
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic against the background of stars. The ecliptic is an important reference plane and is the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system.
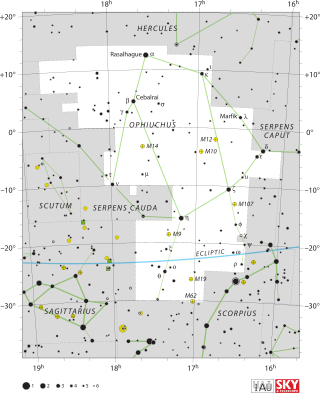
Ophiuchus is a large constellation straddling the celestial equator. Its name comes from the Ancient Greek ὀφιοῦχος (ophioûkhos), meaning "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping a snake. The serpent is represented by the constellation Serpens. Ophiuchus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. An old alternative name for the constellation was Serpentarius.

Scorpius is a zodiac constellation located in the Southern celestial hemisphere, where it sits near the center of the Milky Way, between Libra to the west and Sagittarius to the east. Scorpius is an ancient constellation that pre-dates the Greeks; it is one of the 48 constellations identified by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy in the second century. Its old astronomical symbol is (♏︎).

The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north and south of the ecliptic, which is the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. The orbital paths of the Moon and major planets are within the belt of the zodiac.

A horoscope is an astrological chart or diagram representing the positions of the Sun, Moon, planets, astrological aspects and sensitive angles at the time of an event, such as the moment of a person's birth. The word horoscope is derived from the Greek words ōra and scopos meaning "time" and "observer". It is claimed by proponents of astrology that a horoscope can be used as a method of divination regarding events relating to the point in time it represents, and it forms the basis of the horoscopic traditions of astrology, although practices surrounding astrology have been recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century. Horoscope columns are often featured in print and online newspapers.

In astrology, sidereal and tropical are terms that refer to two different systems of ecliptic coordinates used to divide the ecliptic into twelve "signs". Each sign is divided into 30 degrees, making a total of 360 degrees. The terms sidereal and tropical may also refer to two different definitions of a year, applied in sidereal solar calendars or tropical solar calendars.

In Western astrology, astrological signs are the twelve 30-degree sectors that make up Earth's 360-degree orbit around the Sun. The signs enumerate from the first day of spring, known as the First Point of Aries, which is the vernal equinox. The astrological signs are Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius, and Pisces. The Western zodiac originated in Babylonian astrology, and was later influenced by the Hellenistic culture. Each sign was named after a constellation the sun annually moved through while crossing the sky. This observation is emphasized in the simplified and popular sun sign astrology. Over the centuries, Western astrology's zodiacal divisions have shifted out of alignment with the constellations they were named after by axial precession of the Earth while Hindu astrology measurements correct for this shifting. Astrology was developed in Chinese and Tibetan cultures as well but these astrologies are not based upon the zodiac but deal with the whole sky.

An astrological age is a time period which, according to astrology, parallels major changes in the development of human society, culture, history, and politics. There are twelve astrological ages corresponding to the twelve zodiacal signs in western astrology. One cycle of the twelve astrological ages is called a Great Year, comprising 25,772 solar years, at the end of which another cycle begins.
Scorpius (♏) is a constellation of the zodiac, named after the ancient Greek word for scorpion.

Aries (♈︎) is the first astrological sign in the zodiac, spanning the first 30 degrees of celestial longitude, and originates from the Aries constellation. Under the tropical zodiac, the Sun transits this sign from approximately March 21 to April 19 each year. This time-duration is exactly the first month of the Solar Hijri calendar.

Leo (♌︎) is the fifth sign of the zodiac. It corresponds to the constellation Leo and comes after Cancer and before Virgo. The traditional Western zodiac associates Leo with the period between about July 23 and August 22, and the sign spans the 120th to 150th degree of celestial longitude.

Cancer (♋︎) is the fourth astrological sign in the zodiac, originating from the constellation of Cancer. It spans from 90° to 120° celestial longitude. Under the tropical zodiac, the Sun transits this area between approximately June 22 and July 22.

Pisces (♓︎) is the twelfth and final astrological sign in the zodiac. It is a negative, mutable sign. It spans 330° to 360° of celestial longitude. Under the tropical zodiac, the sun transits this area between February 19 and March 20. In classical interpretations, the symbol of the fish is derived from the ichthyocentaurs, who aided Aphrodite when she was born from the sea.

Taurus (♉︎) is the second astrological sign in the modern zodiac. It spans from 30° to 60° of the zodiac. This sign belongs to the Earth element or triplicity, as well as a fixed modality, quality, or quadruplicity. It is a Venus-ruled sign, the Moon is in its exaltation here at exactly 3°. The Sun transits this sign from approximately April 20 until May 20 in western astrology. Taurus is one of the three earth signs, alongside Capricorn and Virgo. Taurus's opposite sign is Scorpio.
Sagittarius (♐︎) is the ninth astrological sign, which is associated with the constellation Sagittarius and spans 240–270th degrees of the zodiac. Under the tropical zodiac, the sun transits this sign between approximately November 22 and December 21. Greek mythology associates Sagittarius with the centaur Chiron, who mentored Achilles, a Greek hero of the Trojan War, in archery.

Gemini (♊︎) is the third astrological sign in the zodiac. Under the tropical zodiac, the sun transits this sign between about May 21 to June 21. Gemini is represented by the twins, Castor and Pollux, known as the Dioscuri in Greek mythology. It's known as a positive, mutable sign.

Virgo (♍︎) is the sixth astrological sign in the zodiac. It spans the 150–180th degree of the zodiac. Under the tropical zodiac, the Sun transits this area between August 23 and September 22. Depending on the system of astrology, individuals born during these dates may be called Virgos or Virgoans.

Libra (♎︎) is the seventh astrological sign in the zodiac. It spans 180°–210° celestial longitude. The Sun transits this sign on average between September 23 and October 23. The symbol of the scales is based on the Scales of Justice held by Themis, the Greek personification of divine law and custom. She became the inspiration for modern depictions of Lady Justice. The ruling planet of Libra is Venus along with Taurus. Libra is the only zodiac sign that is represented by an object; with the other eleven signs represented by either an animal or mythological character.

Capricorn(♑︎) is the tenth astrological sign in the zodiac out of twelve total zodiac signs, originating from the constellation of Capricornus, the goat. It spans the 270–300th degree of the zodiac, corresponding to celestial longitude. Under the tropical zodiac, the sun transits this area from around December 22 to January 19. Capricorn is one of the three earth signs alongside Taurus and Virgo, a negative sign, and one of the four cardinal signs. Capricorn is ruled by the planet Saturn along with Aquarius. Capricorn's opposite sign is Cancer.

Aquarius (♒︎) is the eleventh astrological sign in the zodiac, originating from the constellation Aquarius. Under the tropical zodiac, the Sun is in the Aquarius sign between about January 20 and February 18. Aquarius is one of the three air signs, alongside Gemini and Libra. The ruling planets of Aquarius are Saturn, and Uranus. The opposite sign of Aquarius is Leo.























