Related Research Articles

Lake Mariout, is a brackish lake in northern Egypt near the city of Alexandria. The lake area covered 200 square kilometres (77 sq mi) and had a navigable canal at the beginning of the 20th century, but at the beginning of the 21st century, it covers only about 50 square kilometres (19 sq mi).

Cusae was a city in Upper Egypt. Its Ancient Egyptian name was qjs, conventionally rendered Qis or Kis. Today, the town is known as El Quseyya, and is located on the west bank of the Nile in the Asyut Governorate.

Hermopolis was a major city in antiquity, located near the boundary between Lower and Upper Egypt.
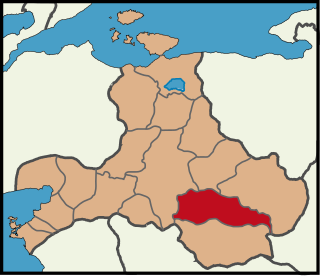
Bigadiç is a municipality and district of Balıkesir Province, Turkey. Its area is 1,108 km2, and its population is 48,917 (2022). As former Ancient bishopric of Achyraus, it remains a Latin Catholic titular see.

Antiochia ad Cragum also known as Antiochetta or Latin: Antiochia Parva is an ancient Hellenistic city on Mount Cragus overlooking the Mediterranean coast, in the region of Cilicia, in Anatolia. In modern-day Turkey the site is encompassed in the village of Güneyköy, District of Gazipaşa, Antalya Province.

Abusir Bana, anciently known as Busiris, is a village in Gharbia governorate, Egypt. The population is 22,214 people, according to the official census of 2006.

Barca, also called Barce, was an ancient city and former bishopric, which survives as both a Latin Catholic and an Orthodox titular see.

Hypaepa or Hypaipa was an Ancient city and (arch)bishopric in ancient Lydia, near the north bank of the Cayster River, and 42 miles from Ephesus, Ephesus and remains a Latin Catholic titular see.
Harpasa was a city and bishopric in ancient Caria in Roman Asia Minor, which only remains a Latin Catholic titular see.

Babylon Fortress is an Ancient Roman fortress, built around 30 BC with the arrival of emperor Augustus in Egypt, on the eastern bank of the Nile Delta, located in the area known today as Coptic Cairo. It is situated in the former area of the Heliopolite Nome, upon the east bank of the Nile, at latitude 30°N, near the commencement of the Pharaonic Canal, from the Nile to the Red Sea.
The Archdiocese of Antinoe is titular diocese of the Roman Catholic Church in the Province of Egypt. It was part of the Patriarchate of Alexandria, and the bishopric was based on Antinoë in the Nile Valley. It was also known as Antinoöpolis.
Ryahovo is a village in northern Bulgaria, and as Ancient Ap(p)iaria a former bishopric, remaining a Latin Catholic titular see.

Justinianopolis in Armenia also known as Iustinianopolis was a Roman and Byzantine era city and bishopric in Lesser Armenia. It has been identified with modern Erzincan, Turkey. It was one of several ancient sites renamed in late Antiquity after Byzantine emperor Justinian I. The city also known as Acilisene and Keltzene.
Dystis was a city and bishopric in Roman Libya, which remains a Latin Catholic titular see.
Sebela was an Ancient city and bishopric in Asia Minor and remains a Latin Catholic titular see.
Zarela, also known as Durzela, Zorzila, Dyrzela, and Zorzela, was a city and bishopric in ancient Pisidia, which remains a Latin Catholic titular see. It site is unlocated.
Tenedos or Bozcaada is an island, former bishopric and Latin Catholic titular see of Asian Turkey in the northeastern part of the Aegean Sea.
Petra in Aegypto was a Hellenistic city and former bishopric in Roman Egypt and remains a Latin Catholic titular see.
Andropolis was an Ancient city and former bishopric in Roman Egypt, and is now a Latin Catholic titular see.
Alia was a town of ancient Phrygia, inhabited in Roman and Byzantine times. It was located in the Roman province of Phrygia Pacatiana, whose capital was Laodicea on the Lycus, and became the seat of a bishop. The names of some of the bishops of Alia are known through their participation in church councils: Caius at the Council of Chalcedon (451), Glaucus at the Second Council of Constantinople (553), Leo at the Second Council of Nicaea (787), and Michael and Georgius, the one a supporter of Patriarch Ignatius of Constantinople, the other a supporter of Photius, at the Council of Constantinople (879).
References
- ↑
- Smith, William, ed. (1854–1857). "Butos". Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography. London: John Murray.
- ↑ Wilkinson, R. H. The Complete Temples of Ancient Egypt, (Thames & Hudson, 2000), p. 104.
- ↑ Michel Lequien, Oriens christianus in quatuor Patriarchatus digestus, Paris, 1740, vol. II, coll. 529-530
- ↑ Klaas A. Worp, A Checklist of Bishops in Byzantine Egypt (A.D. 325 - c. 750), in Zeitschrift für Papyrologie und Epigraphik 100 (1994), pages 283-318
- ↑ Richard Price, Michael Gaddis, The Acts of the Council of Chalcedon, Volume 1 (Liverpool University Press, 2005) p338.
- ↑ http://www.gcatholic.org/dioceses/former/t0362.htm GCatholic - (titular) bishopric
- ↑ Bernard C. Pawley, Observing Vatican II (Cambridge University Press, 2014)p285.
- ↑ Butus at GCatholic.org.