The foreign policy of Denmark is based on its identity as a sovereign state in Europe, the Arctic and the North Atlantic. As such its primary foreign policy focus is on its relations with other nations as a sovereign state compromising the three constituent countries: Denmark, Greenland and the Faroe Islands. Denmark has long had good relations with other nations. It has been involved in coordinating Western assistance to the Baltic states.

Current and historical relations exist between Australia and Denmark. Australia has an embassy in Copenhagen, and Denmark has an embassy in Canberra.

Current and historical relations exist between Armenia and Denmark. Armenia has an embassy in Copenhagen, and Denmark is represented in Armenia, through its embassy in Kyiv, Ukraine. Diplomatic relations were established on 14 January 1992. In 2008, the Armenian Foreign Minister Eduard Nalbandyan called the relations between Armenia and Denmark "friendly" and "highly appreciating". In 2013, Amstream was founded as an independent non-political and non-profit organization in order to initiate means of collaboration and partnerships between Armenia and Scandinavia within business, education and culture. Both countries are members of the Council of Europe.

Croatia–Denmark relations refers to the current and historical relations between Croatia and Denmark. Relations between the two countries are described as "excellent", "friendly" and "well-developed".
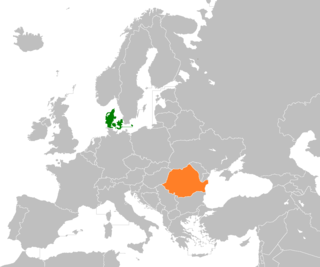
Denmark–Romania relations refers to the bilateral relations between Denmark and Romania. Denmark has an embassy in Bucharest, and Romania has an embassy in Copenhagen. Relations between Denmark and Communist Romania was described in the 1960s as "good" by Prime Minister of Romania Ion Gheorghe Maurer. Both countries are members of the Council of Europe, the European Union and NATO.

Denmark–Nepal relations are foreign relations between Denmark and Nepal. Denmark has had an embassy in Kathmandu from 1992 to 2017 and since then an Honorary Consulate. Nepal has had an embassy in Copenhagen since 2007. Nepal and Denmark established diplomatic relations on 15 December 1967.

Denmark–Georgia relations refers to the current and historical relations between Denmark and Georgia. Denmark is represented in Georgia, through its embassy in Tbilisi. Georgia has an embassy in Copenhagen. Denmark supports Georgia to become a member of the European Union and NATO. The current Georgian ambassador to Denmark is Gigi Gigiadze. Both nations are members of the Council of Europe.
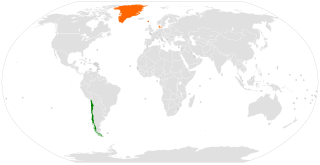
Chile–Denmark relations refers to the current and historical relations between Chile and Denmark. Chile has an embassy in Copenhagen, and Denmark has an embassy in Santiago. Relations between the two countries are described as "friendly" and excellent.

Denmark–Philippines relations refer to the bilateral relations between Denmark and the Philippines. Denmark has an embassy in Manila, and the Philippines has an embassy in Copenhagen.

Denmark – Sri Lanka relations refers to the current and historical relations between Denmark and Sri Lanka. Denmark is represented in Sri Lanka through its embassy in New Delhi, India. Sri Lanka is represented in Denmark through its embassy Oslo, Norway. Bilateral relations are described as warm for a long time. About 13,000 immigrants from Sri Lanka live in Denmark. President of Sri Lanka Chandrika Bandaranaike Kumaratunga visited Denmark in March 1995.
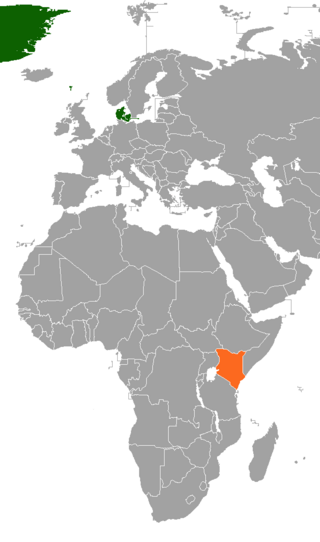
This article discusses the current and historical relations between Denmark and Kenya.
Denmark–Mozambique relations refers to the current and historical relations between Denmark and Mozambique. Denmark has an embassy in Maputo, and Mozambique is represented in Denmark, through its embassy in Stockholm, Sweden with an honorary consulate in Copenhagen. Diplomatic relations were established on 26 June 1975, but relations date back to before Mozambique achieved independence. The Danish Institute for Human Rights has worked with Mozambique since 1997. In 2000, Denmark signed an agreement with Finance Minister Luisa Diogo about implementation of mechanisms.

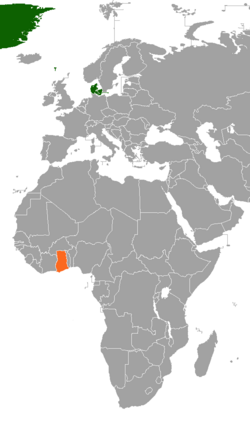
Benin–Denmark relations refers to the current and historical relations between Benin and Denmark. In 2007, the Danish development aid to Benin amounted 236 million DKK. Denmark is one of the largest aid donors to Benin and invested 60 million dollars in Benin in 2011. Neither country has a resident embassy.
Bolivia–Denmark relations refers to bilateral relations between Bolivia and Denmark. Bolivia is accredited to Denmark from its embassy in Berlin, Germany. Denmark is accredited to Bolivia from its embassy in Bogotá, Colombia.

Denmark–Malaysia relations refers to the current and historical relations between Denmark and Malaysia. Denmark has closed its embassy in Kuala Lumpur, which was opened in 1968, reportedly during lack of reciprocity. Malaysia has never maintained a resident embassy in Denmark, despite considerable bilateral trade relations and substantial development assistance disbursed by Denmark. Malaysia is represented in Denmark, through its embassy in Stockholm, Sweden. Diplomatic relations were established in 1963.

Denmark–Zambia relations refers to the historical and current bilateral relationship between Denmark and Zambia. Denmark has an embassy in Lusaka, and Zambia is represented in Denmark, through its embassy in Stockholm, Sweden. In 1980, relations were described as "warm".

Denmark–Switzerland relations refers to the current and historical relations between Denmark and Switzerland. Denmark has an embassy in Bern. Switzerland has an embassy in Copenhagen, but only offers consular services from the Nordic Regional Consular Centre in Stockholm. Diplomatic relations between Denmark and Switzerland were established in 1945.
Denmark – Hungary relations refers to the current and historical relations between Denmark and Hungary. Denmark has an embassy in Budapest. Hungary has an embassy in Copenhagen. Diplomatic relations were established on 10 May 1948. Both countries are full members of the Council of Europe, the European Union and NATO.

Denmark–Venezuela relations refers to the current and historical relations between Denmark and Venezuela. Denmark is accredited to Venezuela from its embassy in Brasilia, Brazil. Venezuela is accredited to Denmark from its embassy in Oslo, Norway. In 1878, the relations between Denmark and Venezuela were described as "friendly".

Denmark–Saudi Arabia relations are the bilateral relations between Denmark and Saudi Arabia. Denmark has an embassy in Riyadh, and Saudi Arabia has an embassy in Copenhagen.