
Kidney dialysis is the process of removing excess water, solutes, and toxins from the blood in people whose kidneys can no longer perform these functions naturally. This is referred to as renal replacement therapy. The first successful dialysis was performed in 1943.

Kidney failure, also known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD), is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as either acute kidney failure, which develops rapidly and may resolve; and chronic kidney failure, which develops slowly and can often be irreversible. Symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications of acute and chronic failure include uremia, hyperkalemia, and volume overload. Complications of chronic failure also include heart disease, high blood pressure, and anaemia.

Uremia is the term for high levels of urea in the blood. Urea is one of the primary components of urine. It can be defined as an excess in the blood of amino acid and protein metabolism end products, such as urea and creatinine, which would be normally excreted in the urine. Uremic syndrome can be defined as the terminal clinical manifestation of kidney failure. It is the signs, symptoms and results from laboratory tests which result from inadequate excretory, regulatory, and endocrine function of the kidneys. Both uremia and uremic syndrome have been used interchangeably to denote a very high plasma urea concentration that is the result of renal failure. The former denotation will be used for the rest of the article.

Hemodialysis, also spelled haemodialysis, or simply dialysis, is a process of filtering the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working normally. This type of dialysis achieves the extracorporeal removal of waste products such as creatinine and urea and free water from the blood when the kidneys are in a state of kidney failure. Hemodialysis is one of three renal replacement therapies. An alternative method for extracorporeal separation of blood components such as plasma or cells is apheresis.

Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of long-term kidney disease, in which either there is a gradual loss of kidney function occurs over a period of months to years, or abnormal kidney structure. Initially generally no symptoms are seen, but later symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications can relate to hormonal dysfunction of the kidneys and include high blood pressure, bone disease, and anemia. Additionally CKD patients have markedly increased cardiovascular complications with increased risks of death and hospitalization.
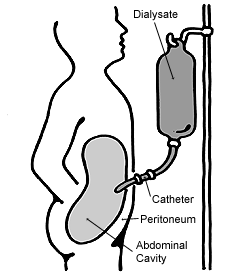
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a type of dialysis that uses the peritoneum in a person's abdomen as the membrane through which fluid and dissolved substances are exchanged with the blood. It is used to remove excess fluid, correct electrolyte problems, and remove toxins in those with kidney failure. Peritoneal dialysis has better outcomes than hemodialysis during the first couple of years. Other benefits include greater flexibility and better tolerability in those with significant heart disease.

Home hemodialysis (HHD) is the provision of hemodialysis to purify the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working normally, in their own home. One advantage to doing dialysis at home is that it can be done more frequently and slowly, which reduces the "washed out" feeling and other symptoms caused by rapid ultrafiltration, and it can often be done at night, while the person is sleeping.

Hemofiltration, also haemofiltration, is a renal replacement therapy which is used in the intensive care setting. It is usually used to treat acute kidney injury (AKI), but may be of benefit in multiple organ dysfunction syndrome or sepsis. During hemofiltration, a patient's blood is passed through a set of tubing via a machine to a semipermeable membrane where waste products and water are removed by convection. Replacement fluid is added and the blood is returned to the patient.
Renal replacement therapy (RRT) is therapy that replaces the normal blood-filtering function of the kidneys. It is used when the kidneys are not working well, which is called kidney failure and includes acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease. Renal replacement therapy includes dialysis, hemofiltration, and hemodiafiltration, which are various ways of filtration of blood with or without machines. Renal replacement therapy also includes kidney transplantation, which is the ultimate form of replacement in that the old kidney is replaced by a donor kidney.
Nils Alwall was a Swedish professor at Lund University, Sweden. He was a pioneer in hemodialysis and the inventor of one of the first practical dialysis machines. Alwall pioneered the technique of ultrafiltration and introduced the principle of hemofiltration. Alwall is referred to as the "father of extracorporeal blood treatment."

Northwest Kidney Centers is a regional, not-for-profit community-based provider of kidney dialysis, public health education, and research into the causes and treatments of chronic kidney disease. Established in Seattle in 1962, it was the world's first out-of-hospital dialysis provider. It offers dialysis throughout the greater Seattle area in 20 free-standing clinics, eight hospitals and its home dialysis program. It opened its first clinic in Everett in 2020, the organization's first in Snohomish county.

Robert Provenzano is an American nephrologist. He is also an Associate Clinical Professor of Medicine at Wayne State University School of Medicine.

Gambro is a global medical technology company that manufactures products for dialysis treatment. The company is involved in developing, manufacturing and supplying products and therapies for kidney and liver dialysis, myeloma kidney therapy, and other extracorporeal therapies for chronic and acute patients. Gambro was founded in Lund, Sweden, in 1964 by Holger Crafoord and has around 8,000 employees, production facilities in nine countries, and sales in more than 100 countries.
Dialysis Clinic, Inc. is a nonprofit medical corporation founded in 1971 and chartered as a 501(c)(3) tax-exempt organization under IRS regulations.
Nathan W. Levin is an American physician and founder of the Renal Research Institute, LLC., a research institute dedicated to improving the outcomes of patients with kidney disease, particularly those requiring dialysis. Levin is one of the most prominent and renowned figures in clinical nephrology as well as nephrology research. He has authored multiple book chapters and over 350 peer-reviewed publications, including articles in leading journals such as Nature, the New England Journal of Medicine, and The Lancet.

The Sindh Institute of Urology & Transplantation (SIUT) is a dialysis & kidney transplant centre located in Pakistan. SIUT was founded by Dr. Adeebul Hasan Rizvi and it is Pakistan's largest kidney disease center, as well as Pakistan's largest public sector health organisation.
Symptom targeted intervention (STI) is a clinical program being used in medical settings to help patients who struggle with symptoms of depression or anxiety or adherence to treatment plans but who are not interested in receiving outpatient mental health treatment. STI is an individualized therapeutic model and clinical program that teaches patients brief, effective ways to cope with difficult thoughts, feelings, and behaviors using evidence-based interventions. Its individualized engagement process employs techniques from solution-focused therapy, using a Rogerian, patient-centered philosophy. This engagement process ensures that even challenging, at-risk, and non-adherent patients are able to participate.
Sree Bhushan Raju M.D., D.M., Diplomate of National Board, is a nephrologist from Telangana, India. He is currently Senior professor and Unit head, Dept of Nephrology, Nizam's Institute of Medical Sciences Panjagutta, Hyderabad. Which is one of the largest Nephrology teaching Department in India having ten DM seats. He is one of the principal investigators of CKD task force by Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) to evaluate the prevalence of CKD in adult urban population in India. He is currently an associate editor of Indian Journal of Nephrology, Indian Journal of Organ Transplantation and Frontiers in Medicine. He is a popular advocator of Public Health and early detection of non-communicable disease. He frequency writes editorials in various Regional and National News papers about quality of care, public health, health care systems

DaVita Inc. provides kidney dialysis services through a network of 2,816 outpatient dialysis centers in the United States, serving 204,200 patients, and 321 outpatient dialysis centers in 10 other countries serving 3,200 patients. The company primarily treats end-stage renal disease (ESRD), which requires patients to undergo dialysis 3 times per week for the rest of their lives unless they receive a donor kidney. The company has a 37% market share in the U.S. dialysis market. It is organized in Delaware and based in Denver.
Stanley Shaldon was a British nephrologist who pioneered several techniques in haemodialysis, including venous access, reuse of dialysis machines, and home haemodialysis.











