
The black rhinoceros or hook-lipped rhinoceros is a species of rhinoceros, native to eastern and southern Africa including Angola, Botswana, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Eswatini, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Although the rhinoceros is referred to as black, its colours vary from brown to grey.

Darkling beetle is the common name of the large family of beetles Tenebrionidae. The number of species in the Tenebrionidae is estimated at more than 20,000 and the family is cosmopolitan in distribution.
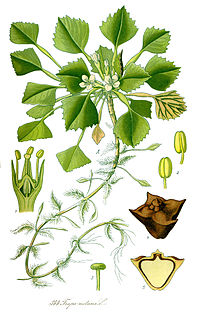
The water caltrop is any of three extant species of the genus Trapa: Trapa natans, Trapa bicornis and the endangered Trapa rossica. It is also known as water chestnut, buffalo nut, bat nut, devil pod, ling nut, lin kok, ling jow, ling kio nut, mustache nut or singhada.
Local extinction, also known as extirpation, is the condition of a species that ceases to exist in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinctions.

The great hornbill also known as the concave-casqued hornbill, great Indian hornbill or great pied hornbill, is one of the larger members of the hornbill family. It is found in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. Its impressive size and colour have made it important in many tribal cultures and rituals. The great hornbill is long-lived, living for nearly 50 years in captivity. It is predominantly frugivorous, but is an opportunist and will prey on small mammals, reptiles and birds.

The eastern black rhinoceros is also known as the East African black rhinoceros or eastern hook-lipped rhinoceros. It is a subspecies of the black rhinoceros. Its numbers are very low due to poaching for its horn and it is listed as critically endangered.

The western black rhinoceros or West African black rhinoceros was a subspecies of the black rhinoceros, declared extinct by the IUCN in 2011. The western black rhinoceros was believed to have been genetically different from other rhino subspecies. It was once widespread in the savanna of sub-Saharan Africa, but its numbers declined due to poaching. The western black rhinoceros resided primarily in Cameroon, but surveys since 2006 have failed to locate any individuals.

The south-central black rhinoceros or south-central hook-lipped rhinoceros is a subspecies of the black rhinoceros. In keeping with the rules of zoological nomenclature, the south-central black rhinoceros should be known as Diceros bicornis keitloa, a nomen novum. Although it is the most numerous of the black rhino subspecies, it is nevertheless designated as critically endangered on the IUCN’s red list. Like other black rhino subspecies, it has a prehensile lip and lives in savanna habitat.

The south-western black rhinoceros is a subspecies of the black rhinoceros, living in southwestern Africa. It is currently listed as near threatened by the IUCN. The biggest threat towards the subspecies Diceros bicornis occidentalis is illegal poaching.

Aegilops bicornis is a species in the family Poaceae native to Palestine and the Levant.

Persicaria bicornis is a North American species of flowering plant in the buckwheat family (Polygonaceae). The common name is pink smartweed. It is native to the central and southwestern United States from northern Texas west to Arizona, east to Louisiana, and north as far as eastern Wyoming, South Dakota, Iowa, and Illinois.

Osmia bicornis, synonym Osmia rufa, is a species of mason bee, and is known as the red mason bee due to its covering of dense gingery hair. It is a solitary bee that nests in holes or stems and is polylectic, meaning it forages pollen from various different flowering plants. These bees can be seen aggregating together and nests in preexisting hollows, choosing not to excavate their own. These bees are not aggressive; they will only sting if handled very roughly and are safe to be closely observed by children. Females only mate once, usually with closely related males. Further, females can determine the sex ratio of their offspring based on their body size, where larger females will invest more in diploid females eggs than small bees. These bees also have trichromatic colour vision and are important pollinators in agriculture.

The southern black rhinoceros or Cape rhinoceros is an extinct subspecies of the black rhinoceros that was once abundant in South Africa from the Cape Province to Transvaal, southern Namibia, and possibly also Lesotho and southern Botswana. It was brought to extinction by excessive hunting and habitat destruction around 1850.

The family Cavoliniidae is a taxonomic group of small floating sea snails, pelagic marine opisthobranch gastropod mollusks.
Aiphanes bicornis is a species of small, pinnately leaved palm which is endemic to Ecuador. First described in 2004 and known from only two locations, the species name refers to the deeply notched tips of its leaflets, which resemble a pair of horns.
Omocerus bicornis is a species of tortoise beetle from South America. It lives on Cordia (Boraginaceae) plants, and is found in Brazil, Surinam, French Guiana, Suriname and Venezuela. It was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1763 work Centuria Insectorum under the name Cassida bicornis, and was later made the type species of the genus Omocerus by Philogène Auguste Joseph Duponchel and Alcide d'Orbigny in 1843.
M. bicornis may refer to:

Dicheros bicornis is a species of beetles belonging to the family Scarabaeidae, subfamily Cetoniinae.

Haplodrassus bicornis is a species of ground spider in the family Gnaphosidae. It is found in the United States and Canada.

Schizocephala is a genus of praying mantises in the monotypic tribe Schizocephalini. It is represented by a single species, Schizocephala bicornis. It is distributed across Pakistan, India, Nepal, Sri Lanka and the Sunda Islands.















