Related Research Articles

The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, the elephant shrew and the Cairo spiny mouse. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle. During pregnancy, the glands and blood vessels in the endometrium further increase in size and number. Vascular spaces fuse and become interconnected, forming the placenta, which supplies oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus. The speculated presence of an endometrial microbiota has been argued against.

The uterus or womb is the main hormone-responsive, secondary sex organ of the female reproductive system in humans, and most other mammals. Events occurring within the uterus are described with the term in utero. In the human, the lower end of the uterus, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the upper end, the fundus, is connected to the fallopian tubes. It is within the uterus that the embryo and later fetus develops during gestation. In the human embryo, the uterus develops from the paramesonephric ducts which fuse into the single organ known as a simplex uterus. The uterus has different forms in many other animals and in some it exists as two separate uteri known as a duplex uterus.

The placenta is a temporary fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas and waste exchange between the physically separate maternal and fetal circulations, and is an important endocrine organ producing hormones that regulate both maternal and fetal physiology during pregnancy. The placenta connects to the fetus via the umbilical cord, and on the opposite aspect to the maternal uterus in a species dependent manner. In humans, a thin layer of maternal decidual (endometrial) tissue comes away with the placenta when it is expelled from the uterus following birth. Placentas are a defining characteristic of placental mammals, but are also found in marsupials and some non-mammals with varying levels of development.

A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated.

The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that make pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eggs and the cyclic release of estrogen and progesterone. The uterine cycle governs the preparation and maintenance of the lining of the uterus (womb) to receive a fertilized egg. These cycles are concurrent and coordinated, normally last between 21 and 35 days in adult women, with a median length of 28 days, and continue for about 30–45 years.

The amnion is a membrane that closely covers the human and various other embryos when first formed. It fills with amniotic fluid, which causes the amnion to expand and become the amniotic sac that provides a protective environment for the developing embryo. The amnion, along with the chorion, the yolk sac and the allantois protect the embryo. In birds, reptiles and monotremes, the protective sac is enclosed in a shell. In marsupials and placental mammals, it is enclosed in a uterus.

The chorion is the outermost fetal membrane around the embryo in mammals, birds and reptiles (amniotes). It develops from an outer fold on the surface of the yolk sac, which lies outside the zona pellucida, known as the vitelline membrane in other animals. In insects it is developed by the follicle cells while the egg is in the ovary.
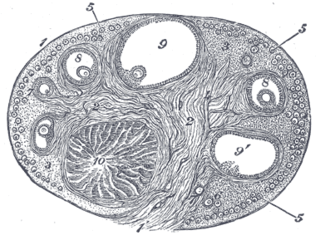
The corpus luteum is a temporary endocrine structure in female ovaries and is involved in the production of relatively high levels of progesterone and moderate levels of estradiol and inhibin A. It is the remains of the ovarian follicle that has released a mature ovum during a previous ovulation.

The female reproductive system is made up of the internal and external sex organs that function in reproduction of new offspring. In humans, the female reproductive system is immature at birth and develops to maturity at puberty to be able to produce gametes, and to carry a foetus to full term. The internal sex organs are the vagina, uterus, Fallopian tubes, and ovaries. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse and birth, and is connected to the uterus at the cervix. The uterus or womb accommodates the embryo which develops into the foetus. The uterus also produces secretions which help the transit of sperm to the Fallopian tubes, where sperm fertilize ova which are produced by the ovaries. The external sex organs are also known as the genitals and these are the organs of the vulva including the labia, clitoris, and vaginal opening.

Adenomyosis is a medical condition characterized by the growth of cells that proliferate on the inside of the uterus (endometrium) atypically located among the cells of the uterine wall (myometrium), as a result, thickening of the uterus occurs. As well as being misplaced in patients with this condition, endometrial tissue is completely functional. The tissue thickens, sheds and bleeds during every menstrual cycle.

Endometritis is inflammation of the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium). Symptoms may include fever, lower abdominal pain, and abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge. It is the most common cause of infection after childbirth. It is also part of spectrum of diseases that make up pelvic inflammatory disease.

