Related Research Articles
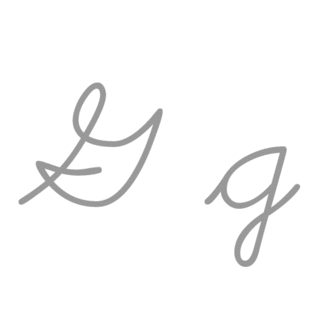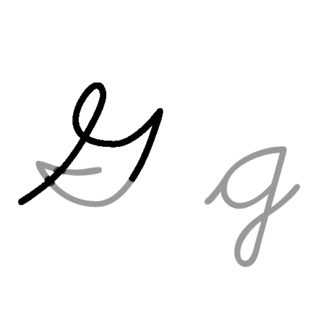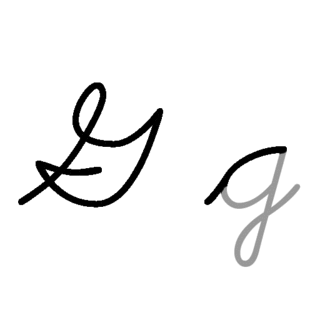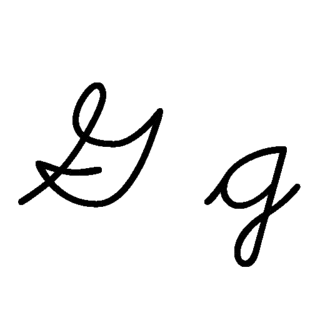
G or g is the seventh letter of the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Its name in English is gee, plural gees.

Herbert George Wells was an English writer. Prolific in many genres, he wrote dozens of novels, short stories, and works of social commentary, history, satire, biography and autobiography. His work also included two books on recreational war games. Wells is now best remembered for his science fiction novels and is often called the "father of science fiction", along with Jules Verne and the publisher Hugo Gernsback.

The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-21 is a supersonic jet fighter and interceptor aircraft, designed by the Mikoyan-Gurevich Design Bureau in the Soviet Union. Its nicknames include: Balalaika, because its planform resembles the stringed musical instrument of the same name; Ołówek, Polish for "pencil", due to the shape of its fuselage, and Én Bạc, meaning "Silver Swallow", in Vietnamese.

Christopher George Latore Wallace, better known by his stage names the Notorious B.I.G., Biggie Smalls, or simply Biggie, was an American rapper and songwriter. Rooted in the New York rap scene and gangsta rap traditions, he is considered one of the greatest rappers of all time. The Notorious B.I.G. became known for his distinctive laidback lyrical delivery, offsetting the lyrics' often grim content and his own intimidating appearance. His music was often semi-autobiographical, telling of hardship and criminality, but also of debauchery and celebration.

The G20 is an international forum for the governments and central bank governors from 19 countries and the European Union (EU). Founded in 1999 with the aim to discuss policy pertaining to the promotion of international financial stability, the G20 has expanded its agenda since 2008 and heads of government or heads of state, as well as finance ministers, foreign ministers and think tanks, have periodically conferred at summits ever since. It seeks to address issues that go beyond the responsibilities of any one.
Dycladia is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae. The genus was described by Felder in 1874.

Sarosa is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae. The genus was erected by Francis Walker in 1854.

In telecommunications, 5G is the fifth generation technology standard for broadband cellular networks, which cellular phone companies began deploying worldwide in 2019, and is the planned successor to the 4G networks which provide connectivity to most current cellphones. 5G networks are predicted to have more than 1.7 billion subscribers worldwide by 2025, according to the GSM Association. Like its predecessors, 5G networks are cellular networks, in which the service area is divided into small geographical areas called cells. All 5G wireless devices in a cell are connected to the Internet and telephone network by radio waves through a local antenna in the cell. The main advantage of the new networks is that they will have greater bandwidth, giving higher download speeds, eventually up to 10 gigabits per second (Gbit/s). Due to the increased bandwidth, it is expected the networks will not exclusively serve cellphones like existing cellular networks, but also be used as general internet service providers for laptops and desktop computers, competing with existing ISPs such as cable internet, and also will make possible new applications in internet of things (IoT) and machine to machine areas. 4G cellphones are not able to use the new networks, which require 5G enabled wireless devices.

Rectiostoma xanthobasis is a species of moth in the family Depressariidae. It was described by Philipp Christoph Zeller in 1876. It is found along the Atlantic Coastal Plain from south-eastern Massachusetts south to central Florida and eastern Texas, and north in the Mississippi Valley to Missouri and Illinois.

Neonegeta is a genus of moths in the family Nolidae. The genus was erected by George Hampson in 1912.
Dycladia basimacula is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Schaus in 1924. It is found in Venezuela and Trinidad.
Dycladia correbioides is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Felder in 1869. It is found in Mexico, Guatemala, Costa Rica, Panama and Colombia.
Dycladia lydia is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Druce in 1900. It is found in southern Brazil.
Dycladia marmana is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Schaus in 1924. It is found in Guyana.
Dycladia melaena is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by George Hampson in 1898. It is found in Bolivia and Espírito Santo, Brazil.
Dycladia vitrina is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Rothschild in 1911. It is found in Honduras and Ecuador.
Sarosa xanthobasis is a moth in the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Herbert Druce in 1898. It is found in Ecuador.
The Euchromiina are a subtribe of tiger moths in the family Erebidae. It was described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1876. Many species in the subtribe are mimics of wasps.

Rectiostoma is a moth genus of the family Depressariidae.
References
- ↑ Beccaloni, G.; Scoble, M.; Kitching, I.; Simonsen, T.; Robinson, G.; Pitkin, B.; Hine, A.; Lyal, C., eds. (2003). "Dycladia xanthobasis". The Global Lepidoptera Names Index . Natural History Museum . Retrieved May 1, 2018.
| This Euchromiina-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |