Related Research Articles

James Wood-Mason was an English zoologist. He was the director of the Indian Museum at Calcutta, after John Anderson. He collected marine animals and lepidoptera, but is best known for his work on two other groups of insects, phasmids and mantids.

Alfred William Alcock was a British physician, naturalist, and carcinologist.

The Echinasteridae are a family of starfish in the monotypic order Spinulosida. The family includes eight genera and about 133 species found on the seabed in various habitats around the world.

The Astropectinidae are a family of sea stars in the order Paxillosida. Usually, these starfish live on the seabed and immerse themselves in soft sediment such as sand and mud.

Comitas is a genus of medium-sized sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the family Pseudomelatomidae.

Gnathophausia zoea is a species of lophogastrid crustacean. It is widely distributed in the Atlantic Ocean from the Arctic Circle to the Equator; in the Pacific Ocean, it is more restricted to tropical areas. The adults may reach 40–50 millimetres (1.6–2.0 in) long, excluding the rostrum, or around 70 mm (2.8 in) including the rostrum.

Calliotropis metallica is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Eucyclidae.

Metapenaeopsis, the velvet shrimps, is a prawn genus in the family Penaeidae. It contains these species:

The family Homolidae, known as carrier crabs or porter crabs, contains 14 genera of marine crabs. They mostly live on the continental slope and continental shelf, and are rarely encountered. Members of the Homolidae have their fifth pereiopods in a sub-dorsal position, which allows them to hold objects in place over the rear half of the carapace. The objects carried include sponges, black corals and gorgonians, and this behaviour may be a defence mechanism against predators. Some species have been observed carrying living sea urchins in a symbiotic relationship which allows them to benefit from the protection of the urchin's dangerous spikes.

Sclerasterias is a genus of starfish in the family Asteriidae. Adult individuals have five arms but small, immature individuals have six. This led to the giving of a separate generic name to the juveniles, Hydrasterias, before it was realised that only one genus was involved. These young individuals often undergo fissiparity. The disc splits into two parts, each bearing three arms, and new arms develop on each part to complete the complement of arms. This sometimes happens repeatedly and may be an adaptation to life in cold, deep seas where most of the species are found.

Nephropsis is a genus of lobsters containing 15 extant species:

Rochinia is a genus of crab in the family Epialtidae, containing the following species:

Metapenaeus is a genus of prawns, containing the following species:

Borsonia symbiotes is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Borsoniidae.
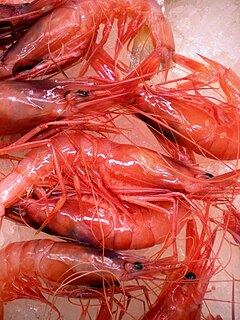
Aristeidae is a family of Dendrobranchiata decapod crustaceans known as deep-sea shrimps, gamba prawns or gamba shrimps. Some species are subject to commercial fisheries.

Aristaeomorpha is a genus of deep water prawns from the family Aristeidae.
Brisinga is a genus of starfish in the family Brisingidae. The species in this genus are primarily found in deep sea habitats.
Solenoceridae is a family of decapods, containing 10 genera. They are marine, inhabiting shallow and offshore waters from the mid-continental shelf, ranging from depths to 1000 meters deep, and are sometimes confused with other commercial shrimp species.

Solenocera is a genus of prawns in the family Solenoceridae. Solenocera occur from 0 to 2,067 meters deep in the ocean.

Acanthephyra is a genus of shrimp in the family Acanthephyridae, with species that live at depths from 0 to 5422.5 meters below the ocean surface.
References
- 1 2 Mah, C. (2015). Mah CL (ed.). "Dictyaster Wood-Mason & Alcock, 1891". World Asteroidea database. World Register of Marine Species . Retrieved 2015-07-23.