The decidua is the modified mucosal lining of the uterus that forms in preparation for pregnancy. It is formed in a process called decidualization under the influence of progesterone. Endometrial cells become highly characteristic. The decidua forms the maternal part of the placenta and remains for the duration of the pregnancy. It is shed off during childbirth—hence why the term is used, "decidua" having the meaning of falling away, as in the word deciduous.

In biology, placentation refers to the formation, type and structure, or arrangement of the placenta. The function of placentation is to transfer nutrients, respiratory gases, and water from maternal tissue to a growing embryo, and in some instances to remove waste from the embryo. Placentation is best known in live-bearing mammals (theria), but also occurs in some fish, reptiles, amphibians, a diversity of invertebrates, and flowering plants. In vertebrates, placentas have evolved more than 100 times independently, with the majority of these instances occurring in squamate reptiles.

In female mammals implantation is the stage in embryonic development in which the blastocyst hatches as the embryo, and adheres to the wall of the uterus. Once this adhesion is successful, the female is considered to be pregnant and the embryo will receive oxygen and nutrients from the mother in order to grow.

Decidualization is a process that results in significant changes to cells of the endometrium in preparation for, and during, pregnancy. This includes morphological and functional changes to endometrial stromal cells (ESCs), the presence of decidual white blood cells (leukocytes), and vascular changes to maternal arteries. The sum of these changes results in the endometrium changing into a structure called the decidua. In humans, the decidua is shed during childbirth.

The fetal membranes or extraembryonic membranes, are membranes associated with the developing fetus. The two chorioamniotic membranes are the amnion and the chorion, which make up the amniotic sac that surrounds and protects the fetus. The other fetal membranes are the allantois and the yolk sac.
Menstruation is the shedding of the uterine lining (endometrium). It occurs on a regular basis in uninseminated sexually reproductive-age females of certain mammal species.
Endometrial cups form during pregnancy in mares and are the source of equine chorionic gonadotropin (eCG) and a placenta-associated structure, which is derived from the fetus. Their purpose is to increase the immunological tolerance of the mare in order to protect the developing foal.

Preimplantation factor, sometimes called PreImplantation Factor or simply PIF, is a peptide secreted by trophoblast cells prior to placenta formation in early embryonic development. Human embryos begin to express PIF at the 2-cell stage, with expression increasing by the morula stage and continuing to do so throughout the first trimester. Expression of preimplantation factor in the blastocyst was discovered as an early correlate of the viability of the eventual pregnancy. Preimplantation factor was identified in 1994 by a lymphocyte platelet-binding assay, where it was thought to be an early biomarker of pregnancy. It has a simple primary structure with a short sequence of fifteen amino acids without any known quaternary structure. A synthetic analogue of preimplantation factor that has an identical amino acid sequence and mimics the normal biological activity of PIF has been developed and is commonly used in research studies, particularly those that aim to study potential adult therapeutics.

Uterine natural killer cells make up approximately 70% of maternal lymphocytes during pregnancy, occupying both the decidua basalis of the endometrium at the implantation site and the mesometrial lymphoid aggregate of pregnancy (MLAp) that surrounds the blood vessels supplying the placenta. This number is at its peak in early pregnancy but declines at parturition.
References
- ↑ Kearns, M; Lala, PK (March 1983). "Life history of decidual cells: a review". American journal of reproductive immunology : AJRI : official journal of the American Society for the Immunology of Reproduction and the International Coordination Committee for Immunology of Reproduction. 3 (2): 78–82. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0897.1983.tb00219.x. PMID 6344664.
- ↑ Li, H; Huang, Q; Liu, Y; Garmire, LX (December 2020). "Single cell transcriptome research in human placenta". Reproduction (Cambridge, England). 160 (6): R155–R167. doi:10.1530/REP-20-0231. PMID 33112783.
- ↑ Gellersen, Birgit; Brosens, Ivo; Brosens, Jan (2007-11-01). "Decidualization of the Human Endometrium: Mechanisms, Functions, and Clinical Perspectives". Seminars in Reproductive Medicine. 25 (6): 445–453. doi:10.1055/s-2007-991042. ISSN 1526-8004. PMID 17960529.[ permanent dead link ]
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 59 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 59 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)