A concretion is a hard, compact mass of matter formed by the precipitation of mineral cement within the spaces between particles, and is found in sedimentary rock or soil. Concretions are often ovoid or spherical in shape, although irregular shapes also occur. The word 'concretion' is derived from the Latin concretio "(act of) compacting, condensing, congealing, uniting", itself from con meaning 'together' and crescere meaning "to grow". Concretions form within layers of sedimentary strata that have already been deposited. They usually form early in the burial history of the sediment, before the rest of the sediment is hardened into rock. This concretionary cement often makes the concretion harder and more resistant to weathering than the host stratum.
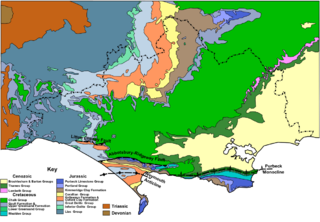
Dorset is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. Covering an area of 2,653 square kilometres (1,024 sq mi); it borders Devon to the west, Somerset to the north-west, Wiltshire to the north-east, and Hampshire to the east. The great variation in its landscape owes much to the underlying geology which includes an almost unbroken sequence of rocks from 200 Ma to 40 Ma and superficial deposits from 2 Ma to the present. In general the oldest rocks appear in the far west of the county, with the most recent (Eocene) in the far east. Jurassic rocks also underlie the Blackmore Vale and comprise much of the coastal cliff in the west and south of the county; and although younger Cretaceous rocks crown some of the highpoints in the west, they are mainly to be found in the centre and east of the county.

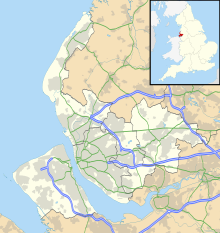
Thingwall is a village on the Wirral Peninsula, in Merseyside, England. The village is situated approximtely 8 km (5.0 mi) to the south west of Birkenhead and 3 km (1.9 mi) north east of Heswall. Historically part of Cheshire, the area is within the Pensby and Thingwall Ward of the Metropolitan Borough of Wirral and the parliamentary constituency of Wirral West.

Irby is a village on the Wirral Peninsula, in Merseyside, England. The village covers an area of 20 square kilometres. To the north of Irby lies the associated hamlet of Irby Hill. It is part of the Greasby, Frankby and Irby Ward of the Metropolitan Borough of Wirral and is within the parliamentary constituency of Wirral West.

Wirral, also known as The Wirral, is a peninsula in North West England. The roughly rectangular peninsula is about 15 miles (24 km) long and 7 miles (11 km) wide and is bounded by the River Dee to the west that forms a boundary with Wales, the River Mersey to the east, and the Irish Sea to the north.

Overstrand is a village on the north coast of Norfolk in England, two miles east of Cromer. It was once a modest fishing station, with all or part of the fishing station being known as Beck Hythe. In the latter part of the 19th century it was catapulted into prominence, and became known as “the village of millionaires”.

The Wirral Country Park is a country park on the Wirral Peninsula, England, lying both in the Metropolitan Borough of Wirral in the county of Merseyside and in the borough of Cheshire West & Chester in the county of Cheshire. It was the first designated country park in Britain, opening in 1973.

Boulder clay is a geological deposit of clay, often full of boulders, which is formed out of the ground moraine material of glaciers and ice-sheets. It was the typical deposit of the Glacial Period in northern Europe and North America.

Thurstaston Common is an area of almost 250 acres (100 ha) of parklands, wood and heath between Frankby and Thurstaston, on the Wirral Peninsula in North West England. The common is jointly owned by the National Trust and the Metropolitan Borough of Wirral. Royden Country Park is nearby and offers additional facilities.

Thurstaston is a village on the Wirral Peninsula, Merseyside, England. It is part of the West Kirby and Thurstaston Ward of the Metropolitan Borough of Wirral and the parliamentary constituency of Wirral West. The village lies on the A540 road between Heswall and Caldy, although it extends some distance down Station Road to the Wirral Way and the River Dee estuary.

The Channels Natural Area Preserve is a 721-acre (2.92 km2) Natural Area Preserve located in Washington and Russell counties, Virginia. It was established in April 2008 to protect a number of significant natural communities and habitats, including high-elevation forests, rock outcrops, and cliffs. Its name comes from a cluster of eroded crevices and sandstone boulders located on a portion of the land.
The Fair Isle wren is a small passerine bird in the wren family. It is a subspecies of the Eurasian wren endemic to Fair Isle, Shetland, Scotland, an island about halfway between mainland Shetland and Orkney. It was first described by the British ornithologist Kenneth Williamson in 1951.

The Spittles is an area of coastal cliff in the county of Dorset on the south coast of England. It is situated between the settlements of Lyme Regis to the west and Charmouth to the east. It forms part of the Jurassic Coast, a World Heritage Site designated in 2001. The cliff contains layers of Blue Lias and clay; in wet seasons the clay causes the layers above to become saturated and hence landslips occur, exposing many fossils. Mary Anning famously found an Ichthyosaurus in the Spittles.

Gad Cliff is a south-facing cliff face, immediately to the east of Worbarrow Tout and Pondfield Cove, on the south coast of the Isle of Purbeck in Dorset, England. Behind it is Gold Down, part of the Lulworth Ranges.

Combs Wood is a 15.1 hectares biological Site of Special Scientific Interest on the southern outskirts of Stowmarket in Suffolk. It is owned and managed by the Suffolk Wildlife Trust.

The Eagles Claw Nature Reserve is a protected nature reserve that is located on the south coast of the state of New South Wales, Australia. The 1-hectare (2.5-acre) reserve protects a strip of rugged coastline in the vicinity of Lookout Point at the town of Eden. The reserve was gazetted on 27 March 1986, to give protection to what was then thought to be the only known mainland breeding colony of little penguins in the state.

West Wood is a 23.6 hectares biological Site of Special Scientific Interest in Little Sampford, north of Thaxted in northwestern Essex. It is owned and managed by the Essex Wildlife Trust.

Gypsy Camp Meadows, Thrandeston is a 2.4 hectare biological Site of Special Scientific Interest north of Thrandeston in Suffolk.

Kimmeridge Ledges is a set of Kimmeridge clay ledges stretching out in to the sea on the Isle of Purbeck, a peninsula on the English Channel coast in Dorset, England.They are located to the southeast of Kimmeridge Bay and south of the villages of Kimmeridge, on the Smedmore Estate.

Stanford Training Area SSSI is part of the British Army Stanford Training Area. It is a 4,678-hectare (11,560-acre) biological and geological Site of Special Scientific Interest north of Thetford in Norfolk. It is a Nature Conservation Review site and part of it is a Geological Conservation Review site. It is also part of the Breckland Special Area of Conservation and Special Protection Area.