
The Libro de los juegos, or Libro de axedrez, dados e tablas, was a Spanish treatise of chess which synthesized the information from other Arabic works on this same topic, dice and tables games, commissioned by Alfonso X of Castile, Galicia and León and completed in his scriptorium in Toledo in 1283. It contains the earliest European treatise on chess as well as being the oldest document on European tables games, and is an exemplary piece of the literary legacy of the Toledo School of Translators.
A horoscope is an astrological chart or diagram representing the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets, astrological aspects and sensitive angles at the time of an event, such as the moment of a person's birth. The word horoscope is derived from the Greek words ōra and scopos meaning "time" and "observer". It is claimed by proponents of astrology that a horoscope can be used as a method of divination regarding events relating to the point in time it represents, and it forms the basis of the horoscopic traditions of astrology, although practices surrounding astrology have been recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century. Horoscope columns are often featured in print and online newspapers.

A chessboard is a game board used to play chess. It consists of 64 squares, 8 rows by 8 columns, on which the chess pieces are placed. It is square in shape and uses two colours of squares, one light and one dark, in a chequered pattern. During play, the board is oriented such that each player's near-right corner square is a light square.

Alquerque is a strategy board game that is thought to have originated in the Middle East. It is considered to be the parent of draughts and Fanorona and the diagonals of its grid are the predecessor of the checkering of the draughts board.

Tables games are a class of board game that includes backgammon and which are played on a tables board, typically with two rows of 12 vertical markings called points. Players roll dice to determine the movement of pieces. Tables games are among the oldest known board games, and many different varieties are played throughout the world. They are called 'tables' games because the boards consist of four quadrants or 'tables'. The vast majority are race games, the tables board representing a linear race track with start and finish points, the aim being to be first to the finish line, but the characteristic features that distinguish tables games from other race games are that they are two-player games using a large number of pieces, usually fifteen per player.

The Pig or sometimes translated as the Boar is the twelfth of the 12-year cycle of animals which appear in Chinese zodiac, in relation to the Chinese calendar and system of horology, and paralleling the system of ten Heavenly Stems and twelve Earthly Branches. Although the term "zodiac" is used in the phrase "Chinese zodiac", there is a major difference between the Chinese usage and Western astrology: the zodiacal animals do not relate to the zodiac as the area of the sky that extends approximately 8° north or south of the ecliptic, the apparent path of the Sun, the Moon, and visible planets across the celestial sphere's constellations, over the course of the year.

In Western astrology, astrological signs are the twelve 30-degree sectors that make up Earth's 360-degree orbit around the Sun. The signs enumerate from the first day of spring, known as the First Point of Aries, which is the vernal equinox. The astrological signs are Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius, and Pisces. The Western zodiac originated in Babylonian astrology, and was later influenced by the Hellenistic culture. Each sign was named after a constellation the sun annually moved through while crossing the sky. This observation is emphasized in the simplified and popular sun sign astrology. Over the centuries, Western astrology's zodiacal divisions have shifted out of alignment with the constellations they were named after by axial precession of the Earth while Hindu astrology measurements correct for this shifting. Astrology was developed in Chinese and Tibetan cultures as well but these astrologies are not based upon the zodiac but deal with the whole sky.
This is a timeline of chess.

Rodrigo "Ruy" López de Segura was a Spanish chess player, author, and Catholic priest whose 1561 treatise Libro de la invención liberal y Arte del juego del Axedrez was one of the first books about modern chess in Europe. He made great contributions to chess opening theory, including in the King's Gambit and the Ruy López opening that bears his name. López was also the strongest player in Spain for about 20 years.

Nard is an historical Persian tables game for two players that is sometimes considered ancestral to backgammon. It is still played today, albeit in a different form. As in other tables games, the playing pieces are moved around a board according to rolls of dice. It uses a standard tables board, but has a different opening layout and rules of play from that of backgammon.

