
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, and previously known as the Malagasy Republic, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately 400 kilometres off the coast of East Africa across the Mozambique Channel. At 592,800 square kilometres (228,900 sq mi) Madagascar is the world's second-largest island country, after Indonesia. The nation comprises the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Following the prehistoric breakup of the supercontinent Gondwana, Madagascar split from the Indian subcontinent around 88 million years ago, allowing native plants and animals to evolve in relative isolation. Consequently, Madagascar is a biodiversity hotspot; over 90% of its wildlife is found nowhere else on Earth. The island's diverse ecosystems and unique wildlife are threatened by the encroachment of the rapidly growing human population and other environmental threats.

The history of Madagascar is distinguished clearly by the early isolation of the landmass from the ancient supercontinent containing Africa and India, and by the island's late colonization by human settlers arriving in outrigger canoes from the Sunda islands and from East Africa. These two factors facilitated the evolution and survival of thousands of endemic plant and animal species, some of which have gone extinct or are currently threatened with extinction due to the government not allocating resources to help the growing population, causing many people to resort to harmful environmental practices as a way of survival. Over the past two thousand years the island has received waves of settlers of diverse origins including Austronesian, Bantu, Arab, South Asian, Chinese and European. The majority of the population of Madagascar today is a mixture of Austronesian and Bantu settlers. Despite popular belief, there has been no genetic input from Arabs or Indians, although one tribe, the Antemoro, claims descent from Somali Arab traders.

The aye-aye is a long-fingered lemur, a strepsirrhine primate native to Madagascar with rodent-like teeth that perpetually grow and a special thin middle finger.

Alfred Grandidier was a French naturalist and explorer.
Nosy Be[ˌnusʲ ˈbe] is an island off the northwest coast of Madagascar. Nosy Be is Madagascar's largest and busiest tourist resort. It has an area of 320.02 square kilometres (123.56 sq mi), and its population was 109,465 according to the provisional results of the 2018 Census.

This list of national parks of Madagascar includes all officially recognized protected areas as of 2015. The protected areas network of Madagascar is managed by the Madagascar National Parks Association (PNM-ANGAP). The network includes three types of protected areas: Strict Nature Reserves, National Parks and Wildlife Reserves. At the 2003 IUCN World Parks Congress in Durban, the Malagasy President, Marc Ravalomanana, announced an initiative to more than triple the area under protection from approximately 4,200,791 acres (17,000.00 km2) to over 14,826,322 acres (60,000.00 km2). This "Durban Vision", as it has been dubbed, involved broadening the definition of protected areas in the country and legislation has been passed to allow the creation of four new categories of protected area: Natural Parks, Natural Monuments, Protected Landscapes, and Natural Resource Reserves. As well as allowing these new objectives for protected areas management, the new legislation also provided for entities other than PNM-ANGAP to manage protected areas, such as government ministries, community associations, NGOs and other civil society organizations, and the private sector.

Madagascar is divided into 23 regions (faritra). These formerly second-tier administrative divisions became the first-level administrative divisions when the former six provinces were dissolved on 4 October 2009:

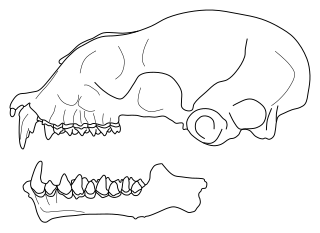
The brown-tailed mongoose, Malagasy brown-tailed mongoose, or salano is a species of mammal in the family Eupleridae. It is endemic to Madagascar. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry forests. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Malagasy is an Austronesian language and the national language of Madagascar. Most people in Madagascar speak it as a first language, as do some people of Malagasy descent elsewhere.

