Related Research Articles

A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electrical signals and power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Some transistors are packaged individually, but many more in miniature form are found embedded in integrated circuits.
A semiconductor device is an electronic component that relies on the electronic properties of a semiconductor material for its function. Its conductivity lies between conductors and insulators. Semiconductor devices have replaced vacuum tubes in most applications. They conduct electric current in the solid state, rather than as free electrons across a vacuum or as free electrons and ions through an ionized gas.
Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a logic family built from bipolar junction transistors. Its name signifies that transistors perform both the logic function and the amplifying function, as opposed to earlier resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and diode–transistor logic (DTL).

A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small current injected at one of its terminals to control a much larger current flowing between the terminals, making the device capable of amplification or switching.

A p–n junction is a boundary or interface between two types of semiconductor materials, p-type and n-type, inside a single crystal of semiconductor. The "p" (positive) side contains an excess of holes, while the "n" (negative) side contains an excess of electrons in the outer shells of the electrically neutral atoms there. This allows electrical current to pass through the junction only in one direction. The p-n junction is created by doping, for example by ion implantation, diffusion of dopants, or by epitaxy. If two separate pieces of material were used, this would introduce a grain boundary between the semiconductors that would severely inhibit its utility by scattering the electrons and holes.
A power semiconductor device is a semiconductor device used as a switch or rectifier in power electronics. Such a device is also called a power device or, when used in an integrated circuit, a power IC.
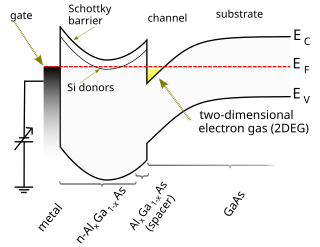
A high-electron-mobility transistor (HEMT), also known as heterostructure FET (HFET) or modulation-doped FET (MODFET), is a field-effect transistor incorporating a junction between two materials with different band gaps as the channel instead of a doped region. A commonly used material combination is GaAs with AlGaAs, though there is wide variation, dependent on the application of the device. Devices incorporating more indium generally show better high-frequency performance, while in recent years, gallium nitride HEMTs have attracted attention due to their high-power performance. Like other FETs, HEMTs are used in integrated circuits as digital on-off switches. FETs can also be used as amplifiers for large amounts of current using a small voltage as a control signal. Both of these uses are made possible by the FET’s unique current–voltage characteristics. HEMT transistors are able to operate at higher frequencies than ordinary transistors, up to millimeter wave frequencies, and are used in high-frequency products such as cell phones, satellite television receivers, voltage converters, and radar equipment. They are widely used in satellite receivers, in low power amplifiers and in the defense industry.
In semiconductor production, doping is the intentional introduction of impurities into an intrinsic semiconductor for the purpose of modulating its electrical, optical and structural properties. The doped material is referred to as an extrinsic semiconductor.
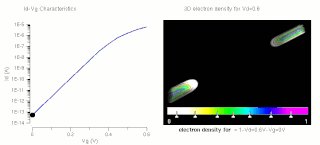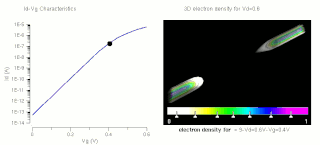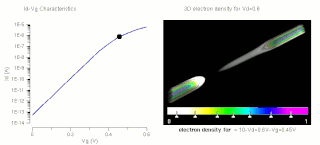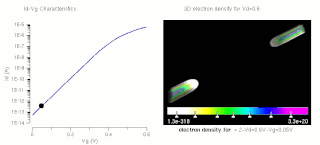
The threshold voltage, commonly abbreviated as Vth or VGS(th), of a field-effect transistor (FET) is the minimum gate-to-source voltage (VGS) that is needed to create a conducting path between the source and drain terminals. It is an important scaling factor to maintain power efficiency.
The heterojunction bipolar transistor (HBT) is a type of bipolar junction transistor (BJT) which uses differing semiconductor materials for the emitter and base regions, creating a heterojunction. The HBT improves on the BJT in that it can handle signals of very high frequencies, up to several hundred GHz. It is commonly used in modern ultrafast circuits, mostly radio frequency (RF) systems, and in applications requiring a high power efficiency, such as RF power amplifiers in cellular phones. The idea of employing a heterojunction is as old as the conventional BJT, dating back to a patent from 1951. Detailed theory of heterojunction bipolar transistor was developed by Herbert Kroemer in 1957.

