Related Research Articles
Scavenger receptors are a large and diverse superfamily of cell surface receptors. Its properties were first recorded in 1970 by Drs. Brown and Goldstein, with the defining property being the ability to bind and remove modified low density lipoproteins (LDL). Today scavenger receptors are known to be involved in a wide range of processes, such as: homeostasis, apoptosis, inflammatory diseases and pathogen clearance. Scavenger receptors are mainly found on myeloid cells and other cells that bind to numerous ligands, primarily endogenous and modified host-molecules together with pathogen-associated molecular patterns(PAMPs), and remove them. The Kupffer cells in the liver are particularly rich in scavenger receptors, includes SR-A I, SR-A II, and MARCO.
A cytokine storm, also called hypercytokinemia, is a pathological reaction in humans and other animals in which the innate immune system causes an uncontrolled and excessive release of pro-inflammatory signaling molecules called cytokines. Cytokines are a normal part of the body's immune response to infection, but their sudden release in large quantities may cause multisystem organ failure and death.

C5a is a protein fragment released from cleavage of complement component C5 by protease C5-convertase into C5a and C5b fragments. C5b is important in late events of the complement cascade, an orderly series of reactions which coordinates several basic defense mechanisms, including formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC), one of the most basic weapons of the innate immune system, formed as an automatic response to intrusions from foreign particles and microbial invaders. It essentially pokes microscopic pinholes in these foreign objects, causing loss of water and sometimes death. C5a, the other cleavage product of C5, acts as a highly inflammatory peptide, encouraging complement activation, formation of the MAC, attraction of innate immune cells, and histamine release involved in allergic responses. The origin of C5 is in the hepatocyte, but its synthesis can also be found in macrophages, where it may cause local increase of C5a. C5a is a chemotactic agent and an anaphylatoxin; it is essential in the innate immunity but it is also linked with the adaptive immunity. The increased production of C5a is connected with a number of inflammatory diseases.

The chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) is also referred to as monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP1) and small inducible cytokine A2. CCL2 is a small cytokine that belongs to the CC chemokine family. CCL2 tightly regulates cellular mechanics and thereby recruits monocytes, memory T cells, and dendritic cells to the sites of inflammation produced by either tissue injury or infection.
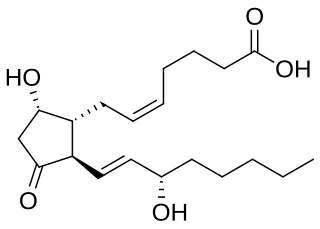
Prostaglandin D2 (or PGD2) is a prostaglandin that binds to the receptor PTGDR (DP1), as well as CRTH2 (DP2). It is a major prostaglandin produced by mast cells – recruits Th2 cells, eosinophils, and basophils. In mammalian organs, large amounts of PGD2 are found only in the brain and in mast cells. It is critical to development of allergic diseases such as asthma. Research carried out in 1989 found PGD2 is the primary mediator of vasodilation (the "niacin flush") after ingestion of niacin (nicotinic acid).

Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)3NO. It is in the class of amine oxides. Although the anhydrous compound is known, trimethylamine N-oxide is usually encountered as the dihydrate. Both the anhydrous and hydrated materials are white, water-soluble solids.
Macrophage-1 antigen is a complement receptor ("CR3") consisting of CD11b and CD18.

HLA-DM is an intracellular protein involved in the mechanism of antigen presentation on antigen presenting cells (APCs) of the immune system. It does this by assisting in peptide loading of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II membrane-bound proteins. HLA-DM is encoded by the genes HLA-DMA and HLA-DMB.
HLA class II histocompatibility antigen gamma chain also known as HLA-DR antigens-associated invariant chain or CD74, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD74 gene. The invariant chain is a polypeptide which plays a critical role in antigen presentation. It is involved in the formation and transport of MHC class II peptide complexes for the generation of CD4+ T cell responses. The cell surface form of the invariant chain is known as CD74. CD74 is a cell surface receptor for the cytokine macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF).

Alpha defensins are a family of mammalian defensin peptides of the alpha subfamily. They are also known as cryptdins and are produced within the small bowel. Cryptdin is a portmanteau of crypt and defensin.

