Related Research Articles
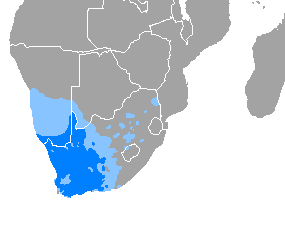
Afrikaans is a West Germanic language, spoken in South Africa, Namibia and Botswana, Zambia and Zimbabwe. It evolved from the Dutch vernacular of South Holland spoken by the predominantly Dutch settlers and enslaved population of the Dutch Cape Colony, where it gradually began to develop distinguishing characteristics in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries.
British English is the set of varieties of the English language native to the island of Great Britain. More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in England, or, more broadly, to the collective dialects of English throughout the British Isles taken as a single umbrella variety, for instance additionally incorporating Scottish English, Welsh English, and Ulster English. Tom McArthur in the Oxford Guide to World English acknowledges that British English shares "all the ambiguities and tensions [with] the word 'British' and as a result can be used and interpreted in two ways, more broadly or more narrowly, within a range of blurring and ambiguity"..

An encyclopedia or encyclopaedia is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge, either general or special, in a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into articles or entries that are arranged alphabetically by article name or by thematic categories, or else are hyperlinked and searchable. Encyclopedia entries are longer and more detailed than those in most dictionaries. Generally speaking, encyclopedia articles focus on factual information concerning the subject named in the article's title; this is unlike dictionary entries, which focus on linguistic information about words, such as their etymology, meaning, pronunciation, use, and grammatical forms.
An emoticon, short for emotion icon, is a pictorial representation of a facial expression using characters—usually punctuation marks, numbers and letters—to express a person's feelings, mood or reaction, without needing to describe it in detail.

The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standard written representation for the sounds of speech. The IPA is used by lexicographers, foreign language students and teachers, linguists, speech–language pathologists, singers, actors, constructed language creators, and translators.

Internet slang is a non-standard or unofficial form of language used by people on the Internet to communicate to one another. An example of Internet slang is "lol" meaning "laugh out loud." Since Internet slang is constantly changing, it is difficult to provide a standardized definition. However, it can be understood to be any type of slang that Internet users have popularized, and in many cases, have coined. Such terms often originate with the purpose of saving keystrokes or to compensate for small character limits. Many people use the same abbreviations in texting, instant messaging, and social networking websites. Acronyms, keyboard symbols, and abbreviations are common types of Internet slang. New dialects of slang, such as leet or Lolspeak, develop as ingroup Internet memes rather than time savers. Many people also use Internet slang in face-to-face, real life communication.

Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing. Human language is characterized by its cultural and historical diversity, with significant variations observed between cultures and across time. Human languages possess the properties of productivity and displacement, which enable the creation of an infinite number of sentences, and the ability to refer to objects, events, and ideas that are not immediately present in the discourse. The use of human language relies on social convention and is acquired through learning.

The Oxford English Dictionary (OED) is the principal historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP), a University of Oxford publishing house. The dictionary, which published its first edition in 1884, traces the historical development of the English language, providing a comprehensive resource to scholars and academic researchers, and provides ongoing descriptions of English language usage in its variations around the world.

Profanity, also known as swearing, cursing, or cussing, involves the use of notionally offensive words for a variety of purposes, including to demonstrate disrespect or negativity, to relieve pain, to express a strong emotion, as a grammatical intensifier or emphasis, or to express informality or conversational intimacy. In many formal or polite social situations, it is considered impolite, and in some religious groups it is considered a sin. Profanity includes slurs, but there are many insults that do not use swear words.

Russian is an East Slavic language, spoken primarily in Russia. It is the native language of the Russians and belongs to the Indo-European language family. It is one of four living East Slavic languages, and is also a part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages. It was the de facto and de jure official language of the former Soviet Union. Russian has remained an official language in independent Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan, and is still commonly used as a lingua franca in Ukraine, Moldova, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to a lesser extent in the Baltic states and Israel.

LOL, or lol, is an initialism for laughing out loud, and a popular element of Internet slang, which can be used to indicate amusement, irony, or double meanings. It was first used almost exclusively on Usenet, but has since become widespread in other forms of computer-mediated communication and even face-to-face communication. It is one of many initialisms for expressing bodily reactions, in particular laughter, as text, including initialisms for more emphatic expressions of laughter such as LMAO and ROFL or ROTFL.

