
Anatolia is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It makes up the majority of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe.

Turkey is a large, roughly rectangular peninsula that bridges southeastern Europe and Asia. Thrace, the European portion of Turkey comprises 3% of the country and 10% of its population. Thrace is separated from Asia Minor, the Asian portion of Turkey, by the Bosporus, the Sea of Marmara and the Dardanelles.

Karabük Province is a landlocked province in the northern part of Anatolia, located about 200 km (124 mi) north of Ankara, 115 km (71 mi) away from Zonguldak and 113 km (70 mi) away from Kastamonu. In 2010 it had a population of 227,610. The main city is Karabük which is located about 100 km (62 mi) south of the Black Sea coast.
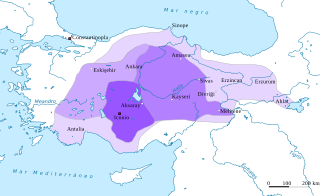
The Sultanate of Rum or Rum Seljuk Sultanate was a Turko-Persian Sunni Muslim ruled state, established over major cities and territories of Anatolia conquered from the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire by the Seljuk Turks following the decisive Battle of Manzikert (1071). The name Rûm was a synonym for the Byzantine Empire and its peoples, as it remains in modern Turkish. It derives from the Arabic name for ancient Rome, الرُّومُ ar-Rūm, itself a loan from Koine Greek Ῥωμαῖοι, "Romans, citizens of the Eastern Roman Empire".

Anatolian beyliks were small principalities in Anatolia governed by Beys, the first of which were founded at the end of the 11th century. A second more extensive period of foundations took place as a result of the decline of the Seljuq Sultanate of Rûm in the second half of the 13th century.

Çiğli is a metropolitan district of İzmir in western Turkey. It covers the northern end of İzmir Metropolitan Municipality around the mouth of the River Gediz, across the Gulf of İzmir from the main city. The Gediz delta is an Important Bird Area but is under threat from urbanization. IAOIZ, the Izmir Atatürk Organized Industrial Zone, is a significant economic hub and there is a major air force base.

The Aegean Region is one of the 7 geographical regions of Turkey.

The Central Anatolia Region is a geographical region of Turkey. The largest city in the region is Ankara.

The Eastern Anatolia Region is a geographical region of Turkey.

The Mediterranean Region is a geographical region of Turkey.

The Southeastern Anatolia Region is a geographical region of Turkey.

Çayönü Tepesi is a Neolithic settlement in southeastern Turkey which prospered from circa 8,630 to 6,800 BC. It is located forty kilometres north-west of Diyarbakır, at the foot of the Taurus mountains. It lies near the Boğazçay, a tributary of the upper Tigris River and the Bestakot, an intermittent stream.

Turkey, officially the Republic of Turkey, is a transcontinental country straddling Southeastern Europe and Western Asia. It is bordered on its northwest by Greece and Bulgaria; north by the Black Sea; northeast by Georgia; east by Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran; southeast by Iraq; south by Syria and the Mediterranean Sea; and west by the Aegean Sea. Istanbul, which straddles Europe and Asia, is the country's largest city, while Ankara is the capital. Approximately 70 to 80 percent of the country's citizens are ethnic Turks, while the largest minority are Kurds at 20 percent.
The geology of Turkey is the product of a wide variety of tectonic processes that have shaped Anatolia over millions of years, a process which continues today as evidenced by frequent earthquakes and occasional volcanic eruptions.

Lake Abant is a freshwater lake in Turkey's Bolu Province in northwest Anatolia, formed as a result of a great landslide. The lake lies at an altitude of 1,328 m (4,357 ft) at a distance of 32 km (20 mi) from the provincial seat of Bolu city. It is a vacation and excursion spot for both Turkish and foreign travellers due to the natural environment, forests, and accessibility by car.. Lake Abant is a natural park.

The Great Seljuk Empire or the Seljuk Empire was a high medieval Turko-Persian Sunni Muslim empire, originating from the Qiniq branch of Oghuz Turks. At its greatest extent, the Seljuk Empire controlled a vast area stretching from western Anatolia and the Levant to the Hindu Kush in the east, and from Central Asia to the Persian Gulf in the south.

As of 2000 about 9300 species of vascular plant were known to grow in Turkey. By comparison, Europe as a whole contains only about 24% more species, despite having thirteen times the area.

The history of Turkey, understood as the history of the region now forming the territory of the Republic of Turkey, includes the history of both Anatolia and Eastern Thrace. These two previously politically distinct regions came under control of the Roman Empire in the second century BCE, eventually becoming the core of the Roman Byzantine Empire.

Dichoropetalum is a genus of flowering plants in the carrot family.

















