
Backgammon is a two-player board game played with counters and dice on tables boards. It is the most widespread Western member of the large family of tables games, whose ancestors date back nearly 5,000 years to the regions of Mesopotamia and Persia. The earliest record of backgammon itself dates to 17th-century England, being descended from the 16th-century game of Irish.
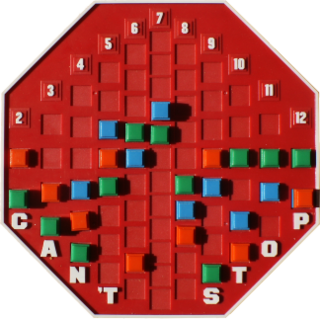
Can't Stop is a board game designed by Sid Sackson originally published by Parker Brothers in 1980; however, that edition has been long out of print in the United States. It was reprinted by Face 2 Face Games in 2007. An iOS version was developed by Playdek and released in 2012. The goal of the game is to "claim" three of the columns before any of the other players can. But the more that the player risks rolling the dice during a turn, the greater the risk of losing the advances made during that turn.

Pig is a simple dice game first described in print by John Scarne in 1945. Players take turns to roll a single dice as many times as they wish, adding all roll results to a running total, but losing their gained score for the turn if they roll a 1.
Liar's dice is a class of dice games for two or more players requiring the ability to deceive and to detect an opponent's deception. In "single hand" liar's dice games, each player has a set of dice, all players roll once, and the bids relate to the dice each player can see plus all the concealed dice. In "common hand" games, there is one set of dice which is passed from player to player. The bids relate to the dice as they are in front of the bidder after selected dice have been re-rolled. Originating during the 15th century, the game subsequently spread to Latin American and European countries. In 1993, a variant, Call My Bluff, won the Spiel des Jahres.

Nard is an historical Persian tables game for two players that is sometimes considered ancestral to backgammon. It is still played today, albeit in a different form. As in other tables games, the playing pieces are moved around a board according to rolls of dice. It uses a standard tables board, but has a different opening layout and rules of play from that of backgammon.

Alhambra is a 2003 tile-based German-style board game designed by Dirk Henn. It was originally published in Germany by Queen Games in a language-interdependent version; an English-specific version was released in North America by the now-defunct Überplay. The game is an Arabian-themed update, set during the construction of the Alhambra palace in 14th century Granada, of the 1998 stock trading board game Stimmt So!, which in turn was an update of the 1992 mafia influence board game Al Capone; the original version was subsequently released as Alhambra: The Card Game. Upon its release, Alhambra won numerous awards, including the Spiel des Jahres award. Its success has led to the release of numerous expansion packs and spin-off games, and is becoming Queen Games' flagship franchise.
Don't Go to Jail is a 1991 Parker Brothers dice game for two or more players inspired by Monopoly. The game is played by rolling ten dice and attempting to roll matches to score points.

Caylus is a strategy oriented, German-style board game designed by William Attia and independently published in 2005 by Ystari in France and England, and Rio Grande Games in North America. Caylus has a mix of building, producing, planning, and bargaining — without direct conflict or dice-rolling mechanics.
Mozaic is a two-player abstract strategy board game, in which players try to score points by placing colored glass gemstones onto a game board to form square patterns. The game was designed by Martin H. Samuel. It was originally produced by Games Above Board, Sunnywood, Inc., of Hong Kong, then licensed and published through Sterling Games in 2003. Giseh Verlag launched the game in Germany at Essen Spiel in 2006. An Axiom-powered electronic version of Mozaic was programmed for the PC platform by Greg Schmidt in 2010.
Tapa (Тапа) is a tables game played in Bulgaria and North Macedonia. It is also played in Greece, where it is known as Plakoto. The word tapa means bottle cap.

The Pirates of the Caribbean Trading Card Game is an out-of-print collectible card game based on the two Disney films Pirates of the Caribbean: The Curse of the Black Pearl and Pirates of the Caribbean: Dead Man's Chest. Upper Deck Entertainment launched this title in June 2006 to roughly correspond to the release of the second film but canceled due to lack of interest.

Starfarers of Catan is a multiplayer board game loosely based on the Settlers of Catan series of games. It was created by Klaus Teuber as an official spin-off and is distributed by Kosmos in German and Mayfair Games in English.

Jacquet is a tables game played on a backgammon-like board and which was once very popular in France and several other parts of Europe. It probably emerged around 1800, but is attested by 1827. In the 20th century it replaced the classic French backgammon equivalent — the game of Trictrac — until Jacquet itself was superseded by Anglo-American games in the 1960s.
Mojo is a two-player, 3 in-a-row abstract strategy board game played with original and unique "thrice-sliced-dice". The pieces, handmade to order in India, are colored with non-toxic vegetable dye. The individual opposite ends of the pieces are marked with pips and numbered similar to regular dice - i.e. they total 7. It takes all 3 pieces of a color to make up a single die.

Catan, previously known as The Settlers of Catan or simply Settlers, is a multiplayer board game designed by Klaus Teuber. It was first published in 1995 in Germany by Franckh-Kosmos Verlag (Kosmos) as Die Siedler von Catan. Players take on the roles of settlers, each attempting to build and develop holdings while trading and acquiring resources. Players gain victory points as their settlements grow and the first to reach a set number of victory points, typically 10, wins. The game and its many expansions are also published by Catan Studio, Filosofia, GP, Inc., 999 Games, Κάισσα (Káissa), and Devir. Upon its release, The Settlers of Catan became one of the first Eurogames to achieve popularity outside Europe. As of 2020, more than 32 million copies in 40 languages had been sold.

Trictrac is a French board game of skill and chance for two players that is played with dice on a game board similar, but not identical, to that of backgammon. It was "the classic tables game" of France in the way that backgammon is in the English-speaking world.

The following is a glossary of terms used in tables games, essentially games played on a Backgammon-type board. Terms in this glossary should not be game-specific, but applicable to a range of tables games.

Irish or the Irish Game was an Anglo-Scottish tables game for two players that was popular from the 16th to the mid-18th centuries before being superseded by its derivative, the "faster paced" backgammon. In its day, Irish was "esteemed among the best games at Tables." Its name notwithstanding, Irish was one of the most international forms of tables games, the equivalent of French toutes tables, Italian tavole reale and Spanish todas tablas, the latter name first being used in the 1283 El Libro de los Juegos, a translation of Arabic manuscripts by the Toledo School of Translators.

Ludus Anglicorum, also called the English Game, is an historical English tables game for two players using a board similar to that used today for Backgammon and other games. It is a "strategic game for serious game-players" and was well known in the Middle Ages. At one time it was considered the most popular tables game in England.

Doublets or queen's game is an historical English tables game for two people which was popular in the 17th and 18th centuries. Although played on a board similar to that now used for backgammon, it is a simple game of hazard bearing little resemblance to backgammon. Very similar games were played in mainland Europe, the earliest recorded dating to the 14th century.














