
Drosophila is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many species to linger around overripe or rotting fruit. They should not be confused with the Tephritidae, a related family, which are also called fruit flies ; tephritids feed primarily on unripe or ripe fruit, with many species being regarded as destructive agricultural pests, especially the Mediterranean fruit fly.

Drosophila melanogaster is a species of fly in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the "vinegar fly" or "pomace fly". Starting with Charles W. Woodworth's 1901 proposal of the use of this species as a model organism, D. melanogaster continues to be widely used for biological research in genetics, physiology, microbial pathogenesis, and life history evolution. As of 2017, five Nobel Prizes have been awarded to drosophilists for their work using the insect.

Allopatric speciation – also referred to as geographic speciation, vicariant speciation, or its earlier name the dumbbell model – is a mode of speciation that occurs when biological populations become geographically isolated from each other to an extent that prevents or interferes with gene flow.

Peripatric speciation is a mode of speciation in which a new species is formed from an isolated peripheral population. Since peripatric speciation resembles allopatric speciation, in that populations are isolated and prevented from exchanging genes, it can often be difficult to distinguish between them. Nevertheless, the primary characteristic of peripatric speciation proposes that one of the populations is much smaller than the other. The terms peripatric and peripatry are often used in biogeography, referring to organisms whose ranges are closely adjacent but do not overlap, being separated where these organisms do not occur—for example on an oceanic island compared to the mainland. Such organisms are usually closely related ; their distribution being the result of peripatric speciation.

The Drosophilidae are a diverse, cosmopolitan family of flies, which includes species called fruit flies, although they are more accurately referred to as vinegar or pomace flies. Another distantly related family of flies, Tephritidae, are true fruit flies because they are frugivorous, and include apple maggot flies and many pests. The best known species of the Drosophilidae is Drosophila melanogaster, within the genus Drosophila, also called the "fruit fly." Drosophila melanogaster is used extensively for studies concerning genetics, development, physiology, ecology and behaviour. Many fundamental biological mechanisms were discovered first in D. melanogaster. The fruit fly is mostly composed of post-mitotic cells, has a very short lifespan, and shows gradual aging. As in other species, temperature influences the life history of the animal. Several genes have been identified that can be manipulated to extend the lifespan of these insects. Additionally, Drosophila subobscura, also within the genus Drosophila, has been reputed as a model organism for evolutionary-biological studies, along with D. sechellia for the evolution of host specialization on the toxic noni fruit and Scaptomyza flava for the evolution of herbivory and specialist on toxic mustard leaves.

Michael Ashburner is a biologist and Emeritus Professor in the Department of Genetics at University of Cambridge. He is also the former joint-head and co-founder of the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI) of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and a Fellow of Churchill College, Cambridge.

Octopamine (molecular formula C8H11NO2; also known as OA, and also norsynephrine, para-octopamine and others) is an organic chemical closely related to norepinephrine, and synthesized biologically by a homologous pathway. Octopamine is often considered the major "fight-or-flight" neurohormone of invertebrates. Its name is derived from the fact that it was first identified in the salivary glands of the octopus.

The Drosophilinae are the largest subfamily in the Drosophilidae. The other subfamily is the Steganinae.
The mechanisms of reproductive isolation are a collection of evolutionary mechanisms, behaviors and physiological processes critical for speciation. They prevent members of different species from producing offspring, or ensure that any offspring are sterile. These barriers maintain the integrity of a species by reducing gene flow between related species.
Odorant-binding proteins (OBPs) are small soluble proteins secreted by auxiliary cells surrounding olfactory receptor neurons, including the nasal mucus of many vertebrate species and in the sensillar lymph of chemosensory sensilla of insects. OBPs are characterized by a specific protein domain that comprises six α-helices joined by three disulfide bonds. Although the function of the OBPs as a whole is not well established, it is believed that they act as odorant transporters, delivering the odorant molecules to olfactory receptors in the cell membrane of sensory neurons.

In molecular biology, mir-46 and mir-47 are microRNA expressed in C. elegans from related hairpin precursor sequences. The predicted hairpin precursor sequences for Drosophila mir-281 are also related and, hence, belong to this family. The hairpin precursors are predicted based on base pairing and cross-species conservation; their extents are not known. In this case, the mature sequences are expressed from the 3' arms of the hairpin precursors.

