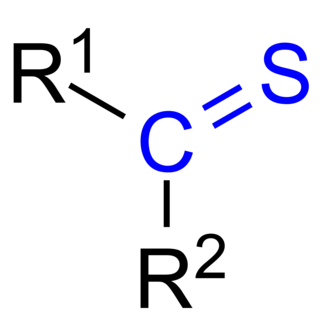In organic chemistry, a thiol, or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form R−SH, where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The −SH functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl group, or a sulfanyl group. Thiols are the sulfur analogue of alcohols, and the word is a blend of "thio-" with "alcohol".
Sulfide (British English also sulphide) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. Sulfide also refers to large families of inorganic and organic compounds, e.g. lead sulfide and dimethyl sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and bisulfide (SH−) are the conjugate acids of sulfide.

In organometallic chemistry, organolithium reagents are chemical compounds that contain carbon–lithium (C–Li) bonds. These reagents are important in organic synthesis, and are frequently used to transfer the organic group or the lithium atom to the substrates in synthetic steps, through nucleophilic addition or simple deprotonation. Organolithium reagents are used in industry as an initiator for anionic polymerization, which leads to the production of various elastomers. They have also been applied in asymmetric synthesis in the pharmaceutical industry. Due to the large difference in electronegativity between the carbon atom and the lithium atom, the C−Li bond is highly ionic. Owing to the polar nature of the C−Li bond, organolithium reagents are good nucleophiles and strong bases. For laboratory organic synthesis, many organolithium reagents are commercially available in solution form. These reagents are highly reactive, and are sometimes pyrophoric.

In organic chemistry, organic peroxides are organic compounds containing the peroxide functional group. If the R′ is hydrogen, the compounds are called hydroperoxides, which are discussed in that article. The O−O bond of peroxides easily breaks, producing free radicals of the form RO•. Thus, organic peroxides are useful as initiators for some types of polymerization, such as the acrylic, unsaturated polyester, and vinyl ester resins used in glass-reinforced plastics. MEKP and benzoyl peroxide are commonly used for this purpose. However, the same property also means that organic peroxides can explosively combust. Organic peroxides, like their inorganic counterparts, are often powerful bleaching agents.
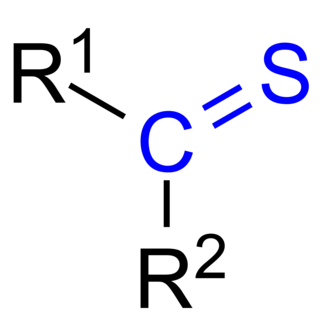
In organic chemistry, thioketones are organosulfur compounds related to conventional ketones in which the oxygen has been replaced by a sulfur. Instead of a structure of R2C=O, thioketones have the structure R2C=S, which is reflected by the prefix "thio-" in the name of the functional group. Thus the simplest thioketone is thioacetone, the sulfur analog of acetone. Unhindered alkylthioketones typically tend to form polymers or rings.

1,4-Benzoquinone, commonly known as para-quinone, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H4O2. In a pure state, it forms bright-yellow crystals with a characteristic irritating odor, resembling that of chlorine, bleach, and hot plastic or formaldehyde. This six-membered ring compound is the oxidized derivative of 1,4-hydroquinone. The molecule is multifunctional: it exhibits properties of a ketone, being able to form oximes; an oxidant, forming the dihydroxy derivative; and an alkene, undergoing addition reactions, especially those typical for α,β-unsaturated ketones. 1,4-Benzoquinone is sensitive toward both strong mineral acids and alkali, which cause condensation and decomposition of the compound.