Ludus latrunculorum, latrunculi, or simply latrones was a two-player strategy board game played throughout the Roman Empire. It is said to resemble chess or draughts, as it is generally accepted to be a game of military tactics. Because of the scarcity of sources, reconstruction of the game's rules and basic structure is difficult, and therefore there are multiple interpretations of the available evidence.

Pretwa is a two-player abstract strategy game from Bihar, India, and it was described by H.J.R. Murray in A History of Board-Games Other Than Chess (1952). The game is related to draughts and Alquerque as pieces are captured by leaping over them. The board is composed of three concentric circles divided by three diameters. Pretwa belongs to a category of games called Indian war games, which also includes the games Lau kata kati, Dash-guti, Egara-guti, Gol-skuish. All Indian war games have one important thing in common, and that is that all the pieces are laid out on the board at every intersection point, with the exception of the central point. This forces the first move to be played on the central point, and captured by the other player's piece.
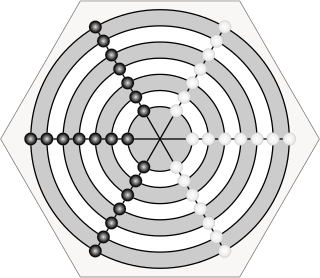
Gol-skuish is a two-player abstract strategy game from India, specifically from Central Provinces, and it was described by H.J.R. Murray in A History of Board-Games Other Than Chess (1952). The game belongs to the draughts and Alquerque family as pieces are captured by leaping over them. The board is composed of seven concentric circles divided by three diameters. Gol-skuish belongs to a specific category of games called Indian War-games which include Lau kata kati, Dash-guti, Egara-guti, and Pretwa. At the beginning of every Indian War-game all the pieces are laid out on the board at every intersection point, with the exception of the central point. This forces the first move of the game to be played on the central point, and captured by the second player's piece.
Catch the hare is a two-player abstract strategy board game from Europe, and perhaps specifically from Spain. It is a hunt game, and since it uses a standard alquerque board from the game alquerque de doze, it is specifically a tiger hunt game. In some variants, some or all of the diagonal lines are missing which makes it difficult to classify as a tiger game in general. One hare is going up against ten to twelve opponents(hunters or hounds). The hare is the "tiger" in this hunt game which is prey and predator at the same time. The hare can capture the opponents by leaping over them. The opponents attempt to surround and trap the hare.

The history of games dates to the ancient human past. Games are an integral part of all cultures and are one of the oldest forms of human social interaction. Games are formalized expressions of play which allow people to go beyond immediate imagination and direct physical activity. Common features of games include uncertainty of outcome, agreed upon rules, competition, separate place and time, elements of fiction, elements of chance, prescribed goals and personal enjoyment.
Grant Acedrex is a medieval chess variant dating back to the time of King Alfonso X of Castile. It appears in the Libro de los Juegos of 1283.

Laquet is an historical Castilian tables game that was described as a new game in the 13th century. It may be the ancestor of Jacquet. Unlike Backgammon and most other tables games, it has an asymmetrical starting position; only three of the four quadrants are used and the pieces may not be 'hit'.

Irish or the Irish Game was an Anglo-Scottish tables game for two players that was popular from the 16th to the mid-18th centuries before being superseded by its derivative, the "faster paced" backgammon. In its day, Irish was "esteemed among the best games at Tables." Its name notwithstanding, Irish was one of the most international forms of tables games, the equivalent of French toutes tables, Italian tavole reale and Spanish todas tablas, the latter name first being used in the 1283 El Libro de los Juegos, a translation of Arabic manuscripts by the Toledo School of Translators.

Ludus Anglicorum, also called the English Game, is an historical English tables game for two players using a board similar to that used today for Backgammon and other games. It is a "strategic game for serious game-players" and was well known in the Middle Ages. At one time it was considered the most popular tables game in England.

Doublets or queen's game is an historical English tables game for two people which was popular in the 17th and 18th centuries. Although played on a board similar to that now used for backgammon, it is a simple game of hazard bearing little resemblance to backgammon. Very similar games were played in mainland Europe, the earliest recorded dating to the 14th century.

















