Related Research Articles
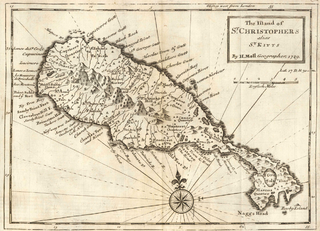
Saint Kitts and Nevis have one of the longest written histories in the Caribbean, both islands being among Spain's and England's first colonies in the archipelago. Despite being only two miles apart and quite diminutive in size, Saint Kitts and Nevis were widely recognized as being separate entities with distinct identities until they were forcibly united in the late 19th century.

West Jersey and East Jersey were two distinct parts of the Province of New Jersey. The political division existed for 28 years, between 1674 and 1702. Determination of an exact location for a border between West Jersey and East Jersey was often a matter of dispute.

The Leeward Islands are a group of islands situated where the northeastern Caribbean Sea meets the western Atlantic Ocean. Starting with the Virgin Islands east of Puerto Rico, they extend southeast to Guadeloupe and its dependencies. In English, the term Leeward Islands refers to the northern islands of the Lesser Antilles chain. The more southerly part of this chain, starting with Dominica, is called the Windward Islands. Dominica was originally considered a part of the Leeward Islands, but was transferred from the British Leeward Islands to the British Windward Islands in 1940.

The British West Indies (BWI) were colonised British territories in the West Indies: Anguilla, the Cayman Islands, Turks and Caicos Islands, Montserrat, the British Virgin Islands, Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica, Grenada, Jamaica, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, British Guiana and Trinidad and Tobago. Other territories included Bermuda, and the former British Honduras.

The Middle Colonies were a subset of the Thirteen Colonies in British America, located between the New England Colonies and the Southern Colonies. Along with the Chesapeake Colonies, this area now roughly makes up the Mid-Atlantic states.

The Province of New Jersey was one of the Middle Colonies of Colonial America and became the U.S. state of New Jersey in 1776. The province had originally been settled by Europeans as part of New Netherland but came under English rule after the surrender of Fort Amsterdam in 1664, becoming a proprietary colony. The English renamed the province after the island of Jersey in the English Channel. The Dutch Republic reasserted control for a brief period in 1673–1674. After that it consisted of two political divisions, East Jersey and West Jersey, until they were united as a royal colony in 1702. The original boundaries of the province were slightly larger than the current state, extending into a part of the present state of New York, until the border was finalized in 1773.

Proprietary colonies were a type of colony in English America which existed during the early modern period. In English overseas possessions established from the 17th century onwards, all land in the colonies belonged to the Crown, which held ultimate authority over their management. All English colonies were divided by the Crown via royal charters into one of three types of colony; proprietary colonies, charter colonies and Crown colonies. Under the proprietary system, individuals or companies, known as proprietors, were granted commercial charters by the Crown to establish overseas colonies. These proprietors were then granted the authority to select the governors and other officials in the colony.

The term British West Indies refers to the former English and British colonies and the present-day overseas territories of the United Kingdom in the Caribbean.

Colonel Daniel Parke Jr. was an American-born military officer, planter, politician and colonial administrator who served as the governor of the Leeward Islands from 1706 to 1710, when he was lynched by a mob in Antigua. Best known for his military service in Europe under the Duke of Marlborough during the War of the Spanish Succession, Parke was the only governor in Britain's American colonies to be murdered.
In the United States, a governor serves as the chief executive and commander-in-chief in each of the fifty states and in the five permanently inhabited territories, functioning as head of state and head of government therein. As such, governors are responsible for implementing state laws and overseeing the operation of the state executive branch. As state leaders, governors advance and pursue new and revised policies and programs using a variety of tools, among them executive orders, executive budgets, and legislative proposals and vetoes. Governors carry out their management and leadership responsibilities and objectives with the support and assistance of department and agency heads, many of whom they are empowered to appoint. A majority of governors have the authority to appoint state court judges as well, in most cases from a list of names submitted by a nominations committee.
Sir William MacBean George Colebrooke, was an English career soldier and colonial administrator who became lieutenant governor of New Brunswick in 1841.

The British Leeward Islands was a British colony from 1671 to 1958, consisting of the English overseas possessions in the Leeward Islands. It ceased to exist from 1816 to 1833, during which time it was split into two separate colonies. It was dissolved in 1958 after the separation of the British Virgin Islands, and the remaining islands became parts of the West Indies Federation.

The situation of the Catholic Church in the Thirteen Colonies was characterized by an extensive religious persecution originating from Protestant sects, which would barely allow religious toleration to Catholics living on American territory. Nonetheless, Catholics were a part of colonial history from the beginning, especially in Maryland, a colony founded by Catholics, and Rhode Island, a colony founded explicitly for religious toleration. The situation was complicated greatly by the evolving role of the English Crown, which acted as both Supreme Governor of the Church of England and the Head of State of the thirteen colonial governments in almost all periods of colonial rule.

Sir Nathaniel Johnson was an English Army officer, politician and colonial administrator who sat in the House of Commons of England representing the constituency of Newcastle-upon-Tyne from 1680 to 1689. He also served as the governor of the Leeward Islands and the governor of Carolina.

Major-General Sir Evan John Murray-Macgregor of Macgregor, 2nd Baronet, was a Scottish colonial administrator and senior British army officer.