
A melanocytic nevus is usually a noncancerous condition of pigment-producing skin cells. It is a type of melanocytic tumor that contains nevus cells. A mole can be either subdermal or a pigmented growth on the skin, formed mostly of a type of cell known as a melanocyte. The high concentration of the body's pigmenting agent, melanin, is responsible for their dark color. Moles are a member of the family of skin lesions known as nevi, occurring commonly in humans. Some sources equate the term "mole" with "melanocytic nevus", but there are also sources that equate the term "mole" with any nevus form.

Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Skin cancer is the most commonly diagnosed form of cancer in humans. There are three main types of skin cancers: basal-cell skin cancer (BCC), squamous-cell skin cancer (SCC) and melanoma. The first two, along with a number of less common skin cancers, are known as nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC). Basal-cell cancer grows slowly and can damage the tissue around it but is unlikely to spread to distant areas or result in death. It often appears as a painless raised area of skin that may be shiny with small blood vessels running over it or may present as a raised area with an ulcer. Squamous-cell skin cancer is more likely to spread. It usually presents as a hard lump with a scaly top but may also form an ulcer. Melanomas are the most aggressive. Signs include a mole that has changed in size, shape, color, has irregular edges, has more than one color, is itchy or bleeds.

Sebaceous hyperplasia is a disorder of the sebaceous glands in which they become enlarged, producing flesh-colored or yellowish, shiny, often umbilicated bumps. Sebaceous hyperplasia, primarily affecting older patients in high-concentration areas like the face, head, and neck, typically has a 2-4 mm diameter and causes no symptoms. The lesions are often surrounded by telangiectatic blood vessels, also known as "crown vessels," and a central dell, which is in line with the origin of the lesions.

Nevus is a nonspecific medical term for a visible, circumscribed, chronic lesion of the skin or mucosa. The term originates from nævus, which is Latin for "birthmark"; however, a nevus can be either congenital or acquired. Common terms, including mole, birthmark, and beauty mark, are used to describe nevi, but these terms do not distinguish specific types of nevi from one another.

Telogen effluvium is a scalp disorder characterized by the thinning or shedding of hair resulting from the early entry of hair in the telogen phase. It is in this phase that telogen hairs begin to shed at an increased rate, where normally the approximate rate of hair loss is 125 hairs per day.

A seborrheic keratosis is a non-cancerous (benign) skin tumour that originates from cells, namely keratinocytes, in the outer layer of the skin called the epidermis. Like liver spots, seborrheic keratoses are seen more often as people age.

Tinea capitis is a cutaneous fungal infection (dermatophytosis) of the scalp. The disease is primarily caused by dermatophytes in the genera Trichophyton and Microsporum that invade the hair shaft. The clinical presentation is typically single or multiple patches of hair loss, sometimes with a 'black dot' pattern, that may be accompanied by inflammation, scaling, pustules, and itching. Uncommon in adults, tinea capitis is predominantly seen in pre-pubertal children, more often boys than girls.

Actinic keratosis (AK), sometimes called solar keratosis or senile keratosis, is a pre-cancerous area of thick, scaly, or crusty skin. Actinic keratosis is a disorder of epidermal keratinocytes that is induced by ultraviolet (UV) light exposure. These growths are more common in fair-skinned people and those who are frequently in the sun. They are believed to form when skin gets damaged by UV radiation from the sun or indoor tanning beds, usually over the course of decades. Given their pre-cancerous nature, if left untreated, they may turn into a type of skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma. Untreated lesions have up to a 20% risk of progression to squamous cell carcinoma, so treatment by a dermatologist is recommended.

A dysplastic nevus or atypical mole is a nevus (mole) whose appearance is different from that of common moles. In 1992, the NIH recommended that the term "dysplastic nevus" be avoided in favor of the term "atypical mole". An atypical mole may also be referred to as an atypical melanocytic nevus, atypical nevus, B-K mole, Clark's nevus, dysplastic melanocytic nevus, or nevus with architectural disorder.

Lentigo maligna is where melanocyte cells have become malignant and grow continuously along the stratum basale of the skin, but have not invaded below the epidermis. Lentigo maligna is not the same as lentigo maligna melanoma, as detailed below. It typically progresses very slowly and can remain in a non-invasive form for years.
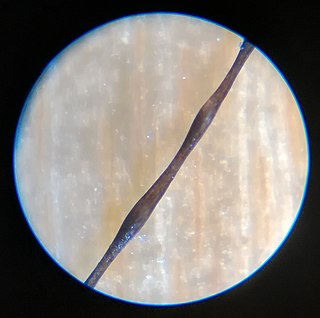
Monilethrix is a rare autosomal dominant hair disease that results in short, fragile, broken hair that appears beaded. It comes from the Latin word for necklace (monile) and the Greek word for hair (thrix). Hair becomes brittle, and breaks off at the thinner parts between the beads. It appears as a thinning or baldness of hair and was first described in 1897 by Walter Smith

Skin biopsy is a biopsy technique in which a skin lesion is removed to be sent to a pathologist to render a microscopic diagnosis. It is usually done under local anesthetic in a physician's office, and results are often available in 4 to 10 days. It is commonly performed by dermatologists. Skin biopsies are also done by family physicians, internists, surgeons, and other specialties. However, performed incorrectly, and without appropriate clinical information, a pathologist's interpretation of a skin biopsy can be severely limited, and therefore doctors and patients may forgo traditional biopsy techniques and instead choose Mohs surgery.
MoleMax was the first digital epiluminescence microscopy (dermatoscopy) system developed in cooperation with medical faculty Department of Dermatology of the Medical University of Vienna. It is currently owned and distributed by DermaMedicalSystems.

Pili torti is characterized by short and brittle hairs that appear flattened and twisted when viewed through a microscope.
Teledermatology is a subspecialty in the medical field of dermatology and probably one of the most common applications of telemedicine and e-health. In teledermatology, telecommunication technologies are used to exchange medical information over a distance using audio, visual, and data communication. Applications comprise health care management such as diagnoses, consultation, and treatment as well as (continuous) education.

Trichoscopy is a method of hair and scalp evaluation and is used for diagnosing hair and scalp diseases. The method is based on dermoscopy. In trichoscopy hair and scalp structures may be visualized at many-fold magnification. Currently magnifications ranging from 10-fold to 70-fold are most popular in research and clinical practice.
Antonella Tosti is an Italian physician and scientist with major contributions in the field of dermatology, including developing dermoscopy for the diagnosis and care of hair diseases, a world recognized expert in hair disorders. Her contributions to knowledge about nails include research about videodermoscopy of the hyponychium and the nail plate.

Lidia Rudnicka is a Polish-American dermatologist with contributions to the field of scleroderma research, hair diseases and melanoma prevention.

A nevoid melanoma is a malignant neoplastic lesion of the skin. It is a type of melanoma, the most dangerous form of skin cancer. Nevoid melanomas are clinically significant because they are difficult to distinguish from a benign nevus of the skin, which requires no treatment and is common on most individuals. Nevoid morphologies represent up to 3% of all cases of melanoma.
International Dermoscopy Society (IDS) is a non-governmental organization offering comprehensive promotion of dermoscopy, also known as dermatoscopy. It has over 16,000 international members from over 160 different countries.

















