
Utopia Planitia is a large plain within Utopia, the largest recognized impact basin on Mars and in the Solar System with an estimated diameter of 3,300 km (2,100 mi). It is the Martian region where the Viking 2 lander touched down and began exploring on September 3, 1976, and the Zhurong rover touched down on May 14, 2021, as a part of the Tianwen-1 mission. It is located at the antipode of Argyre Planitia, centered at 46.7°N 117.5°E. It is also in the Casius quadrangle, Amenthes quadrangle, and the Cebrenia quadrangle of Mars. The region is in the broader North Polar/Borealis Basin that covers most of the Northern Hemisphere of Mars.

The Des Plaines crater or Des Plaines disturbance is recognized as an impact crater in Cook County, Illinois, United States. It is located beneath the eastern part of the city of Des Plaines, which is a suburb of Chicago.

Einstein is a large lunar impact crater that lies along the western limb of the Moon, which makes it difficult to observe from the Earth. The visibility of this formation is subject to libration effects, but even under the best conditions not much detail can be observed except from lunar orbit. Nearby craters of note include Moseley just to the north, Dalton along the eastern rim, Vasco da Gama just to the southeast, and Bohr to the south-southeast. The formation Vallis Bohr is visible to the south.

Degas is a rayed crater on Mercury at latitude 37.5 N, longitude 127 W. Its diameter is 54 kilometres (34 mi). It was named after the French impressionist painter Edgar Degas in 1979. The rays consist of light colored material blasted out during the crater's formation. Craters older than Degas are covered by the ray material, while younger craters are seen superimposed on the rays. Degas forms a crater pair with Brontë to the north. Both lie near the center of Sobkou Planitia.
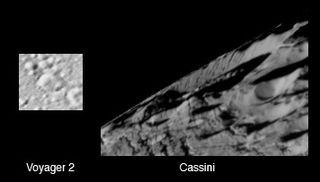
Duban is a crater in the northern hemisphere of Saturn's moon Enceladus. Duban was first seen in Voyager 2 images, though the crater has also been seen in much higher resolution Cassini images. It is located at 58.38°N 282.91°W and is 19 kilometers across. In the Cassini image, evidence for significant tectonic deformation can be seen along the northwest rim of the crater.

Tempe Terra is a heavily cratered highland region in the northern hemisphere of the planet Mars. Located at the northeastern edge of the Tharsis volcanic province, Tempe Terra is notable for its high degree of crustal fracturing and deformation. The region also contains many small shield volcanoes, lava flows, and other volcanic structures.

S P Crater is a cinder cone volcano in the San Francisco volcanic field, 25 miles (40 km) north of Flagstaff, Arizona, United States. It is surrounded by several other cinder cones which are older and more eroded. It is a striking feature on the local landscape, with a well-defined lava flow that extends for 4.3 miles (7 km) to the north. American astronauts use the crater to train for moonwalking.

Balch is a crater on Venus at latitude 29.9, longitude 282.9 in Devana Chasma, Central Beta Regio. It is 40 km in diameter and named after Emily Balch, though it was originally designated Somerville crater. This crater is one of the few examples of tectonically modified craters seen on Venus. Approximately half the crater was subsumed into a valley. The absence of such craters indicates a possible cessation of tectonic deformation on Venus at some point in history.

The Noachis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Noachis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-27.

The Cebrenia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the northeastern portion of Mars' eastern hemisphere and covers 120° to 180° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Cebrenia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-7. It includes part of Utopia Planitia and Arcadia Planitia. The southern and northern borders of the Cebrenia quadrangle are approximately 3,065 km (1,905 mi) and 1,500 km (930 mi) wide, respectively. The north to south distance is about 2,050 km (1,270 mi). The quadrangle covers an approximate area of 4.9 million square km, or a little over 3% of Mars' surface area.

The Diacria quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the northwestern portion of Mars' western hemisphere and covers 180° to 240° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Diacria quadrangle is also referred to as MC-2. The Diacria quadrangle covers parts of Arcadia Planitia and Amazonis Planitia.

The Arabia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Arabia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-12.