Lemurs of Madagascar is a 2010 reference work and field guide for the lemurs of Madagascar, giving descriptions and biogeographic data for the known species. The primary contributor is Russell Mittermeier, president of Conservation International, and the cover art and illustrations were drawn by Stephen D. Nash. Currently in its third edition, the book provides details about all known lemur species, general information about lemurs and their history, and also helps travelers identify species they may encounter. Four related pocket field guides have also been released, containing color illustrations of each species, miniature range maps, and species checklists.
Triaenops menamena is a bat in the genus Triaenops found on Madagascar, mainly in the drier regions. It was known as Triaenops rufus until 2009, when it was discovered that that name had been incorrectly applied to the species. Triaenops rufus is a synonym of Triaenops persicus, a Middle Eastern species closely related to T. menamena— the Malagasy species had previously been placed as a subspecies of T. persicus by some authors. Triaenops menamena is mostly found in forests, but also occurs in other habitats. It often roosts in large colonies and eats insects such as butterflies and moths. Because of its wide range, common occurrence, and tolerance of habitat degradation, it is not considered to be threatened.

Pipistrellus raceyi, also known as Racey's pipistrelle, is a bat from Madagascar, in the genus Pipistrellus. Although unidentified species of Pipistrellus had been previously reported from Madagascar since the 1990s, P. raceyi was not formally named until 2006. It is apparently most closely related to the Asian species P. endoi, P. paterculus, and P. abramus, and its ancestors probably reached Madagascar from Asia. P. raceyi has been recorded at four sites, two in the eastern and two in the western lowlands. In the east, it is found in open areas and has been found roosting in a building; in the west it occurs in dry forest. Because of uncertainties about its ecology, it is listed as "Data Deficient" on the IUCN Red List.

Isalorhynchus is an extinct genus of hyperodapedontine rhynchosaur from the late Triassic period of Toliara Province, southwestern Madagascar. It is known from the holotype MDE-R18, a nearly complete maxilla and from other specimens from the same locality, Malio River area. It was found in the Makay Formation of the Morondava Basin. It was first named by Eric Buffetaut in 1983 and the type species is Isalorhynchus genovefae. The majority of Isalorhynchus specimens are isolated jaw bones, but two nearly complete skeletons were found in 1998. Langer et al., 2000 concluded that Isalorhynchus is a synonym of Hyperodepedon and referred it to a new species of Hyperodepedon. Whatley, 2005 retained this genus as valid with a description of new materials in her PhD thesis. Montefeltro et al., 2010 and Langer et al., 2010 accepted Isalorhynchus as valid genus.

Durrell's vontsira is a mammal in the family Eupleridae of the order Carnivora, native to Madagascar. It is most closely related to the brown-tailed mongoose, with which it forms the genus Salanoia. The two are genetically similar, but morphologically distinct, leading scientists to recognize them as separate species. After an individual was observed in 2004, the animal became known to science and S. durrelli was described as a new species in 2010. It is found only in the Lac Alaotra area.
Anarsia vinsonella is a moth of the family Gelechiidae. It is found on Mauritius and Réunion in the Indian Ocean.

Hery Martial Rajaonarimampianina Rakotoarimanana is a Malagasy politician who was President of Madagascar from January 2014 to September 2018, resigning to run for re-election. Previously he served as Minister of Finance under President Andry Rajoelina, and he was the Rajoelina political movement's candidate in the 2013 presidential election. He won the vote in a second round, defeating Jean-Louis Robinson, the candidate of Marc Ravalomanana's party. Once he was elected, Rajaonarimampianina held the world record of the head of state with the longest name as well as family name.
Dichomeris monorbella is a moth in the family Gelechiidae. It was described by Viette in 1988. It is found in Madagascar.
Lecithocera ojejyella is a moth in the family Lecithoceridae. It was described by Viette in 1986. It is found in Madagascar.
Lecithocera kambanella is a moth in the family Lecithoceridae. It was described by Viette in 1986. It is found in Madagascar.

Sahonachelys is an extinct genus of pelomedusoid turtle from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) Maevarano Formation of Madagascar. The genus contains a single species, Sahonachelys mailakavava.















