
Mantidae is one of the largest families in the order of praying mantises, based on the type species Mantis religiosa; however, most genera are tropical or subtropical. Historically, this was the only family in the order, and many references still use the term "mantid" to refer to any mantis. Technically, however, "mantid" refers only to members of the family Mantidae, and not the 14 remaining families of mantises. Some of the most recent classifications have promoted a number of the mantid subfamilies to the rank of family, e.g. Iridopterygidae, Sibyllidae, Tarachodidae, Thespidae, and Toxoderidae, while other classifications have reduced the number of subfamilies without elevating to higher rank.

Empusidae is a family of plant-mimicking mantises, consisting of 10 genera, holding almost 30 species. Unlike many other mantis families, the Empusidae are a monophyletic lineage. Empusidae mantises are ambush predators, with mouthparts adapted to feeding on other insects and small animals. The majority of Empusidae species are distributed throughout Africa, but they are also found in Southeast Asia and in the southern parts of Europe.

Hymenopus coronatus is a mantis from the tropical forests of Southeast Asia. It is known by various common names including walking flower mantis and (pink) orchid mantis. It is one of several species known as flower mantises from their resemblance and behaviour. They are known to grab their prey with blinding speed.

Flower mantises are praying mantis species that display behaviors of mimicry. These insects have specific colorations and behaviors that mimic flowers in their surrounding habitats. The flower mantises are non-nocturnal group with a single ancestry, but the majority of the known species belong to family Hymenopodidea. These animals use a special form of camouflage referred to as Aggressive mimicry, which is used not only to avoid predation but to attract prey as well. This strategy has been observed in other mantises including the stick mantis and dead-leaf mantis. The observed behavior of these mantises includes positioning themselves on a plant and either inserting themselves within the irradiance or on the foliage of the plants until a prey insect comes within range. Many species of flower mantises are popular as pets.
Deroplatys desiccata, known by the common name giant dead leaf mantis, is a praying mantis from Southeast Asia. This is the type species of genus Deroplatys.

Hierodula is a genus of praying mantids in the tribe Hierodulini, found throughout Asia. Many species are referred to by the common name giant Asian mantis because of their large size compared to other mantids. Their large size and vibrant coloration make Hierodula mantids popular in the pet trade. Some widespread species include H. membranacea and H. patellifera; however this has been considered a 'catch all' genus and is currently subject to review. In 2020, three species were moved to a new genus, Titanodula.

Dead leaf mantis is a common name given to various species of praying mantis that mimic dead leaves. It is most often used in reference to species within genus Deroplatys because of their popularity as exotic pets. Examples include D. desiccata, D. lobata, and D. philippinica. Other species to which the term may apply include Acanthops falcataria, A. falcata, and Phyllocrania paradoxa.

Odontomantis planiceps, also known as Asian ant mantis, is a common species of praying mantis.
Deroplatys philippinica, with the common name Philippines dead leaf mantis, is a species of dead leaf mantis.

Theopropus elegans, common name banded flower mantis, is a species of praying mantis native to Southeast Asia.
Deroplatys angustata is a species of praying mantis in the family Deroplatyinae.

Deroplatys gorochovi is a species of praying mantis in the subfamily Deroplatyinae and the new (2019) family Deroplatyidae.
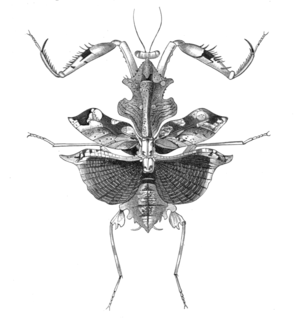
Deroplatys sarawaca is a species of praying mantis in the family Deroplatyidae. It is native to Borneo, including in Sarawak Province of Malaysia on the island. The holotype female is stored in the OUMNH collections.

Deroplatys trigonodera is a species of praying mantis in the family Deroplatyidae.

Deroplatys truncata is a species of praying mantis in the family Deroplatyidae.

Mantises are an order (Mantodea) of insects that contains over 2,400 species in about 460 genera in 33 families. The largest family is the Mantidae ("mantids"). Mantises are distributed worldwide in temperate and tropical habitats. They have triangular heads with bulging eyes supported on flexible necks. Their elongated bodies may or may not have wings, but all Mantodea have forelegs that are greatly enlarged and adapted for catching and gripping prey; their upright posture, while remaining stationary with forearms folded, has led to the common name praying mantis.

Helvia is a genus of praying mantises in the family Hymenopodidae found in Southeast Asia. It is monotypic, being represented by the single species, Helvia cardinalis.
Deroplatys cordata is a species of praying mantis in the family Deroplatyidae.

Orthodera is a genus of praying mantises that can be found in Australia and Southeast Asia, with one species said to be the only native species of mantis of New Zealand.