Macrophage receptor with collagenous structure (MARCO) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MARCO gene. MARCO is a class A scavenger receptor that is found on particular subsets of macrophages. Scavenger receptors are pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) found most commonly on immune cells. Their defining feature is that they bind to polyanions and modified forms of a type of cholesterol called low-density lipoprotein (LDL). MARCO is able to bind and phagocytose these ligands and pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), leading to the clearance of pathogens and cell signaling events that lead to inflammation. As part of the innate immune system, MARCO clears, or scavenges, pathogens, which leads to inflammatory responses. The scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) domain at the end of the extracellular side of MARCO binds ligands to activate the subsequent immune responses. MARCO expression on macrophages has been associated with tumor development and also with Alzheimer's disease, via decreased responses of cells when ligands bind to MARCO.

A HEAT repeat is a protein tandem repeat structural motif composed of two alpha helices linked by a short loop. HEAT repeats can form alpha solenoids, a type of solenoid protein domain found in a number of cytoplasmic proteins. The name "HEAT" is an acronym for four proteins in which this repeat structure is found: Huntingtin, elongation factor 3 (EF3), protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), and the yeast kinase TOR1. HEAT repeats form extended superhelical structures which are often involved in intracellular transport; they are structurally related to armadillo repeats. The nuclear transport protein importin beta contains 19 HEAT repeats.
U-937 cells are a pro-monocytic model cell line used in biomedical research. They were isolated from the histiocytic lymphoma of a 37-year-old male patient in 1974. Due to the relative uniformity of expanded cultures and lower maintenance requirements these cells have been since used as an important tool for studying phagocyte differentiation and different kinds of cell-to-cell interactions. U-937 cells mature and differentiate in response to a number of soluble stimuli, adopting the morphology and characteristics of monocytes, macrophages or dendritic cells.

C-type lectin domain family 10 member A (CLEC10A) also designated as CD301 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CLEC10A gene. CLEC10A is part of the C-type lectin superfamily and binds to N-Acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc). It is mainly expressed on myeloid cells and also on oocytes and very early stages of embryogenesis. CLEC10A is used as a marker of the CD1c+ dendritic cell subgroup, also called cDC2. The actions of CLEC10A are diverse, depending on the ligand and environment.
Synthetic antibodies are affinity reagents generated entirely in vitro, thus completely eliminating animals from the production process. Synthetic antibodies include recombinant antibodies, nucleic acid aptamers and non-immunoglobulin protein scaffolds. As a consequence of their in vitro manufacturing method the antigen recognition site of synthetic antibodies can be engineered to any desired target and may extend beyond the typical immune repertoire offered by natural antibodies. Synthetic antibodies are being developed for use in research, diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Synthetic antibodies can be used in all applications where traditional monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies are used and offer many inherent advantages over animal-derived antibodies, including comparatively low production costs, reagent reproducibility and increased affinity, specificity and stability across a range of experimental conditions.
N-acylethanolamine acid amide hydrolase (NAAA) EC 3.5.1.- is a member of the choloylglycine hydrolase family, a subset of the N-terminal nucleophile hydrolase superfamily. NAAA has a molecular weight of 31 kDa. The activation and inhibition of its catalytic site is of medical interest as a potential treatment for obesity and chronic pain. While it was discovered within the last decade, its structural similarity to the more familiar acid ceramidase (AC) and functional similarity to fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) allow it to be studied extensively.
Pauline Johnson is an English immunologist and microbiologist at the University of British Columbia. Her research focuses on innate and adaptive immune mechanisms — in particular, the mobility of proteins in membranes, lymphocyte cell surface molecules, T cell signalling, leukocyte adhesion, and macrophages in lung inflammation.

