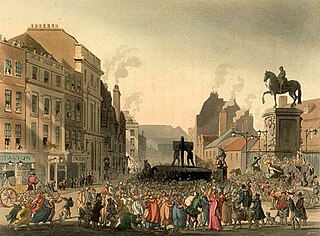Christopher Marlowe, also known as Kit Marlowe, was an English playwright, poet, and translator of the Elizabethan era. Marlowe is among the most famous of the Elizabethan playwrights. Based upon the "many imitations" of his play Tamburlaine, modern scholars consider him to have been the foremost dramatist in London in the years just before his mysterious early death. Some scholars also believe that he greatly influenced William Shakespeare, who was baptised in the same year as Marlowe and later succeeded him as the preeminent Elizabethan playwright. Marlowe was the first to achieve critical reputation for his use of blank verse, which became the standard for the era. His plays are distinguished by their overreaching protagonists. Themes found within Marlowe's literary works have been noted as humanistic with realistic emotions, which some scholars find difficult to reconcile with Marlowe's "anti-intellectualism" and his catering to the prurient tastes of his Elizabethan audiences for generous displays of extreme physical violence, cruelty, and bloodshed.

A nursery rhyme is a traditional poem or song for children in Britain and other European countries, but usage of the term dates only from the late 18th/early 19th century. The term Mother Goose rhymes is interchangeable with nursery rhymes.

Humpty Dumpty is a character in an English nursery rhyme, probably originally a riddle and one of the best known in the English-speaking world. He is typically portrayed as an anthropomorphic egg, though he is not explicitly described as such. The first recorded versions of the rhyme date from late eighteenth-century England and the tune from 1870 in James William Elliott's National Nursery Rhymes and Nursery Songs. Its origins are obscure, and several theories have been advanced to suggest original meanings.

Faust is the protagonist of a classic German legend based on the historical Johann Georg Faust. The erudite Faust is highly successful yet dissatisfied with his life, which leads him to make a pact with the Devil at a crossroads, exchanging his soul for unlimited knowledge and worldly pleasures. The Faust legend has been the basis for many literary, artistic, cinematic, and musical works that have reinterpreted it through the ages. "Faust" and the adjective "Faustian" imply sacrificing spiritual values for power, knowledge, or material gain.

"Hey Diddle Diddle" is an English nursery rhyme. It has a Roud Folk Song Index number of 19478.

The Tragical History of the Life and Death of Doctor Faustus, commonly referred to simply as Doctor Faustus, is an Elizabethan tragedy by Christopher Marlowe, based on German stories about the title character Faust. It was probably written in 1592 or 1593, shortly before Marlowe's death. Two different versions of the play were published in the Jacobean era several years later.

"London Bridge Is Falling Down" is a traditional English nursery rhyme and singing game, which is found in different versions all over the world. It deals with the dilapidation of London Bridge and attempts, realistic or fanciful, to repair it. It may date back to bridge-related rhymes and games of the Late Middle Ages, but the earliest records of the rhyme in English are from the 17th century. The lyrics were first printed in close to their modern form in the mid-18th century and became popular, particularly in Britain and the United States, during the 19th century.

"Simple Simon" is an English language nursery rhyme. It has a Roud Folk Song Index number of 19777.

"Ring a Ring o' Roses", "Ring a Ring o' Rosie", or "Ring Around the Rosie", is a nursery rhyme, folk song and playground singing game. Descriptions first emerge in the mid-19th century, but are reported as dating from decades before, and similar rhymes are known from across Europe, with various lyrics. It has a Roud Folk Song Index number of 7925.

"This Little Pig Went to Market" is an English-language nursery rhyme and fingerplay. It has a Roud Folk Song Index number of 19297.

"Who Killed Cock Robin" is an English nursery rhyme. It has a Roud Folk Song Index number of 494.
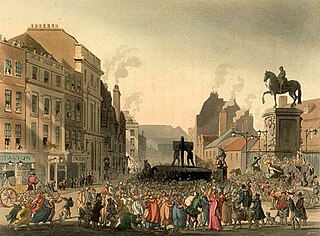
"As I was going by Charing Cross", is an English language nursery rhyme. The rhyme was first recorded in the 1840s, but it may have older origins in street cries and verse of the seventeenth century. It refers to the equestrian statue of King Charles I in Charing Cross, London, and may allude to his death or be a puritan satire on royalist reactions to his execution. It was not recorded in its modern form until the mid-nineteenth century. It has a Roud Folk Song Index number of 20564.
"Goosey Goosey Gander" is an English-language nursery rhyme. It has a Roud Folk Song Index number of 6488.

"There Was an Old Woman Who Lived in a Shoe" is a popular English language nursery rhyme, with a Roud Folk Song Index number of 19132. Debates over its meaning and origin have largely centered on attempts to match the old woman with historical female figures who have had large families, although King George II (1683–1760) has also been proposed as the rhyme's subject.
"Taffy was a Welshman" is an English language nursery rhyme which was popular between the eighteenth and twentieth centuries. It has a Roud Folk Song Index number of 19237.
"Oh, Dear! What Can the Matter Be?", also known as "Johnny's So Long at the Fair" is a traditional nursery rhyme that can be traced back as far as the 1770s in England. There are several variations on its lyrics. It has Roud Number 1279.

"Ride a Cock Horse to Banbury Cross" is an English language nursery rhyme connected with the English town Banbury in Oxfordshire. It has a Roud Folk Song Index number of 21143.

"Matthew, Mark, Luke and John", also known as the "Black Paternoster", is an English children's bedtime prayer and nursery rhyme. It has a Roud Folk Song Index number of 1704. It may have origins in ancient Babylonian prayers and was being used in a Christian version in late Medieval Germany. The earliest extant version in English can be traced to the mid-sixteenth century. It was mentioned by English Protestant writers as a "popish" or magical charm. It is related to other prayers, including a "Green" and "White Paternoster", which can be traced to late Medieval England and with which it is often confused. It has been the inspiration for a number of literary works by figures including Henry Wadsworth Longfellow and musical works by figures such as Gustav Holst. It has been the subject of alternative versions and satires.
I do not likethee, Doctor Fell is an epigram, said to have been translated by satirical English poet Tom Brown in 1680. Later it has been recorded as a nursery rhyme and a proverb.

Gammer Gurton's Garland: or, The Nursery Parnassus, edited by the literary antiquary Joseph Ritson, is one of the earliest collections of English nursery rhymes. It was first published as a chapbook in 1784, but was three times reprinted in expanded editions during the following century, as were several unrelated children's books with similar titles. Gammer Gurton's Garland put into print for the first time some of our best-known nursery rhymes.