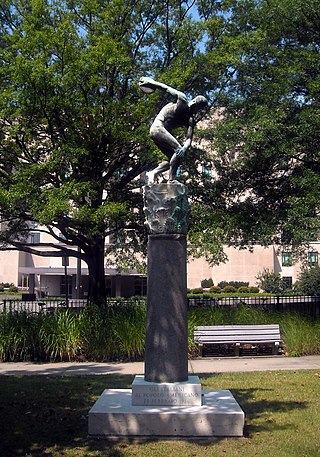The discus throw, also known as disc throw, is a track and field sport in which the participant athlete throws an oblate spheroid weight — called a discus — in an attempt to mark a farther distance than other competitors. It is an ancient sport, as demonstrated by the fifth-century-BC Myron statue Discobolus. Although not part of the current pentathlon, it was one of the events of the ancient Greek pentathlon, which can be dated back to at least 708 BC, and it is part of the modern decathlon.

Year 450 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Second year of the decemviri. The denomination 450 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The discus throw is a track and field event in which athletes throw a heavy disc as far as they can.
Myron of Eleutherae was an Athenian sculptor from the mid-5th century BC. He was born in Eleutherae on the borders of Boeotia and Attica. According to Natural History, a Latin encyclopedia by Pliny the Elder, a scholar in Ancient Rome, Ageladas of Argos was his teacher.

Robert S. Garrett was an American athlete, as well as investment banker and philanthropist in Baltimore, Maryland and financier of several important archeological excavations. Garrett was the first modern Olympic champion in discus throw as well as shot put.
Events from the year 1956 in art.

The Discobolus by Myron is an ancient Greek sculpture completed at the start of the Classical period in around 460–450 BC that depicts an ancient Greek athlete throwing a discus. Its Greek original in bronze lost, the work is known through numerous Roman copies, both full-scale ones in marble, which is cheaper than bronze, such as the Palombara Discobolus, the first to be recovered, and smaller scaled versions in bronze.

The Discophoros, also spelled Discophorus, was a bronze sculpture by the classical Greek sculptor Polyclitus, creator of the Doryphoros and Diadumenos, and its many Roman marble copies. It is not, however, to be confused with Discobolus of Myron, which shows a discus being thrown, not carried.

David is a life-size marble sculpture by Gian Lorenzo Bernini. The sculpture was one of many commissions to decorate the villa of Bernini's patron Cardinal Scipione Borghese – where it still resides today, as part of the Galleria Borghese. It was completed in the course of eight months from 1623 to 1624.

The men's discus throw was one of two throwing events on the Athletics at the 1896 Summer Olympics programme. The discus throw was the fourth event held. It was contested on 6 April. 9 athletes competed, including one each from France, Sweden, the United States, and Great Britain as well as three Greeks and two Danes.

František Janda-Suk was a Czech athlete who competed for Bohemia in the 1900 Summer Olympics and in the 1912 Summer Olympics and Czechoslovakia at the 1924 Summer Olympics.

An equestrian statue of Venezuelan military and political leader Simón Bolívar by the American artist Felix de Weldon is located in Washington, D.C., at Virginia Avenue NW, 18th Street NW, and C Street NW, near the United States Department of Interior and the Pan American Union Building of the Organization of American States. It was surveyed as part of the Smithsonian Institution's Save Outdoor Sculpture! survey in 1993.

Major General James B. McPherson is a public artwork by American artist Louis Rebisso, located at McPherson Square in Washington, D.C., United States. Major General James B. McPherson was originally surveyed as part of the Smithsonian's Save Outdoor Sculpture! survey in 1993. The monument is a bronze equestrian statue of Civil War hero James B. McPherson. The statue is a contributing monument to the Civil War Monuments in Washington, DC, of the National Register of Historic Places.

Continuum is a public artwork by American sculptor Charles O. Perry located in front of the National Air and Space Museum in Washington, DC, United States.

The Daguerre Memorial is a bronze and granite sculpture by Jonathan Scott Hartley in Washington, D.C. It was erected in memory of Louis Daguerre.

Chief Justice John Marshall is a bronze sculpture of John Marshall, by American sculptor William Wetmore Story. It is located at the Supreme Court, 1 First Street, Washington, D.C., N.E.
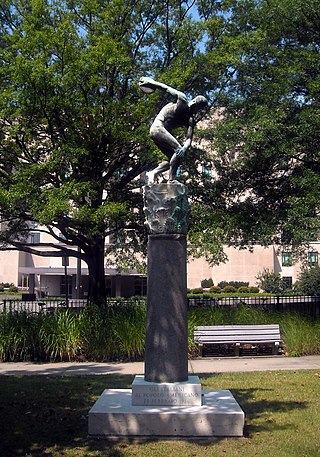
Edward J. Kelly Park is a park located in the Foggy Bottom neighborhood of Washington, D.C. The park is located at the southeast corner of Virginia Avenue and 21st Street NW.

The Big 4 is a sculpture made of steel bars located outside the headquarters of the Channel Four Television Corporation in London. It is designed to represent the logo of Channel 4 while providing a basis for a number of art installations. As of November 2012 seven installations have been made on the statue's steel framework, including those to coincide with the 2012 Summer Paralympics, covered with both newsprint and umbrellas, and a design to simulate the statue breathing. A further dressing to celebrate the devolution of Channel 4 from London to a series of regionally-based offices, alongside the Horseferry Road HQ has recently been approved and will be erected later in 2019.
Eurybus of Athens was an ancient Greek athlete listed by Eusebius of Caesarea as a victor in the stadion race of the 27th Olympiad. His name is also referred as Eurybates or Eurybotos and possibly Eurybotas elsewhere in Pausanias, both of the latter two have been anglicised to "Eurybotus" by editors, although elsewhere the distinction is preserved. He was the second winner from Athens preceded only by Pantacles.

Christian Georg Kohlrausch re-discovered the Discus – see Discus throw. Since the end of the Ancient Olympic Games, the discus was only known from sculpture like the Discobolus and drawings. The exact dimensions (shape), weight and the technique of throwing had not been recorded and handed down.