
Erosion is the action of surface processes that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as physical or mechanical erosion; this contrasts with chemical erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres.

Geomorphology is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features generated by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or near Earth's surface. Geomorphologists seek to understand why landscapes look the way they do, to understand landform and terrain history and dynamics and to predict changes through a combination of field observations, physical experiments and numerical modeling. Geomorphologists work within disciplines such as physical geography, geology, geodesy, engineering geology, archaeology, climatology, and geotechnical engineering. This broad base of interests contributes to many research styles and interests within the field.

A slump is a form of mass wasting that occurs when a coherent mass of loosely consolidated materials or a rock layer moves a short distance down a slope. Movement is characterized by sliding along a concave-upward or planar surface. Causes of slumping include earthquake shocks, thorough wetting, freezing and thawing, undercutting, and loading of a slope.

In materials science, creep is the tendency of a solid material to undergo slow deformation while subject to persistent mechanical stresses. It can occur as a result of long-term exposure to high levels of stress that are still below the yield strength of the material. Creep is more severe in materials that are subjected to heat for long periods and generally increases as they near their melting point.

Mass wasting, also known as mass movement, is a general term for the movement of rock or soil down slopes under the force of gravity. It differs from other processes of erosion in that the debris transported by mass wasting is not entrained in a moving medium, such as water, wind, or ice. Types of mass wasting include creep, solifluction, rockfalls, debris flows, and landslides, each with its own characteristic features, and taking place over timescales from seconds to hundreds of years. Mass wasting occurs on both terrestrial and submarine slopes, and has been observed on Earth, Mars, Venus, Jupiter's moon Io, and on many other bodies in the Solar System.

Colluvium is a general name for loose, unconsolidated sediments that have been deposited at the base of hillslopes by either rainwash, sheetwash, slow continuous downslope creep, or a variable combination of these processes. Colluvium is typically composed of a heterogeneous range of rock types and sediments ranging from silt to rock fragments of various sizes. This term is also used to specifically refer to sediment deposited at the base of a hillslope by unconcentrated surface runoff or sheet erosion.

Soil mechanics is a branch of soil physics and applied mechanics that describes the behavior of soils. It differs from fluid mechanics and solid mechanics in the sense that soils consist of a heterogeneous mixture of fluids and particles but soil may also contain organic solids and other matter. Along with rock mechanics, soil mechanics provides the theoretical basis for analysis in geotechnical engineering, a subdiscipline of civil engineering, and engineering geology, a subdiscipline of geology. Soil mechanics is used to analyze the deformations of and flow of fluids within natural and man-made structures that are supported on or made of soil, or structures that are buried in soils. Example applications are building and bridge foundations, retaining walls, dams, and buried pipeline systems. Principles of soil mechanics are also used in related disciplines such as geophysical engineering, coastal engineering, agricultural engineering, hydrology and soil physics.

A mudflow, also known as mudslide or mud flow, is a form of mass wasting involving fast-moving flow of debris and dirt that has become liquified by the addition of water. Such flows can move at speeds ranging from 3 meters/minute to 5 meters/second. Mudflows contain a significant proportion of clay, which makes them more fluid than debris flows, allowing them to travel farther and across lower slope angles. Both types of flow are generally mixtures of particles with a wide range of sizes, which typically become sorted by size upon deposition.
Drainage density is a quantity used to describe physical parameters of a drainage basin. First described by Robert E. Horton, drainage density is defined as the total length of channel in a drainage basin divided by the total area, represented by the following equation:

Sediment transport is the movement of solid particles (sediment), typically due to a combination of gravity acting on the sediment, and the movement of the fluid in which the sediment is entrained. Sediment transport occurs in natural systems where the particles are clastic rocks, mud, or clay; the fluid is air, water, or ice; and the force of gravity acts to move the particles along the sloping surface on which they are resting. Sediment transport due to fluid motion occurs in rivers, oceans, lakes, seas, and other bodies of water due to currents and tides. Transport is also caused by glaciers as they flow, and on terrestrial surfaces under the influence of wind. Sediment transport due only to gravity can occur on sloping surfaces in general, including hillslopes, scarps, cliffs, and the continental shelf—continental slope boundary.

