
Mites are small arachnids. Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari. However, most recent genetic analyses do not recover the two as each other's closest relative within Arachnida, rendering the group non-monophyletic. Most mites are tiny, less than 1 mm (0.04 in) in length, and have a simple, unsegmented body plan. The small size of most species makes them easily overlooked; some species live in water, many live in soil as decomposers, others live on plants, sometimes creating galls, while others are predators or parasites. This last type includes the commercially destructive Varroa parasite of honey bees, as well as scabies mites of humans. Most species are harmless to humans, but a few are associated with allergies or may transmit diseases.

The red-backed salamander is a small, hardy woodland salamander species in the family Plethodontidae. It is also known as the redback salamander, eastern red-backed salamander, or the northern red-backed salamander to distinguish it from the southern red-backed salamander. The species inhabits wooded slopes in eastern North America, west to Missouri, south to North Carolina, and north from southern Quebec and the Maritime provinces in Canada to Minnesota. It is one of 56 species in the genus Plethodon. Red-backed salamanders are notable for their color polymorphism and primarily display two color morph varieties, which differ in physiology and anti-predator behavior.

Mange is a type of skin disease caused by parasitic mites. Because various species of mites also infect plants, birds and reptiles, the term "mange", or colloquially "the mange", suggesting poor condition of the skin and fur due to the infection, is sometimes reserved for pathological mite-infestation of nonhuman mammals. Thus, mange includes mite-associated skin disease in domestic mammals, in livestock, and in wild mammals. Severe mange caused by mites has been observed in wild bears. Since mites belong to the arachnid subclass Acari, another term for mite infestation is acariasis.

Pselaphinae are a subfamily of beetles in the family Staphylinidae, the rove beetles. The group was originally regarded as a separate family named Pselaphidae. Newton and Thayer (1995) placed them in the Omaliine group of the family Staphylinidae based on shared morphological characters.

Sminthurus viridis is a member of the Collembola, the springtails, an order in the subphylum Hexapoda. The species is known by common names such as clover springtail, lucerne flea, or lucerne earth flea.

The Acariformes, also known as the Actinotrichida, are the more diverse of the two superorders of mites. Over 32,000 described species are found in 351 families, with an estimated total of 440,000 to 929,000 species, including undescribed species.
Polydiscia deuterosminthurus is a species of mite recently discovered in the autonomous community of Navarre in Spain.

The Antillean fruit-eating bat is one of two leaf-nosed bat species belonging to the genus Brachyphylla. The species occurs in the Caribbean from Puerto Rico to St. Vincent and Barbados. Fossil specimens have also been recorded from New Providence, Bahamas.

Andinobates virolinensis is a species of frog in the family Dendrobatidae. It is endemic to Colombia where it is confined to the Santander and Cundinamarca departments on the Cordillera Oriental.

Prostigmata is a suborder of mites belonging to the order Trombidiformes, which contains the "sucking" members of the "true mites" (Acariformes).

Riccardoella limacum or the white snail mite is a member of the Acari (mite) family which is parasitic primarily on snails. Slug mites are very small, white, and can be seen to move very rapidly over the surface of their host, particularly under the shell rim and near the pulmonary aperture. While once thought to be benign mucophages, more recent studies have shown that they actually subsist on the host's blood, and may bore into the host's body to feed.

Steneotarsonemus spinki, the panicle rice mite, spinki mite, or rice tarsonemid mite, is a species of mite in the family Tarsonemidae, the white mites. It is a serious pest of rice in tropical Asia, Central America, and the Caribbean.

Springtails form the largest of the three lineages of modern hexapods that are no longer considered insects. Although the three orders are sometimes grouped together in a class called Entognatha because they have internal mouthparts, they do not appear to be any more closely related to one another than they are to all insects, which have external mouthparts.
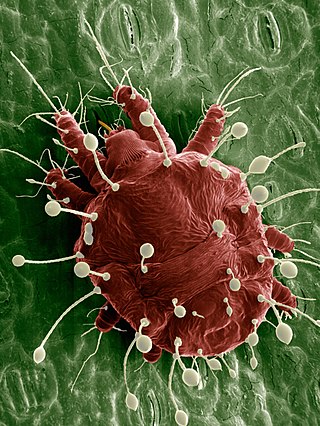
Raoiella indica, commonly known as the red palm mite, is a species of mite belonging to the family Tenuipalpidae. A pest of several species of palm in the Middle East and South East Asia, it is now becoming established throughout the Caribbean. The invasion of this species is the biggest mite explosion ever observed in the Americas.

Chrysomela populi is a species of broad-shouldered leaf beetle belonging to the family Chrysomelidae, subfamily Chrysomelinae.
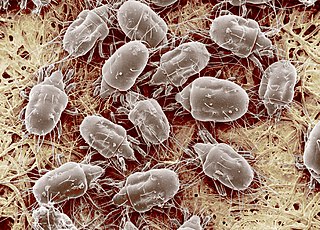
Tyrophagus putrescentiae is a cosmopolitan mite species. Together with the related species T. longior, it is commonly referred to as the mould mite or the cheese mite. The genus name translates from Greek to "cheese eater."

Folsomia candida is a species of springtail in the family Isotomidae. It is found in soil in many locations around the world, having been spread inadvertently by humans. It reproduces by parthenogenesis and has been used as a model organism in research.

Paedophryne swiftorum is a species of frog from Papua New Guinea discovered in 2008 and formally described in January 2012. It lives among leaf litter on the tropical rainforest floor and was named after the Swift family who had provided funds for establishing the Kamiali Biological Station where the new species was found.

Siju Dobakkol, also known as Siju Cave or Bat Cave in English, is one of the most well-known and significant caves in India. Located in the Garo Hills of the North East Indian state of Meghalaya, near Napak Lake and the Simsang River game reserve, it is a renowned limestone cave famous for its impressive stalagmite and stalactite formations. Siju Dobakkol is home to tens of thousands of bats, and holds great significance in the field of biospeleology, being one of the most thoroughly researched caves in the Indian subcontinent.
Lauritz Sverdrup Sømme is a Norwegian entomologist. His work has focused on insects in houses and stored foods, and especially the wintering and cold tolerance of certain arthropods. Sømme has been on several expeditions to the Antarctic, participated in field trips to Svalbard, and visited various other extreme places on Earth in his research on arthropods and cold tolerance.
















