
Oman is a country on the southeast coast of the Arabian Peninsula, situated in West Asia, bordering the Arabian Sea, Gulf of Oman, and Persian Gulf, between Yemen and the United Arab Emirates (UAE). The coast of Oman was an important part in the Omani empire and sultanate.

The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is a country situated in West Asia, the largest country on the Arabian Peninsula, bordering the Persian Gulf and the Red Sea. Its extensive coastlines provide great leverage on shipping through the Persian Gulf and the Suez Canal. The kingdom occupies 80% of the Arabian Peninsula. Most of the country's boundaries with the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Oman, and the Republic of Yemen are undefined, so the exact size of the country remains unknown. The Saudi government estimate is at 2,217,949 square kilometres, while other reputable estimates vary between 2,149,690 and 2,240,000 sq. kilometres. Less than 7% of the total area is suitable for cultivation, and in the early 1960s, population distribution varied greatly among the towns of the eastern and western coastal areas, the densely populated interior oases, and the vast, almost empty deserts.

The United Arab Emirates is situated in the Middle East and West Asia, bordering the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf, between Oman and Saudi Arabia; it is at a strategic location along the northern approaches to the Strait of Hormuz, a vital transit point for world crude oil. The UAE lies between 22°50′ and 26° north latitude and between 51° and 56°25′ east longitude. It shares a 19 km (12 mi) border with Qatar on the northwest, a 530 km (330 mi) border with Saudi Arabia on the west, south, and southeast, and a 450 km (280 mi) border with Oman on the southeast and northeast.

The Arabian Peninsula, or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. At 3,237,500 km2 (1,250,000 sq mi), comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.

Najd is the central region of Saudi Arabia, in which about a third of the country's modern population resides. It is the home of the House of Saud, from which it pursued unification with Hejaz since the time of the Emirate of Diriyah.

Al-Jawf Province, also spelled Al-Jouf, is one of the provinces of Saudi Arabia, located in the north of the country, partially bordered by Jordan to the west. It is one of the earliest inhabited regions of Arabian Peninsula, with evidence of human habitation dating back to the Stone Age and the Acheulean tool culture. Human settlement continued unbroken throughout the Copper Age, a period that saw the kingdom of Qidar fight against the Assyrian state for its independence. It is also in this period that references to Arabs first appear in historical texts. A Christian kingdom later emerged under the rule of the Bani Kalb tribe and survived until the arrival of Islam and the Islamic conquest of Al-Jawf. Following the region's Islamization it fell under the control of the Tayy tribe. Al-Jawf was incorporated into the third Saudi state at the time of its formation in 1932. In the 20th century the region was a site of conflict between the Al-Rashid family and the Al-Shaalan family, though it eventually came under the rule of King Abdulaziz bin Abdul Rahman Al Saud.

Asir, officially the Asir Province, is a province in the southwest of Saudi Arabia, which is named after the ʿAsīr tribe. It has an area of 76,693 square kilometres (29,611 sq mi), and an estimated population of 2,024,285. ʿAsīr is surrounded by Mecca Province to the north and west, Al-Bahah Province to the northwest, Riyadh Province to the northeast, Najran Province to the southeast, and Jazan Province and the Yemeni Muhafazah (Governorate) of Saada to the south.

Abha is the capital of 'Asir Region in Saudi Arabia. It is situated 2,270 metres above sea level in the fertile Asir Mountains of south-western Saudi Arabia, near Asir National Park. Abha's mild climate makes it a popular tourist destination for Saudis. Saudis also call the city the Bride of Mountain due to its position above the sea.

Al Baha is a city in south western Saudi Arabia located in the Sarawat Mountains. It is the capital of Al Bahah Region, and is one of the Kingdom's prime tourist attractions. It enjoys a pleasant climate and is surrounded by more than forty forests, including Raghdan, Al-Zaraeb and Baidan. Al Baha is the headquarters of the Governor, local councils and branches of governmental departments. Receiving the state's special attention, the city of Al Baha abounds in educational, tourist and health institutions. It is considered the capital of the Ghamdi and Zahrani tribes in Saudi Arabia, and most of its inhabitants are from the native tribes.
Al-Ghamdi is an Arabic family name denoting a member of the Ghamd tribe of Saudi Arabia.

The Sarawat Mountains, also known as the Sarat in singular case, is a part of the Hijaz Mountains in the western part of the Arabian Peninsula. In a broad sense, it runs parallel to the eastern coast of the Red Sea, and thus encompasses the mountains of Fifa', 'Asir and Taif. In a narrow sense, the Sarawat start in Taif city in Saudi Arabia, and extend to the Gulf of Aden in the south, running along the entire western coast of Yemen, in what used to be North Yemen, and extend eastwards into part of what used to be South Yemen, thus running parallel to the Gulf of Aden.