Coble creep, a form of diffusion creep, is a mechanism for deformation of crystalline solids. Contrasted with other diffusional creep mechanisms, Coble creep is similar to Nabarro–Herring creep in that it is dominant at lower stress levels and higher temperatures than creep mechanisms utilizing dislocation glide. Coble creep occurs through the diffusion of atoms in a material along grain boundaries. This mechanism is observed in polycrystals or along the surface in a single crystal, which produces a net flow of material and a sliding of the grain boundaries.
Landslide mitigation refers to several human-made activities on slopes with the goal of lessening the effect of landslides. Landslides can be triggered by many, sometimes concomitant causes. In addition to shallow erosion or reduction of shear strength caused by seasonal rainfall, landslides may be triggered by anthropic activities, such as adding excessive weight above the slope, digging at mid-slope or at the foot of the slope. Often, individual phenomena join to generate instability over time, which often does not allow a reconstruction of the evolution of a particular landslide. Therefore, landslide hazard mitigation measures are not generally classified according to the phenomenon that might cause a landslide. Instead, they are classified by the sort of slope stabilization method used:
In geology, a deformation mechanism is a process occurring at a microscopic scale that is responsible for changes in a material's internal structure, shape and volume. The process involves planar discontinuity and/or displacement of atoms from their original position within a crystal lattice structure. These small changes are preserved in various microstructures of materials such as rocks, metals and plastics, and can be studied in depth using optical or digital microscopy.
Dislocation creep is a deformation mechanism in crystalline materials. Dislocation creep involves the movement of dislocations through the crystal lattice of the material, in contrast to diffusion creep, in which diffusion is the dominant creep mechanism. It causes plastic deformation of the individual crystals, and thus the material itself.
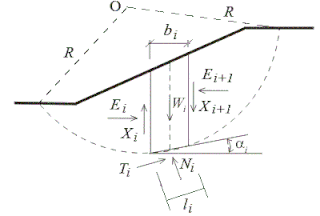
Slope stability analysis is a static or dynamic, analytical or empirical method to evaluate the stability of slopes of soil- and rock-fill dams, embankments, excavated slopes, and natural slopes in soil and rock. It is performed to assess the safe design of a human-made or natural slopes and the equilibrium conditions. Slope stability is the resistance of inclined surface to failure by sliding or collapsing. The main objectives of slope stability analysis are finding endangered areas, investigation of potential failure mechanisms, determination of the slope sensitivity to different triggering mechanisms, designing of optimal slopes with regard to safety, reliability and economics, and designing possible remedial measures, e.g. barriers and stabilization.

In hydrology stream competency, also known as stream competence, is a measure of the maximum size of particles a stream can transport. The particles are made up of grain sizes ranging from large to small and include boulders, rocks, pebbles, sand, silt, and clay. These particles make up the bed load of the stream. Stream competence was originally simplified by the “sixth-power-law,” which states the mass of a particle that can be moved is proportional to the velocity of the river raised to the sixth power. This refers to the stream bed velocity which is difficult to measure or estimate due to the many factors that cause slight variances in stream velocities.

Grain boundary sliding (GBS) is a material deformation mechanism where grains slide against each other. This occurs in polycrystalline material under external stress at high homologous temperature and low strain rate and is intertwined with creep. Homologous temperature describes the operating temperature relative to the melting temperature of the material. There are mainly two types of grain boundary sliding: Rachinger sliding, and Lifshitz sliding. Grain boundary sliding usually occurs as a combination of both types of sliding. Boundary shape often determines the rate and extent of grain boundary sliding.

The landscape polewards of around 30 degrees latitude on Mars has a distinctively different appearance to that nearer the equator, and is said to have undergone terrain softening. Softened terrain lacks the sharp ridge crests seen near the equator, and is instead smoothly rounded. This rounding is thought to be caused by high concentrations of water ice in soils. The term was coined in 1986 by Steve Squyres and Michael Carr from examining imagery from the Viking missions to Mars.
Nabarro–Herring creep is a mode of deformation of crystalline materials that occurs at low stresses and held at elevated temperatures in fine-grained materials. In Nabarro–Herring creep, atoms diffuse through the crystals, and the creep rate varies inversely with the square of the grain size so fine-grained materials creep faster than coarser-grained ones. NH creep is solely controlled by diffusional mass transport. This type of creep results from the diffusion of vacancies from regions of high chemical potential at grain boundaries subjected to normal tensile stresses to regions of lower chemical potential where the average tensile stresses across the grain boundaries are zero. Self-diffusion within the grains of a polycrystalline solid can cause the solid to yield to an applied shearing stress, the yielding being caused by a diffusional flow of matter within each crystal grain away from boundaries where there is a normal pressure and toward those where there is a normal tension. Atoms migrating in the opposite direction account for the creep strain. The creep strain rate is derived in the next section. NH creep is more important in ceramics than metals as dislocation motion is more difficult to effect in ceramics.
Hillslope evolution is the changes in the erosion rates, erosion styles and form of slopes of hills and mountains over time.






















