Berlin is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constituent states, Berlin is surrounded by the State of Brandenburg and contiguous with Potsdam, Brandenburg's capital. Berlin's urban area, which has a population of around 4.5 million, is the second most populous urban area in Germany after the Ruhr. The Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has around 6.2 million inhabitants and is Germany's third-largest metropolitan region after the Rhine-Ruhr and Rhine-Main regions.

The Berlin Wall was a guarded concrete barrier that encircled West Berlin of the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) from 1961 to 1989, separating it from East Berlin and the German Democratic Republic (GDR). Construction of the Berlin Wall was commenced by the government of the GDR on 13 August 1961. It included guard towers placed along large concrete walls, accompanied by a wide area that contained anti-vehicle trenches, beds of nails and other defenses. The primary intention for the Wall's construction was to prevent East German citizens from fleeing to the West.

Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second-most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south. Its 16 constituent states are bordered by Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr.
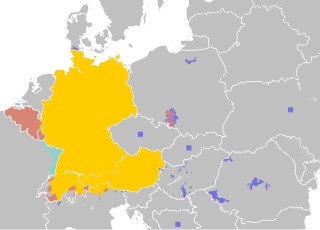
German, or more precisely High German, is a West Germanic language mainly spoken in Western Europe and Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italian province of South Tyrol. It is also an official language of Luxembourg and Belgium, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. Outside Germany, it is also spoken by German communities in France (Alsace), Czech Republic, Poland, Slovakia, and Hungary (Sopron).

The German Empire, also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Second Reich, or simply Germany, was the period of the German Reich from the unification of Germany in 1871 until the November Revolution in 1918, when the German Reich changed its form of government from a monarchy to a republic.

East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic was a country in Central Europe that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. Until 1989, it was commonly viewed as a communist state, and it described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state". Before the establishment, its territory was administered and occupied by Soviet forces with the autonomy of the native communists following the Berlin Declaration abolishing German sovereignty in World War II; when the Potsdam Agreement established the Soviet-occupied zone, bounded on the east by the Oder–Neisse line. The GDR was dominated by the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED) a communist party from 1949 to 1989 before being democratized and liberalized under the impact of the Revolutions of 1989 against the communist states, helping East Germany be united with the West. Unlike West Germany, SED did not see its state as the successor of the German Reich (1871–1945) and abolished the goal of unification in the constitution (1974). Under the SED rule, GDR was often judged as a Soviet satellite state; most scholars and academics described it as a totalitarian regime.

The Holy Roman Empire, officially known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed in the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.

Nazi Germany was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a dictatorship.

The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party, was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported the ideology of Nazism. Its precursor, the German Workers' Party, existed from 1919 to 1920. The Nazi Party emerged from the extremist German nationalist, racist and populist Freikorps paramilitary culture, which fought against the communist uprisings in post–World War I Germany. The party was created to draw workers away from communism and into völkisch nationalism. Initially, Nazi political strategy focused on anti–big business, anti-bourgeois, and anti-capitalist rhetoric, which was later downplayed to gain the support of business leaders. By the 1930s, the party's main focus shifted to antisemitic and anti-Marxist themes. The party had little popular support until the Great Depression, where worsening living standards and vast unemployment drove Germans into political extremism.

Operation Barbarossa was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. It was the largest land offensive in human history, with over 10 million combatants taking part. The operation, code-named after Frederick Barbarossa, a 12th-century Holy Roman emperor and German king, put into action Nazi Germany's ideological goal of conquering the western Soviet Union to repopulate it with Germans. The German Generalplan Ost aimed to use some of the conquered people as forced labour for the Axis war effort while acquiring the oil reserves of the Caucasus as well as the agricultural resources of various Soviet territories including Ukraine and Byelorussia. Their ultimate goal was to create more Lebensraum for Germany, and the eventual extermination of the indigenous Slavic peoples by mass deportation to Siberia, Germanisation, enslavement, and genocide.

World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945. The vast majority of the world's countries, including all of the great powers, fought as part of two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis. Many participants threw their economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind this total war, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and the delivery of the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in history, resulting in an estimated 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides, starvation, massacres, and disease. In the wake of the Axis defeat, Germany and Japan were occupied, and war crimes tribunals were conducted against German and Japanese leaders.

West Germany is the colloquial English term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 October 1990. During the Cold War, the western portion of Germany and the associated territory of West Berlin were parts of the Western Bloc. West Germany was formed as a political entity during the Allied occupation of Germany after World War II, established from 12 states formed in the three Allied zones of occupation held by the United States, the United Kingdom, and France. The FRG's provisional capital was the city of Bonn, and the Cold War era country is retrospectively designated as the Bonn Republic.

The German Shepherd is a German breed of working dog of medium to large size. The breed was developed by Max von Stephanitz using various traditional German herding dogs from 1899.

The Germany national football team represents Germany in men's international football and played its first match in 1908. The team is governed by the German Football Association, founded in 1900. Between 1949 and 1990, separate German national teams were recognised by FIFA due to Allied occupation and division: the DFB's team representing the Federal Republic of Germany, the Saarland team representing the Saar Protectorate (1950–1956) and the East Germany team representing the German Democratic Republic (1952–1990). The latter two were absorbed along with their records; the present team represents the reunified Federal Republic. The official name and code "Germany FR (FRG)" was shortened to "Germany (GER)" following reunification in 1990.

Deutsche Welle, abbreviated to DW, is a German public, state-owned international broadcaster funded by the German federal tax budget. The service is available in 32 languages. DW's satellite television service consists of channels in English, German, Spanish, Persian and Arabic. The work of DW is regulated by the Deutsche Welle Act, meaning that content is intended to be independent of government influence. DW is a member of the European Broadcasting Union (EBU).

Adolf Hitler was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Germany from 1933 until his suicide in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and then taking the title of Führer und Reichskanzler in 1934. During his dictatorship, he initiated World War II in Europe by invading Poland on 1 September 1939. He was closely involved in military operations throughout the war and was central to the perpetration of the Holocaust: the genocide of about six million Jews and millions of other victims.

World War I or the First World War, often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. It was fought between two coalitions, the Allies and the Central Powers. Fighting took place throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia, especially East Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died as a result of genocide, while the 1918 Spanish flu pandemic was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war.

Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine provinces, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous city and province. Austria is bordered by Germany to the northwest, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The country occupies an area of 83,871 km2 (32,383 sq mi) and has a population of 9 million.
Nazism, the common name in English for National Socialism, is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Nazi Germany. During Hitler's rise to power in 1930s Europe, it was frequently referred to as Hitlerism. The later related term "neo-Nazism" is applied to other far-right groups with similar ideas which formed after the Second World War.