Inuktitut, also known as Eastern Canadian Inuktitut, is one of the principal Inuit languages of Canada. It is spoken in all areas north of the North American tree line, including parts of the provinces of Newfoundland and Labrador, Quebec, to some extent in northeastern Manitoba as well as the Northwest Territories and Nunavut. It is one of the aboriginal languages written with Canadian Aboriginal syllabics.

The Klingon Dictionary (TKD) is a book by Marc Okrand describing the Klingon language. First published in 1985 and then again with an addendum in 1992, it includes pronunciation, grammar and vocabulary. It has sold more than three hundred thousand copies and has been translated into five languages.
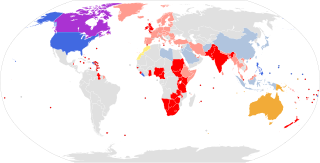
Despite the various English dialects spoken from country to country and within different regions of the same country, there are only slight regional variations in English orthography, the two most notable variations being British and American spelling. Many of the differences between American and British/English in the Commonwealth of Nations date back to a time before spelling standards were developed. For instance, some spellings seen as "American" today were once commonly used in Britain, and some spellings seen as "British" were once commonly used in the United States.
Adobe InCopy is a professional word processor made by Adobe Inc. that integrates with Adobe InDesign. InCopy is used for general word processing, in contrast to InDesign, which is used to publish printed material, including newspapers and magazines. The software enables editors to write, edit, and design documents. The software includes standard word processing features such as spell check, track changes, and word count, and has various viewing modes that allow editors to visually inspect design elements — just as it looks to the designer working in Adobe InDesign.
Sri Lankan English (SLE) is the English language as it is used in Sri Lanka, a term dating from 1972. Sri Lankan English is principally categorised as the Standard Variety and the Nonstandard Variety, which is called as "Not Pot English". The classification of SLE as a separate dialect of English is controversial. English in Sri Lanka is spoken by approximately 23.8% of the population, and widely used for official and commercial purposes. Sri Lankan English being the native language of approximately 5,400 people thus challenges Braj Kachru's placement of it in the Outer Circle. Furthermore, it is taught as a compulsory second language in local schools from grade one to thirteen, and Sri Lankans pay special attention on learning English both as children and adults. It is considered even today that access and exposure to English from one's childhood in Sri Lanka is to be born with a silver spoon in one's mouth.

Grant Barrett is an American lexicographer, specializing in slang, jargon and new usage, and the author and compiler of language-related books and dictionaries. He is a co-host and co-producer of the American weekly, hour-long public radio show and podcast A Way with Words. He has made regular appearances on Christopher Kimball's Milk Street Radio, is often consulted as a language commentator, and has written for The New York Times and The Washington Post, and served as a lexicographer for Oxford University Press and Cambridge University Press.
The Dictionary of Modern Greek, more commonly known as Babiniotis Dictionary, is a well-known dictionary of Modern Greek published in Greece by Lexicology Centre and supervised by Greek linguist Georgios Babiniotis.

This list comprises widespread modern beliefs about English language usage that are documented by a reliable source to be misconceptions.
Singapore embraces an English-based bilingual education system. Students are taught subject-matter curriculum with English as the medium of instruction, while the official mother tongue of each student - Mandarin Chinese for Chinese, Malay for Malays and Tamil for South Indians – is taught as a second language. Additionally, Higher Mother Tongue (HMT) is offered as an additional and optional examinable subject to those with the interest and ability to handle the higher standards demanded by HMT. The content taught to students in HMT is of a higher level of difficulty and is more in-depth so as to help students achieve a higher proficiency in their respective mother tongues. The choice to take up HMT is offered to students in the Primary and Secondary level. Thereafter, in junior colleges, students who took HMT at the secondary level have the choice to opt out of mother tongue classes entirely. Campaigns by the government to encourage the use of official languages instead of home languages have been largely successful, although English seems to be becoming the dominant language in most homes. To date, many campaigns and programmes have been launched to promote the learning and use of mother tongue languages in Singapore. High ability students may take a third language if they choose to do so.
References
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-22. Retrieved 2010-10-04.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ Tamasi, S. (2008). "NEGOTIATING MEDICAL COMMUNICATION: The Discourse of Hospital Communication: Tracing Complexities in Contemporary Health Organizations" (PDF). American Speech. 83: 99–107. doi:10.1215/00031283-2008-005.
- ↑ Keats, Jonathon. (2010). Virtual words : language on the edge of science and technology. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 121. ISBN 978-0-19-539854-0.