Dan Theodorescu is an American physician and academic. He is the Director of the Samuel Oschin Comprehensive Cancer Institute at the Cedars-Sinai Medical Center and leader of Cedars-Sinai CANCER. From 2010 until 2018, Theodorescu was Director of the University of Colorado Cancer Center and a professor of Surgery-Urology. He has been appointed Paul Mellon Chair at the University of Virginia and Paul Bunn Chair and Distinguished University Professor at the University of Colorado.
Cells destined for apoptosis release molecules referred to as find-me signals. These signal molecules are used to attract phagocytes which engulf and eliminate damaged cells. Find-me signals are typically released by the apoptotic cells while the cell membrane remains intact. This ensures that the phagocytic cells are able to remove the dying cells before their membranes are compromised. A leaky membrane leads to secondary necrosis which may cause additional inflammation, therefore, it is best to remove dying cells before this occurs. One cell is capable of releasing multiple find-me signals. Should a cell lack the ability to release its find-me signal, other cells may release additional find-me signals to overcome the discrepancy.
Epitope Detection in Monocytes (EDIM) is a technology that uses the innate immune system's mechanisms to detect biomarkers or antigens in immune cells. It is a non-invasive form of liquid biopsy, i.e. biopsy from blood, which analyzes activated macrophages (CD14+/CD16+) for disease-specific epitopes, such as tumor cell components.
References
- 1 2 "Keeping grandparents and grandchildren together for as long as possible" . Retrieved 2024-09-16.
- ↑ Bowdish D. M., Davidson D. J., Speert D. P., Hancock R. E. (2004). "The human cationic peptide LL-37 induces activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 kinase pathways in primary human monocytes". Journal of Immunology. 172 (6): 3758–65. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.6.3758 . PMID 15004180.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Bowdish D.M., Davidson D. J., Lau Y.E., Lee K., Scott M. G., Hancock R. E. (2005). "Impact of LL-37 on anti-infective immunity". Journal of Leukocyte Biology. 77 (4): 451–9. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0704380 . PMID 15569695.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Bowdish D.M., Davidson D.J., Hancock R.E. (2005). "A re-evaluation of the role of host defence peptides in mammalian immunity". Current Protein & Peptide Science. 6 (1): 35–51. doi:10.2174/1389203053027494. PMID 15638767.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Bowdish D. M., Davidson D. J., Scott M. G., Hancock R. E. (2005). "Immunomodulatory activities of small host defense peptides". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 49 (5): 1727–32. doi:10.1128/AAC.49.5.1727-1732.2005. PMC 1087655 . PMID 15855488.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Bowdish D.M., Sakamoto K., Kim M. J., Kroos M., Mukhopadhyay S., Leifer C. A., Tryggvason K., Gordon S., Russell D. G. (2009). "MARCO, TLR2, and CD14 Are Required for Macrophage Cytokine Responses to Mycobacterial Trehalose Dimycolate and Mycobacterium tuberculosis". PLOS Pathogens. 5 (6): e1000474. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000474 . PMC 2688075 . PMID 19521507.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Verschoor C. P., Johnstone J., Loeb M., Bramson J. L., Bowdish D. M. (2014). "Anti-pneumococcal deficits of monocyte-derived macrophages from the advanced-age, frail elderly and related impairments in PI3K-AKT signaling". Human Immunology. 75 (12): 1192–6. doi:10.1016/j.humimm.2014.10.004. PMID 25446401.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Verschoor C.P., Johnstone J., Millar J., Parsons R., Lelic A., Loeb M., Bramson J. L., Bowdish D. M. (2014). "Alterations to the Frequency and Function of Peripheral Blood Monocytes and Associations with Chronic Disease in the Advanced-Age, Frail Elderly". PLOS ONE. 9 (8): e104522. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...9j4522V. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104522 . PMC 4126708 . PMID 25105870.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Thevaranjan N., Puchta A., Schulz C., Naidoo A., Szamosi J. C., Verschoor C. P., Loukov D., Schenck L. P., Jury J., Foley K. P., Schertzer J. D., Larché M. J., Davidson D. J., Verdú E. F., Surette M. G., Bowdish D. M. E. (2017). "Age-Associated Microbial Dysbiosis Promotes Intestinal Permeability, Systemic Inflammation, and Macrophage Dysfunction". Cell Host & Microbe. 21 (4): 455–466. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2017.03.002. PMC 5392495 . PMID 28407483.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)