The inner ear is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the temporal bone of the skull with a system of passages comprising two main functional parts:

The ileum is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine may be used instead of ileum. Its main function is to absorb vitamin B12, bile salts, and whatever products of digestion that were not absorbed by the jejunum.

The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the pancreatic duct to aid in digestion. The small intestine is about 5.5 metres long and folds many times to fit in the abdomen. Although it is longer than the large intestine, it is called the small intestine because it is narrower in diameter.

In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and stores it. The bile is then released via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats.

The seminal vesicles are a pair of convoluted tubular accessory glands that lie behind the urinary bladder of male mammals. They secrete fluid that partly composes the semen.

A Meckel's diverticulum, a true congenital diverticulum, is a slight bulge in the small intestine present at birth and a vestigial remnant of the vitelline duct. It is the most common malformation of the gastrointestinal tract and is present in approximately 2% of the population, with males more frequently experiencing symptoms.

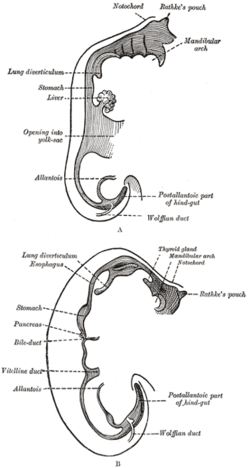
The allantois is a hollow sac-like structure filled with clear fluid that forms part of a developing amniote's conceptus. It helps the embryo exchange gases and handle liquid waste.
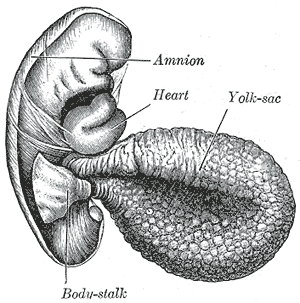
The yolk sac is a membranous sac attached to an embryo, formed by cells of the hypoblast layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle by the Terminologia Embryologica (TE), though yolk sac is far more widely used. In humans, the yolk sac is important in early embryonic blood supply, and much of it is incorporated into the primordial gut during the fourth week of embryonic development.

Gastroschisis is a birth defect in which the baby's intestines extend outside of the abdomen through a hole next to the belly button. The size of the hole is variable, and other organs including the stomach and liver may also occur outside the baby's body. Complications may include feeding problems, prematurity, intestinal atresia, and intrauterine growth restriction.

In medicine or biology, a diverticulum is an outpouching of a hollow structure in the body. Depending upon which layers of the structure are involved, diverticula are described as being either true or false.
Kidney development, or nephrogenesis, describes the embryologic origins of the kidney, a major organ in the urinary system. This article covers a 3 part developmental process that is observed in most reptiles, birds and mammals, including humans. Nephrogenesis is often considered in the broader context of the development of the urinary and reproductive organs.

The urachus is a fibrous remnant of the allantois, a canal that drains the urinary bladder of the fetus that joins and runs within the umbilical cord. The fibrous remnant lies in the space of Retzius, between the transverse fascia anteriorly and the peritoneum posteriorly.

In human anatomy, the median umbilical ligament is an unpaired midline ligamentous structure upon the lower inner surface of the anterior abdominal wall. It is covered by the median umbilical fold.

The bilaminar embryonic disc, bilaminar blastoderm or embryonic disc is the distinct two-layered structure of cells formed in an embryo. In the development of the human embryo this takes place by day eight. It is formed when the inner cell mass, also known as the embryoblast, forms a bilaminar disc of two layers, an upper layer called the epiblast and a lower layer called the hypoblast, which will eventually form into fetus. These two layers of cells are stretched between two fluid-filled cavities at either end: the primitive yolk sac and the amniotic sac.

Human embryonic development or human embryogenesis is the development and formation of the human embryo. It is characterised by the processes of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, the development of the human body entails growth from a one-celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilization occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form the single cell zygote and the germinal stage of development commences. Embryonic development in the human, covers the first eight weeks of development; at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus. The eight weeks has 23 stages.
The development of the reproductive system is the part of embryonic growth that results in the sex organs and contributes to sexual differentiation. Due to its large overlap with development of the urinary system, the two systems are typically described together as the genitourinary system.

Nasolacrimal duct obstruction is the obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct and may be either congenital or acquired. Obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct leads to the excess overflow of tears called epiphora.
The development of the digestive system in the human embryo concerns the epithelium of the digestive system and the parenchyma of its derivatives, which originate from the endoderm. Connective tissue, muscular components, and peritoneal components originate in the mesoderm. Different regions of the gut tube such as the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, etc. are specified by a retinoic acid gradient that causes transcription factors unique to each region to be expressed. Differentiation of the gut and its derivatives depends upon reciprocal interactions between the gut endoderm and its surrounding mesoderm. Hox genes in the mesoderm are induced by a Hedgehog signaling pathway secreted by gut endoderm and regulate the craniocaudal organization of the gut and its derivatives. The gut system extends from the oropharyngeal membrane to the cloacal membrane and is divided into the foregut, midgut, and hindgut.
A urethral diverticulum is a condition where the urethra or the periurethral glands push into the connective tissue layers (fascia) that surround it.