The miR-8 microRNA precursor, is a short non-coding RNA gene involved in gene regulation. miR-8 in Drosophila melanogaster is expressed from the 3' arm of related precursor hairpins, along with miR-200, miR-236, miR-429 and human and mouse homolog miR-141. Members of this precursor family have now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide range of species. The bounds of the precursors are predicted based on conservation and base pairing and are not generally known.
Gerald Mayer Rubin is an American biologist, notable for pioneering the use of transposable P elements in genetics, and for leading the public project to sequence the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Related to his genomics work, Rubin's lab is notable for development of genetic and genomics tools and studies of signal transduction and gene regulation. Rubin also serves as a vice president of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and executive director of the Janelia Research Campus.
Bateman's principle, in evolutionary biology, is that in most species, variability in reproductive success is greater in males than in females. It was first proposed by Angus John Bateman (1919–1996), an English geneticist. Bateman suggested that, since males are capable of producing millions of sperm cells with little effort, while females invest much higher levels of energy in order to nurture a relatively small number of eggs, the female plays a significantly larger role in their offspring's reproductive success. Bateman's paradigm thus views females as the limiting factor of parental investment, over which males will compete in order to copulate successfully.

Michael Morris Rosbash is an American geneticist and chronobiologist. Rosbash is a professor and researcher at Brandeis University and investigator at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. Rosbash's research group cloned the Drosophila period gene in 1984 and proposed the Transcription Translation Negative Feedback Loop for circadian clocks in 1990. In 1998, they discovered the cycle gene, clock gene, and cryptochrome photoreceptor in Drosophila through the use of forward genetics, by first identifying the phenotype of a mutant and then determining the genetics behind the mutation. Rosbash was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 2003. Along with Michael W. Young and Jeffrey C. Hall, he was awarded the 2017 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries of molecular mechanisms controlling the circadian rhythm".
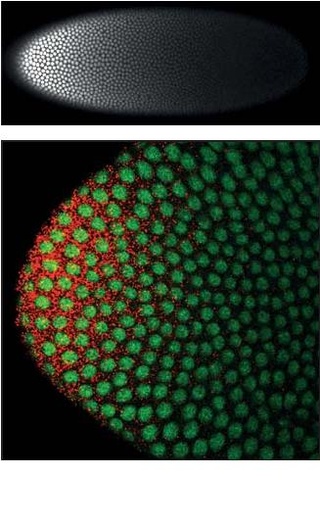
Homeotic protein bicoid is encoded by the bcd maternal effect gene in Drosophilia. Homeotic protein bicoid concentration gradient patterns the anterior-posterior (A-P) axis during Drosophila embryogenesis. Bicoid was the first protein demonstrated to act as a morphogen. Although bicoid is important for the development of Drosophila and other higher dipterans, it is absent from most other insects, where its role is accomplished by other genes.

Drosophila subobscura is a species of fruit fly in the family Drosophilidae. Originally found around the Mediterranean, it has spread to most of Europe and the Near East. It has been introduced into the west coasts of Canada, the United States, and Chile. Its closest relative is Drosophila madeirensis, found in the Madeira Islands, followed by D. guanche, found in the Canary Islands. These three species form the D. subobscura species subgroup. When they mate, males and females perform an elaborate courtship dance, in which the female can either turn away to end the mating ritual, or stick out her proboscis in response to the male's, allowing copulation to proceed. D. subobscura has been regarded as a model organism for its use in evolutionary-biological studies.

Reinforcement is a process within speciation where natural selection increases the reproductive isolation between two populations of species by reducing the production of hybrids. Evidence for speciation by reinforcement has been gathered since the 1990s, and along with data from comparative studies and laboratory experiments, has overcome many of the objections to the theory. Differences in behavior or biology that inhibit formation of hybrid zygotes are termed prezygotic isolation. Reinforcement can be shown to be occurring by measuring the strength of prezygotic isolation in a sympatric population in comparison to an allopatric population of the same species. Comparative studies of this allow for determining large-scale patterns in nature across various taxa. Mating patterns in hybrid zones can also be used to detect reinforcement. Reproductive character displacement is seen as a result of reinforcement, so many of the cases in nature express this pattern in sympatry. Reinforcement's prevalence is unknown, but the patterns of reproductive character displacement are found across numerous taxa, and is considered to be a common occurrence in nature. Studies of reinforcement in nature often prove difficult, as alternative explanations for the detected patterns can be asserted. Nevertheless, empirical evidence exists for reinforcement occurring across various taxa and its role in precipitating speciation is conclusive.
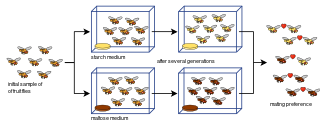
Laboratory experiments of speciation have been conducted for all four modes of speciation: allopatric, peripatric, parapatric, and sympatric; and various other processes involving speciation: hybridization, reinforcement, founder effects, among others. Most of the experiments have been done on flies, in particular Drosophila fruit flies. However, more recent studies have tested yeasts, fungi, and even viruses.
Semotivirus is the only genus of viruses in the family Belpaoviridae. Species exist as retrotransposons in a eukaryotic host's genome. BEL/pao transposons are only found in animals.