A power MOSFET is a specific type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) designed to handle significant power levels. Compared to the other power semiconductor devices, such as an insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) or a thyristor, its main advantages are high switching speed and good efficiency at low voltages. It shares with the IGBT an isolated gate that makes it easy to drive. They can be subject to low gain, sometimes to a degree that the gate voltage needs to be higher than the voltage under control.
An avalanche transistor is a bipolar junction transistor designed for operation in the region of its collector-current/collector-to-emitter voltage characteristics beyond the collector-to-emitter breakdown voltage, called avalanche breakdown region. This region is characterized by avalanche breakdown, which is a phenomenon similar to Townsend discharge for gases, and negative differential resistance. Operation in the avalanche breakdown region is called avalanche-mode operation: it gives avalanche transistors the ability to switch very high currents with less than a nanosecond rise and fall times. Transistors not specifically designed for the purpose can have reasonably consistent avalanche properties; for example 82% of samples of the 15V high-speed switch 2N2369, manufactured over a 12-year period, were capable of generating avalanche breakdown pulses with rise time of 350 ps or less, using a 90V power supply as Jim Williams writes.
In semiconductor electronics fabrication technology, a self-aligned gate is a transistor manufacturing approach whereby the gate electrode of a MOSFET is used as a mask for the doping of the source and drain regions. This technique ensures that the gate is naturally and precisely aligned to the edges of the source and drain.
The Heterojunction-emitter bipolar transistor (HEBT), is a somewhat unusual arrangement with respect to emitter blocking of minority carriers. This is accomplished by using heterostructure confinement in the emitter, introducing an energy barrier to minority-carrier charge flow from the base. This is important as loss of minority carriers from the base to the emitter degrades analog performance. The main difference of the HEBT from the Heterojunction bipolar transistor (HBT) is that the emitter–base interface is the same as in a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) with the blocking energy gap being moved back into the emitter bulk region.
An extrinsic semiconductor is one that has been doped; during manufacture of the semiconductor crystal a trace element or chemical called a doping agent has been incorporated chemically into the crystal, for the purpose of giving it different electrical properties than the pure semiconductor crystal, which is called an intrinsic semiconductor. In an extrinsic semiconductor it is these foreign dopant atoms in the crystal lattice that mainly provide the charge carriers which carry electric current through the crystal. The doping agents used are of two types, resulting in two types of extrinsic semiconductor. An electron donor dopant is an atom which, when incorporated in the crystal, releases a mobile conduction electron into the crystal lattice. An extrinsic semiconductor which has been doped with electron donor atoms is called an n-type semiconductor, because the majority of charge carriers in the crystal are negative electrons. An electron acceptor dopant is an atom which accepts an electron from the lattice, creating a vacancy where an electron should be called a hole which can move through the crystal like a positively charged particle. An extrinsic semiconductor which has been doped with electron acceptor atoms is called a p-type semiconductor, because the majority of charge carriers in the crystal are positive holes.
A tetrode transistor is any transistor having four active terminals.

The germanium alloy-junction transistor, or alloy transistor, was an early type of bipolar junction transistor, developed at General Electric and RCA in 1951 as an improvement over the earlier grown-junction transistor.
A diffused junction transistor is a transistor formed by diffusing dopants into a semiconductor substrate. The diffusion process was developed later than the alloy junction and grown junction processes for making bipolar junction transistors (BJTs).
A definition in semiconductor physics, carrier lifetime is defined as the average time it takes for a minority carrier to recombine. The process through which this is done is typically known as minority carrier recombination.

The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs are devices with three terminals: source, gate, and drain. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source.