The ten Arabic numerals 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 are the most commonly used symbols for writing numbers. The term often also implies a positional notation using the numerals, as well as the use of a decimal base, in particular when contrasted with other systems such as Roman numerals. However, the symbols are also used to write numbers in other bases such as octal, as well as for writing non-numerical information such as trademarks or license plate identifiers.
The duodecimal system, also known as base twelve or dozenal, is a positional numeral system using twelve as its base. In duodecimal, the number twelve is denoted "10", meaning 1 twelve and 0 units; in the decimal system, this number is instead written as "12" meaning 1 ten and 2 units, and the string "10" means ten. In duodecimal, "100" means twelve squared, "1000" means twelve cubed, and "0.1" means a twelfth.
In mathematics and computing, the hexadecimal numeral system is a positional numeral system that represents numbers using a radix (base) of sixteen. Unlike the decimal system representing numbers using ten symbols, hexadecimal uses sixteen distinct symbols, most often the symbols "0"–"9" to represent values 0 to 9, and "A"–"F" to represent decimal values from ten to fifteen.
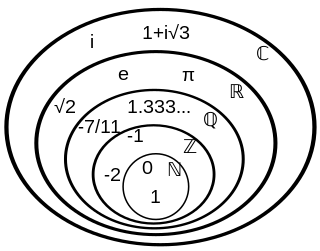
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can be represented by symbols, called numerals; for example, "5" is a numeral that represents the number five. As only a relatively small number of symbols can be memorized, basic numerals are commonly organized in a numeral system, which is an organized way to represent any number. The most common numeral system is the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, which allows for the representation of any non-negative integer using a combination of ten fundamental numeric symbols, called digits. In addition to their use in counting and measuring, numerals are often used for labels, for ordering, and for codes. In common usage, a numeral is not clearly distinguished from the number that it represents.
Scientific notation is a way of expressing numbers that are too large or too small to be conveniently written in decimal form, since to do so would require writing out an inconveniently long string of digits. It may be referred to as scientific form or standard index form, or standard form in the United Kingdom. This base ten notation is commonly used by scientists, mathematicians, and engineers, in part because it can simplify certain arithmetic operations. On scientific calculators, it is usually known as "SCI" display mode.
Sexagesimal, also known as base 60, is a numeral system with sixty as its base. It originated with the ancient Sumerians in the 3rd millennium BC, was passed down to the ancient Babylonians, and is still used—in a modified form—for measuring time, angles, and geographic coordinates.

Babylonian cuneiform numerals, also used in Assyria and Chaldea, were written in cuneiform, using a wedge-tipped reed stylus to print a mark on a soft clay tablet which would be exposed in the sun to harden to create a permanent record.

The modern 24-hour clock is the convention of timekeeping in which the day runs from midnight to midnight and is divided into 24 hours. This is indicated by the hours passed since midnight, from 00(:00) to 23(:59), with 24(:00) as an option to indicate the end of the day. This system, as opposed to the 12-hour clock, is the most commonly used time notation in the world today, and is used by the international standard ISO 8601.
A numerical digit or numeral is a single symbol used alone or in combinations, to represent numbers in a positional numeral system. The name "digit" comes from the fact that the ten digits of the hands correspond to the ten symbols of the common base 10 numeral system, i.e. the decimal digits.
In arithmetic, long division is a standard division algorithm suitable for dividing multi-digit Hindu-Arabic numerals that is simple enough to perform by hand. It breaks down a division problem into a series of easier steps.

Positional notation usually denotes the extension to any base of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. More generally, a positional system is a numeral system in which the contribution of a digit to the value of a number is the value of the digit multiplied by a factor determined by the position of the digit. In early numeral systems, such as Roman numerals, a digit has only one value: I means one, X means ten and C a hundred. In modern positional systems, such as the decimal system, the position of the digit means that its value must be multiplied by some value: in 555, the three identical symbols represent five hundreds, five tens, and five units, respectively, due to their different positions in the digit string.
Engineering notation or engineering form (also technical notation) is a version of scientific notation in which the exponent of ten is always selected to be divisible by three to match the common metric prefixes, i.e. scientific notation that aligns with powers of a thousand, for example, 531×103 instead of 5.31×105 (but on calculator displays written without the ×10 to save space). As an alternative to writing powers of 10, SI prefixes can be used, which also usually provide steps of a factor of a thousand. On most calculators, engineering notation is called "ENG" mode as scientific notation is denoted SCI.
Different conventions exist around the world for date and time representation, both written and spoken.
Date and time notation in the United States differs from that used in nearly all other countries. It is inherited from one historical branch of conventions from the United Kingdom. American styles of notation have also influenced customs of date notation in Canada, creating confusion in international commerce.
In Spain, date notation follows the DD/MM/YYYY format. Time notation depends on the level of formality and varies in written and spoken formats. Official time is given using the 24-hour clock, and the 12-hour clock is often used in informal speech.
Date and time notation in Sweden mostly follows the ISO 8601 standard: dates are generally written in the form YYYY-MM-DD. Although this format may be abbreviated in a number of ways, almost all Swedish date notations state the month between the year and the day. Months are not capitalised when written. The week number may also be used in writing and in speech. Times are generally written using 24-hour clock notation, with full stops as separators, although 12-hour clock notation is more frequently used in speech.
In Cyprus the all-numeric form for dates is in the little endianness order of "day month year". Years are written with either 2 or 4 digits. For example, either 24/5/2004 or 24/5/04. In the Turkish occupied part in Northern Cyprus, the traditional all-numeric form of writing Gregorian dates is the little-endian day.month.year order, using a dot on the line as the separator.
Date and time notation in Italy records the date using the day–month–year format. The time is written using the 24-hour clock (06:28); in spoken language and informal contexts the 12-hour clock is more commonly adopted, but without using "a.m." or "p.m." suffixes (6:28).

In Greece, the standard time is Eastern European Time. Daylight saving time, which moves one hour ahead to UTC+03:00 is observed from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October. Greece adopted EET in 1916.