Hydroperoxides or peroxols are compounds of the form ROOH, where R stands for any group, typically organic, which contain the hydroperoxy functional group. Hydroperoxide also refers to the hydroperoxide anion and its salts, and the neutral hydroperoxyl radical (•OOH) consist of an unbond hydroperoxy group. When R is organic, the compounds are called organic hydroperoxides. Such compounds are a subset of organic peroxides, which have the formula ROOR. Organic hydroperoxides can either intentionally or unintentionally initiate explosive polymerisation in materials with unsaturated chemical bonds.
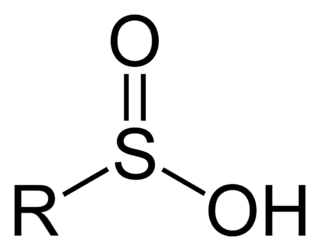
Sulfinic acids are oxoacids of sulfur with the structure RSO(OH). In these organosulfur compounds, sulfur is pyramidal.
A polysulfane is a chemical compound of formula H2Sn, where n > 1. Compounds containing 2 – 8 sulfur atoms have been isolated, longer chain compounds have been detected, but only in solution. H2S2 is colourless, higher members are yellow with the colour increasing with the sulfur content. In the chemical literature the term polysulfanes is sometimes used for compounds containing −(S)n−, e.g. organic polysulfanes R1−(S)n−R2.

Thiuram disulfides are a class of organosulfur compounds with the formula (R2NCSS)2. Many examples are known, but popular ones include R = Me and R = Et. They are disulfides obtained by oxidation of the dithiocarbamates. These compounds are used in sulfur vulcanization of rubber as well as in the manufacture of pesticides and drugs. They are typically white or pale yellow solids that are soluble in organic solvents.
Thiosulfuric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula H2S2O3. It has attracted academic interest as a simple, easily accessed compound that is labile. It has few practical uses.

Hydrogen disulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula H2S2. This hydrogen chalcogenide is a pale yellow volatile liquid with a camphor-like odor. It decomposes readily to hydrogen sulfide and elemental sulfur.
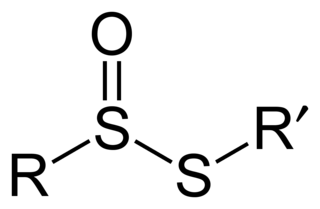
In organosulfur chemistry, thiosulfinate is a functional group consisting of the linkage R-S(O)-S-R. Thiolsulfinates are also named as alkanethiosulfinic acid esters.
Dithionous acid is a sulfur oxoacid with the chemical formula H2S2O4. It is unstable in pure form, but its salts, known as dithionites, are stable.

Thiourea dioxide or thiox is an organosulfur compound that is used in the textile industry. It functions as a reducing agent. It is a white solid, and exhibits tautomerism.

In organosulfur chemistry, sulfenamides are a class of organosulfur compounds characterized by the general formula R−S−N(−R)2, where the R groups are hydrogen, alkyl, or aryl. Sulfenamides have been used extensively in the vulcanization of rubber using sulfur. They are related to the oxidized compounds known as sulfinamides and sulfonamides.

Thiosulfurous acid is a hypothetical chemical compound with the formula HS−S(=O)−OH or HO−S(=S)−OH. Attempted synthesis leads to polymers. It is a low oxidation state (+1) sulfur acid. It is the Arrhenius acid for disulfur monoxide. Salts derived from thiosulfurous acid, which are also unknown, are named "thiosulfites" or "sulfurothioites". The ion is S=SO2−
2.
Hydrogen thioperoxide, also called oxadisulfane or sulfanol, is the chemical with the structure H–S–O–H. It can be considered as the simple sulfur-substituted analog of the common hydrogen peroxide (H–O–O–H) chemical, and as the simplest hydrogen chalcogenide containing more than one type of chalcogen. The chemical has been described as the "missing link" between hydrogen peroxide and hydrogen disulfide (H–S–S–H), though it is substantially less stable than either of the other two. It is the inorganic parent structure of the sulfenic acid class of organic compounds (R–S–O–H) and also the oxadisulfide linkage (R1–S–O–R2), where "R" is any organic structure. Sulfur is present in oxidation state 0.
Hydrogen chalcogenides are binary compounds of hydrogen with chalcogen atoms. Water, the first chemical compound in this series, contains one oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms, and is the most common compound on the Earth's surface.

Sulfoxylic acid (H2SO2) (also known as hyposulfurous acid or sulfur dihydroxide) is an unstable oxoacid of sulfur in an intermediate oxidation state between hydrogen sulfide and dithionous acid. It consists of two hydroxy groups attached to a sulfur atom. Sulfoxylic acid contains sulfur in an oxidation state of +2. Sulfur monoxide (SO) can be considered as a theoretical anhydride for sulfoxylic acid, but it is not actually known to react with water.