The Amenthes quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Amenthes quadrangle is also referred to as MC-14. The quadrangle covers the area from 225° to 270° west longitude and from 0° to 30° north latitude on Mars. Amenthes quadrangle contains parts of Utopia Planitia, Isidis Planitia, Terra Cimmeria, and Tyrrhena Terra.

The Lunae Palus quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is also referred to as MC-10. Lunae Planum and parts of Xanthe Terra and Chryse Planitia are found in the Lunae Palus quadrangle. The Lunae Palus quadrangle contains many ancient river valleys.

The Ceraunius Fossae are a set of fractures in the northern Tharsis region of Mars. They lie directly south of the large volcano Alba Mons and consist of numerous parallel faults and tension cracks that deform the ancient highland crust. In places, younger lava flows cover the fractured terrain, dividing it into several large patches or islands. They are found in the Tharsis quadrangle.

Dalilah Muhammad is an American track and field athlete who specializes in the 400 meters hurdles. She is the 2016 Rio Olympics champion and 2020 Tokyo Olympics silver medalist, becoming at the latter the then-second-fastest woman of all time in the event with her personal best of 51.58 seconds. Muhammad was second at both the 2013 and 2017 World Championships to take her first gold in 2019, setting the former world record of 52.16 s. She was the second female 400 m hurdler in history, after Sally Gunnell, to have won the Olympic, World titles and broken the world record. At both the 2019 World Championships and Tokyo Games, she also took gold as part of women's 4 × 400 metres relay team.

Ashley Spencer is an American track and field athlete who competes in the 400 metres and the 400 metres hurdles. In the 400m hurdles, she is the 2016 Olympic bronze medalist. In the 400m, she is the 2012 World Junior Champion and the 2016 World Indoor silver medalist. She is coached by 1996 Olympic bronze medalist Tonya Buford-Bailey.

NASA's Magellan spacecraft mission discovered that Venus has a geologically young surface with a relatively uniform age of 500±200 Ma. The age of Venus was revealed by the observation of over 900 impact craters on the surface of the planet. These impact craters are nearly uniformly distributed over the surface of Venus and less than 10% have been modified by plains of volcanism or deformation. These observations indicate that a catastrophic resurfacing event took place on Venus around 500 Ma, and was followed by a dramatic decline in resurfacing rate. The radar images from the Magellan missions revealed that the terrestrial style of plate tectonics is not active on Venus and the surface currently appears to be immobile.
Irruputuncu is a volcano in the commune of Pica, Tamarugal Province, Tarapacá Region, Chile, as well as San Pedro de Quemes Municipality, Nor Lípez Province, Potosí Department, Bolivia. The mountain's summit is 5,163 m (16,939 ft) high and has two summit craters—the southernmost 200 m (660 ft)-wide one has active fumaroles. The volcano also features lava flows, block and ash flows and several lava domes. The volcano is part of the Andean Central Volcanic Zone (CVZ).
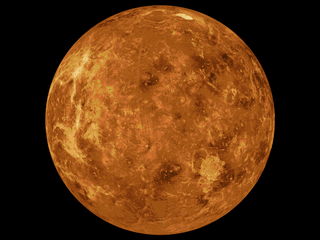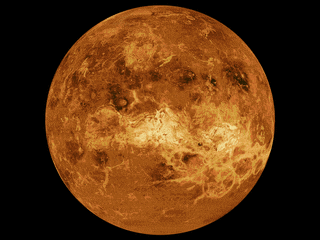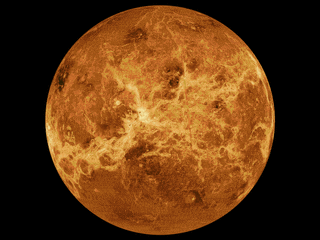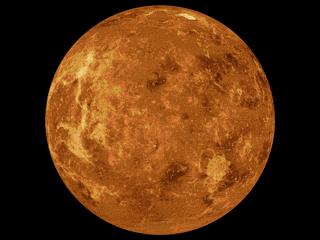
The mapping of Venus refers to the process and results of human description of the geological features of the planet Venus. It involves surface radar images of Venus, construction of geological maps, and the identification of stratigraphic units, volumes of rock with a similar age.




















