Related Research Articles

The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's North Pole.

The shallot is a botanical variety of the onion. Until 2010, the shallot was classified as a separate species, Allium ascalonicum, a name that is a synonym of Allium cepa, the species name of the onion. A. cepa is the correct name for the shallot species.
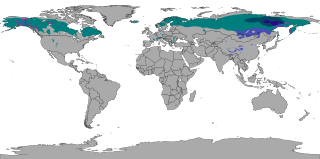
The subarctic climate is a climate characterised by long, usually very cold winters, and short, cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, generally at latitudes from 50° to 70°N poleward of the humid continental climates. Subarctic or boreal climates are the source regions for the cold air that affects temperate latitudes to the south in winter. These climates represent Köppen climate classification Dfc, Dwc, Dsc, Dfd, Dwd and Dsd.

Jerky is lean trimmed meat that has been cut into strips and dried (dehydrated) to prevent spoilage. Normally, this drying includes the addition of salt to prevent bacteria growth before the meat has finished the dehydrating process. The word "jerky" derives from the Quechua word ch'arki which means "dried, salted meat". All that is needed to produce basic "jerky" is a low-temperature drying method, and salt to inhibit bacterial growth.

Sunset, also known as sundown, is the daily disappearance of the Sun below the horizon due to Earth's rotation. As viewed from everywhere on Earth, the equinox Sun sets due west at the moment of both the Spring and Autumn equinox. As viewed from the Northern Hemisphere, the sun sets to the northwest in the Northern hemisphere's spring and summer, and to the southwest in the autumn and winter; these seasons are reversed for the Southern Hemisphere.

Red Dawn is a 1984 American action film directed by John Milius with a screenplay by Kevin Reynolds and Milius. It stars Patrick Swayze, Charlie Sheen, C. Thomas Howell, Lea Thompson, Jennifer Grey, Ben Johnson, Harry Dean Stanton, Ron O'Neal, William Smith and Powers Boothe. It was the first film to be released in the U.S. with a PG-13 rating.

Ice diving is a type of penetration diving where the dive takes place under ice. Because diving under ice places the diver in an overhead environment typically with only a single entry/exit point, it requires special procedures and equipment. Ice diving is done for purposes of recreation, scientific research, public safety and other professional or commercial reasons.

The sika deer, also known as the spotted deer or the Japanese deer, is a species of deer native to much of East Asia and introduced to other parts of the world. Previously found from northern Vietnam in the south to the Russian Far East in the north, it is now uncommon except in Japan, where the species is overabundant.

The white-tailed deer, also known as the whitetail or Virginia deer, is a medium-sized deer native to North America, Central America, Ecuador, and South America as far south as Peru and Bolivia. It has also been introduced to New Zealand, all the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean, and some countries in Europe, such as the Czech Republic, Finland, France, Germany, Romania and Serbia. In the Americas, it is the most widely distributed wild ungulate.

The red deer is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or hart, and a female is called a hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Iran, and parts of western Asia. It also inhabits the Atlas Mountains in Morocco and Tunisia, being the only species of deer to inhabit Africa. Red deer have been introduced to other areas, including Australia, New Zealand, the United States, Canada, Peru, Uruguay, Chile and Argentina. In many parts of the world, the meat (venison) from red deer is used as a food source.

Freeze drying, also known as lyophilization or cryodesiccation, is a low temperature dehydration process that involves freezing the product, lowering pressure, then removing the ice by sublimation. This is in contrast to dehydration by most conventional methods that evaporate water using heat.

Velvet antler is the whole cartilaginous antler in a precalcified growth stage of the Cervidae family including the species of deer such as elk, moose, and caribou. Velvet antler is covered in a hairy, velvet-like "skin" known as velvet and its tines are rounded, because the antler has not calcified or finished developing. Velvet antler preparations are sold in China as part of traditional Chinese medicine, and in the United States and some other countries as a dietary supplement.

Polar deserts are the regions of Earth that fall under an ice cap climate. Despite rainfall totals low enough to normally classify as a desert, polar deserts are distinguished from true deserts by low annual temperatures and evapotranspiration. Most polar deserts are covered in ice sheets, ice fields, or ice caps.

Aquarium fish feed is plant or animal material intended for consumption by pet fish kept in aquariums or ponds. Fish foods normally contain macronutrients, trace elements and vitamins necessary to keep captive fish in good health. Approximately 80% of fishkeeping hobbyists feed their fish exclusively prepared foods that most commonly are produced in flake, pellet or tablet form. Pelleted forms, some of which sink rapidly, are often used for larger fish or bottom feeding species such as loaches or catfish. Some fish foods also contain additives such as sex hormones or beta carotene to artificially enhance the color of ornamental fish.

The Dudhwa National Park is a national park in the Terai belt of marshy grasslands in northern Uttar Pradesh, India. It stretches over an area of 490.3 km2 (189.3 sq mi), with a buffer zone of 190 km2 (73 sq mi). It is part of the Dudhwa Tiger Reserve in the Kheri and Lakhimpur districts. The park is located on the Indo-Nepali border in the Lakhimpur Kheri District, and has buffers of reserved forest areas on the northern and southern sides. It represents one of the few remaining protected areas of the diverse and productive Terai ecosystem, supporting many endangered species, obligate species of tall wet grasslands and species of restricted distribution.

Inca cuisine originated in pre-Columbian times within the Inca civilization from the 13th to the 16th century. The Inca civilization stretched across many regions, and so there was a great diversity of plants and animals used for food, many of which remain unknown outside Peru. The most important staples were various tubers, roots, and grains. Maize was of high prestige, but could not be grown as extensively as it was further north. The most common sources of meat were guinea pigs and llamas, and dried fish was common.

The Java mouse-deer is a species of even-toed ungulate in the family Tragulidae. When it reaches maturity it is about the size of a rabbit, making it the smallest living ungulate. It is found in forests in Java and perhaps Bali, although sightings there have not been verified.

Cryo-preservation or cryo-conservation is a process where organelles, cells, tissues, extracellular matrix, organs, or any other biological constructs susceptible to damage caused by unregulated chemical kinetics are preserved by cooling to very low temperatures. At low enough temperatures, any enzymatic or chemical activity which might cause damage to the biological material in question is effectively stopped. Cryopreservation methods seek to reach low temperatures without causing additional damage caused by the formation of ice crystals during freezing. Traditional cryopreservation has relied on coating the material to be frozen with a class of molecules termed cryoprotectants. New methods are being investigated due to the inherent toxicity of many cryoprotectants. Cryoconservation of animal genetic resources is done with the intention of conservation of the breed.

Meat hanging is the culinary process of dry-aging meat to develop its flavor and tenderness.

Periglaciation describes geomorphic processes that result from seasonal thawing of snow in areas of permafrost, the runoff from which refreezes in ice wedges and other structures. "Periglacial" suggests an environment located on the margin of past glaciers. However, freeze and thaw cycles influence landscapes outside areas of past glaciation. Therefore, periglacial environments are anywhere that freezing and thawing modify the landscape in a significant manner.