Related Research Articles

Proposition 209 is a California ballot proposition which,upon approval in November 1996,amended the state constitution to prohibit state governmental institutions from considering race,sex,or ethnicity,specifically in the areas of public employment,public contracting,and public education. Modeled on the Civil Rights Act of 1964,the California Civil Rights Initiative was authored by two California academics,Glynn Custred and Tom Wood. It was the first electoral test of affirmative action policies in North America. It passed with 55% in favor to 45% opposed,thereby banning affirmative action in the state's public sector.
Same-sex marriage has been legal in California since June 28,2013. The State of California first issued marriage licenses to same-sex couples from June 16,2008 to November 5,2008,a period of approximately 4 months,2 weeks and 6 days,as a result of the Supreme Court of California finding in the case of In re Marriage Cases that barring same-sex couples from marriage violated the Constitution of California. The issuance of such licenses was halted from November 5,2008 through June 27,2013 due to the passage of Proposition 8—a state constitutional amendment barring same-sex marriages. The granting of same-sex marriages recommenced following the U.S. Supreme Court's decision in Hollingsworth v. Perry,which restored the effect of a federal district court ruling that overturned Proposition 8 as unconstitutional.
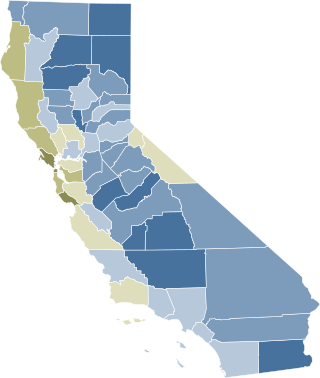
Proposition 8,known informally as Prop 8,was a California ballot proposition and a state constitutional amendment intended to ban same-sex marriage;it passed in the November 2008 California state elections and was later overturned in court. The proposition was created by opponents of same-sex marriage in advance of the California Supreme Court's May 2008 appeal ruling,In re Marriage Cases,which followed the short-lived 2004 same-sex weddings controversy and found the previous ban on same-sex marriage unconstitutional. Proposition 8 was ultimately ruled unconstitutional by a federal court in 2010,although the court decision did not go into effect until June 26,2013,following the conclusion of proponents' appeals.

The legality of abortion in the United States and the various restrictions imposed on the procedure vary significantly,depending on the laws of each state or other jurisdiction,although there is no uniform federal law. Some states prohibit abortion at all stages of pregnancy,with few exceptions;others permit it up to a certain point in a woman's pregnancy,while some allow abortion throughout a woman's pregnancy. In states where abortion is legal,several classes of restrictions on the procedure may exist,such as parental consent or notification laws,requirements that patients be shown an ultrasound before obtaining an abortion,mandatory waiting periods,and counseling requirements.
Brian K. Zahra is a justice of the Michigan Supreme Court. He was appointed to fill a vacancy by Governor Rick Snyder in 2011. Zahra won his bid for reelection in 2022 to retain his seat for eight more years,per the Michigan Constitution.
Elizabeth Ann "Beth" Tripp Clement is an American lawyer who serves as the chief justice of the Michigan Supreme Court since 2022. She has served as an associate justice of the Michigan Supreme Court since 2017,after being appointed by Governor Rick Snyder.
Abortion in Michigan is legal throughout pregnancy. A state constitutional amendment to explicitly guarantee abortion rights was placed on the ballot in 2022 as Michigan Proposal 22–3;it passed with 57 percent of the vote,adding the right to abortion and contraceptive use to the Michigan Constitution. The amendment largely prevents the regulation of abortion before fetal viability,unless said regulations are to protect the individual seeking an abortion,and it also makes it unconstitutional to make laws restricting abortions which would protect the life and health,physical and/or mental,of the pregnant individual seeking abortion.

The 2022 California elections took place on November 8,2022. The statewide direct primary election was held on June 7,2022.

The 2022 Kansas abortion referendum was a rejected legislatively referred constitutional amendment to the Kansas Constitution that appeared on the ballot on August 2,2022,alongside primary elections for statewide offices,with early voting from July 13. If enacted,the amendment would have declared that the Kansas Constitution does not guarantee a right to abortion,giving the Kansas state government power to prosecute individuals involved in abortions,and further declared that the Kansas government is not required to fund abortions.
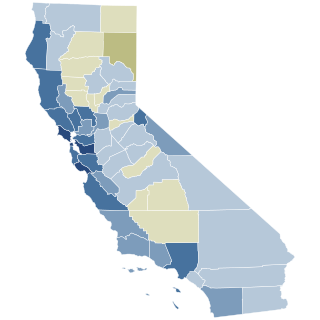
Proposition 1,titled Constitutional Right to Reproductive Freedom and initially known as Senate Constitutional Amendment 10 (SCA 10),was a California ballot proposition and state constitutional amendment that was voted on in the 2022 general election on November 8. Passing with more than two-thirds of the vote,the proposition amended the Constitution of California to explicitly grant the right to an abortion and contraceptives,making California among the first states in the nation to codify the right. The decision to propose the codification of abortion rights in the state constitution was precipitated in May 2022 by Politico's publishing of a leaked draft opinion showing the United States Supreme Court overturning Roe v. Wade and Planned Parenthood v. Casey in Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization. The decision reversed judicial precedent that previously held that the United States Constitution protected the right to an abortion.
Reproductive Freedom for All v. Board of State Canvassers was a 2022 decision by the Michigan Supreme Court overturning a decision by the Michigan Board of State Canvassers that had refused to certify a ballot petition,2022 Michigan Proposal 3,concerning abortion rights. In a 5–2 decision,the Court granted a complaint for mandamus relief and ordered the Board to certify the petition and ordered the Michigan Secretary of State to include the ballot proposition on the Fall 2022 ballot.

