service and is headquartered in Crookston, Minnesota.

The St. Croix Valley Railroad is a Class III short line railroad that operates over 36 miles of track in eastern Minnesota. The railroad is owned by KBN Incorporated jointly between Independent Locomotive Service of Bethel MN and Midwest Locomotive Services of Atwater MN, with the railroad headquartered in Rush City, Minnesota.

The Northern Plains Railroad is a short line railroad that operates over 344 miles (554 km) of track in the northern U.S. state of Minnesota and the northern U.S. state of North Dakota.

The Iowa Northern Railway is a Class III shortline railroad operating in the U.S. state of Iowa.

The Minneapolis, St. Paul and Sault Ste. Marie Railroad (MStP&SSM) was a Class I railroad subsidiary of the Canadian Pacific Railway in the Midwestern United States. Commonly known since its opening in 1884 as the Soo Line after the phonetic spelling of Sault, it was merged with several other major CP subsidiaries on January 1, 1961, to form the Soo Line Railroad.

Wayzata station is a historic train depot in Wayzata, Minnesota, United States. Constructed and operated by the Great Northern Railway, the station was in service from 1906 until 1971. The depot is positioned along Lake Minnetonka in downtown Wayzata with steps leading down to the lakeshore. Although no longer transporting passenger trains, the BNSF Railway line going through Wayzata is still active today.
The following is a brief history of the North American rail system, mainly through major changes to Class I railroads, the largest class by operating revenue.

The Burlington, Cedar Rapids and Northern Railway (BCR&N) was a railroad that operated in the United States from 1876 to 1903. It was formed to take over the operations of the bankrupt Burlington, Cedar Rapids and Minnesota Railway, which was, in turn, the result of merging several predecessor lines, the construction of which began in 1869. The corporate headquarters were in Cedar Rapids, Iowa, and it had operations in Iowa and in Minnesota. It was succeeded by the Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railway.

The Wayzata Subdivision or Wayzata Sub is a railway line that runs about 93 miles (150 km) from Willmar to Minneapolis, Minnesota. Currently operated by BNSF Railway, this was part of the Great Northern Railway's transcontinental line from Minneapolis to Seattle, Washington. Today, BNSF's Northern Transcon travels up the Staples Subdivision instead, which is a more direct route to Fargo, North Dakota. West of Target Field station the Wayzata Sub sees about 4-6 trains a day, consisting of manifest, grain, and ethanol traffic. The Wayzata Sub also occasionally sees other commodities such as coal and oil trains, and can sometimes receive intermodal or Amtrak reroutes when needed.
The MN&S Spur is a 18.5-mile (29.8 km) railroad line operated by the Progressive Rail Inc. The route runs through suburbs immediately west of Minneapolis, Minnesota, from MN&S Junction in Crystal south to Auto Club Junction in Bloomington near the Minnesota River. This path is parallel to Minnesota State Highway 100, which is about half a mile east of the rail line.
The Bass Lake Spur is a railroad line owned by the Canadian Pacific Railway that runs 6.8 miles (10.9 km) from Minneapolis, Minnesota west to the suburb of Minnetonka. The primary operator on the line is the Twin Cities and Western Railroad which has trackage rights on the entire line and uses it to run trains from their main line to BNSF Railway's Wayzata Subdivision.
The Dakota Rail Trail runs 28.1 miles (42.6 km) from Wayzata to Lester Prairie, Minnesota. It is on part of the former track bed of the Hutchinson Spur of the Great Northern Railway. The railway line helped bring wheat and raw materials from Central Minnesota to the flour mills, factories and warehouses in Minneapolis from 1885 until 2001. The railway line, from which there are views of the countryside, was also designed to bring tourists to the communities on Lake Minnetonka in the late 1880s.
The Winona and St. Peter Railroad was a railroad in the Midwestern United States. It was founded in 1861 in Winona, Minnesota. The first 11 miles (18 km) from Winona to Stockton, Minnesota, were completed by the end of 1862, making the it the second operational railroad in Minnesota, after the St. Paul and Pacific Line from Saint Paul to St. Anthony Falls.
References
- ↑ Gale, Dennis (March 14, 1982). "Branch line sale could be confirmed soon line". Rapid City Journal . p. 42. Retrieved May 3, 2018– via Newspapers.com.

- ↑ Gale, Dennis (June 5, 1982). "Dakota Rail buys Milwaukee branch line". Rapid City Journal . p. 5. Retrieved May 3, 2018– via Newspapers.com.

- ↑ "Dakota Rail operation is looking better". Sioux City Journal . November 22, 1984. p. 48. Retrieved May 3, 2018– via Newspapers.com.

- ↑ Hillinger, Charles (April 13, 1986). "Workin' the short line". Billings Gazette . p. 39. Retrieved May 3, 2018– via Newspapers.com.

- ↑ Lewis, Edward A. (1991). American Shortline Railway Guide (4th ed.). Waukesha, WI: Kalmbach Publishing. p. 77. ISBN 0-89024-109-0. OCLC 25150373.
- ↑ "RailAmerica acquires Prairie Holding". The Palm Beach Post . September 9, 1995. p. 27. Retrieved May 3, 2018– via Newspapers.com.