The Asir Mountains is a mountainous region in southwestern Saudi Arabia running parallel to the Red Sea. It comprises areas in the Region of 'Asir, but generally, it also includes areas near the border with Yemen. The mountains cover approximately 100,000 square kilometres (40,000 sq mi) and consists of mountains, plains, and valleys of the Arabian highlands. Sensu lato, they are part of the Sarawat Mountains, defining the latter as the mountain range which runs parallel to the Tihamah throughout the western portion of the Arabian Peninsula, particularly the western parts of Saudi Arabia and Yemen.

Bareq, is one of the governorates of Asir in the north-west of the region, 120 km (75 mi) north of Abha. It occupies a distinct location midway between Tihama and Asir, 412 m (1,352 ft) above sea level. With an estimated population of 75,351, it is well off economically; the city has grown rapidly and has many government services and public utilities available. It is one of Asir's winter resorts because of its natural environment and mild winter weather. Bareq has valleys.

The wildlife of Saudi Arabia is substantial and varied. Saudi Arabia is a very large country forming the biggest part of the Arabian Peninsula. It has several geographic regions, each with a diversity of plants and animals adapted to their own particular habitats. The country has several extensive mountain ranges, deserts, highlands, steppes, hills, wadis, volcanic areas, lakes and over 1300 islands. The Saudi Arabian coastline has a combined length of 2,640 km (1,640 mi) and consists of the Gulf of Aqaba and the Red Sea to the west while a shorter eastern coastline can be found along the Persian Gulf.
Jabal Al-Majāz is a mountain in the Sarawat range, 'Asir Region of Saudi Arabia, near the Yemeni border. At 2,902 m (9,521 ft) in height, it is one of the tallest mountains in the Saudi Kingdom.

Soudah is a mountainous area in the Asir region of Saudi Arabia. At 3,015 metres above sea level, it includes Saudi Arabia’s highest peak, Jabal Soudah. The area is known for its dense juniper tree covered mountains.
Jabal Ad-Dhoor is a mountain of Saudi Arabia located at 18°10′51″N 43°10′33″E.

The Dhofar Mountains are a mountain range in the southeastern part of the Arabian Peninsula. In a broad sense, they extend from Dhofar Governorate in Oman to Hadhramaut Governorate in Yemen, and are located between the Hajar in the northern part of Oman, and the Sarawat in the western part of Yemen. Otherwise, the range in the eastern part of Yemen, particularly near Mukalla, is referred to as the Hadhramaut or "Mahrat".
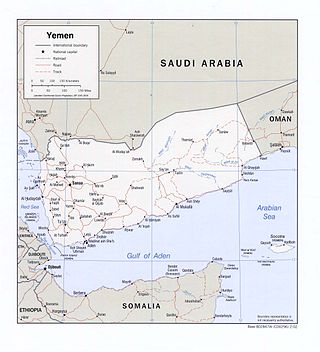
The Saudi Arabia–Yemen border is 1,307 km (812 mi) in length and runs from the Red Sea coast in the west to the tripoint with Oman in the east.
Harir Mountain is located in Yemen, and is one of the largest mountains in Dhale Governorate. The name of Harir Mountain is mentioned in Al-Hamdani's "Description of the Arabian Peninsula" book. Also in "The History of Yemeni Tribes" by Hamza Ali Luqman. Also mentioned by many Yemeni and Arab historians and writers, as well as in history and geography school textbooks. Harir Mountain is located in the east of Dhale governorate and within the administrative division of Al Hussein District. It's 20 kilometers from Dhale, and it is a mountain range that extends from Naqil (Al-Maadi) to the south, until Zahert Al-Atry to the north. Small mountains, rocky outcrops, valleys, and reefs branch off from it, as well as deep abysses to the west and east. The mountain range ends at Al-Hamayer and Al-Hasswa and Seelat Ghafinah in Shaka Valley near Aqram Mountain and at Lakmat El-Nub, Seelat Hamam, and EL-Haza to the west. And the village of Adina Wahid Ali which overlooks Murat Valley and Adina to the east. Harir Mountain is bordered from the south and east by Halimayn District. And from the north is the Shuaib district, and to the west is Shaka, Khella, Al-Hussein, and Al-Sha'ari land. Its altitude is 7800 feet above sea level. At the top of the mountain, there is a flat area on which villages have been built and residences have been constructed, interspersed with valleys and green agricultural terraces.