2022 Michigan Proposal 3,the Right to Reproductive Freedom Initiative,also known as Reproductive Freedom for All,was a citizen-initiated proposed constitutional amendment in the state of Michigan,which was voted on as part of the 2022 Michigan elections. The amendment,which passed,codified reproductive rights,including access to abortion,in the Constitution of Michigan.

The 2023 Ohio reproductive rights initiative,officially titled "The Right to Reproductive Freedom with Protections for Health and Safety" and listed on the ballot as Issue 1,was a citizen-initiated constitutional amendment adopted on November 7,2023,by a majority (56.8%) of voters. It codified reproductive rights in the Ohio Constitution,including contraception,fertility treatment,miscarriage care,and abortion up to the point of fetal viability,restoring Roe v. Wade-era access to abortion in Ohio.

Florida Amendment 4 was a proposed amendment to the Florida Constitution,which failed on November 5,2024. Through a statewide referendum,the amendment achieved 57% support among voters in the U.S. state of Florida,short of the 60% supermajority required by law. Despite its failure to pass,the double digit percentage majority that it received is considered by some to be indicative of a nationwide consensus on abortion,similar to similar referendums in other moderately conservative swing states such as Michigan,Ohio,Missouri,and Arizona,the last of which had an abortion rights amendment pass with a 3/5 majority,although unlike Florida it did not actually need one.

The 2022 Vermont reproductive rights initiative,officially titled the "Reproductive Liberty Amendment",and listed on the ballot as Proposition 5,was a legislatively referred constitutional amendment that was adopted on November 8,2022,by a landslide majority of 76.8% of voters. It codified reproductive rights in the Constitution of Vermont. It was signed into the constitution by Republican governor Phil Scott on 13 December 2022.

New York Proposal 1 was a 2024 ballot proposal for a legislatively referred constitutional amendment to the New York Constitution called the Amendment to Protect Against Unequal Treatment,and informally known as the Equal Rights Amendment. It includes several rights in the New York State Constitution's Equal Protection Clause,with its chief purpose to preserve the right to abortion. It also adds a prohibition of discrimination on attributes such ethnicity,gender identity,disability,or reproductive autonomy.

South Dakota Amendment G was a proposed constitutional amendment that appeared on the ballot on November 5,2024. If passed,the amendment would have established a right to abortion in the Constitution of South Dakota up until approximately the beginning of the third trimester of pregnancy. The amendment failed to pass,making it the second referendum about abortion since Dobbs to come out as anti-abortion and preserve the state's ban.

Arizona Proposition 139 is a constitutional amendment that was approved by voters on November 5,2024,establishing a right to abortion in the Constitution of Arizona up until fetal viability.

2024 Missouri Constitutional Amendment 3,also known as the Right to Reproductive Freedom Initiative,was a constitutional amendment that appeared on the ballot on November 5,2024. The initiative amended the Constitution of Missouri to legalize abortion in Missouri until fetal viability. The amendment narrowly passed.

Initiative 128 was a ballot initiative that appeared on the ballot on November 5,2024,to establish in the Constitution of Montana a right to abortion up to fetal viability. The initiative was approved by 58 percent of voters.
References
- ↑ "David F. Viviano – MICHIGAN SUPREME COURT HISTORICAL SOCIETY".
- ↑ 2013-2014 Michigan Manual: Justice David F. Viviano
- ↑ "Gov. Rick Snyder appoints Judge David Viviano to Michigan Supreme Court". mLIVE Michigan. Feb 27, 2013. Retrieved May 13, 2021.
- 1 2 The Logic Behind Dobbs Was Always Crap, and Michigan Is a Case in Point. "Leave it to the states," they said, disingenuously, Esquire Magazine , Charles P. Pierce, September 9, 2022, Retrieved September 11, 2022.
- ↑ Veronica Stracqualursi (8 September 2022). "Michigan Supreme Court orders abortion rights initiative to appear on November ballot". CNN. Retrieved 2022-09-09.
- ↑ "Michigan Supreme Court approves proposal to put abortion rights petition on November ballot". WXYZ. 2022-09-08. Retrieved 2022-09-09.