
Quadraphonic sound – equivalent to what is now called 4.0 surround sound – uses four audio channels in which speakers are positioned at the four corners of a listening space. The system allows for the reproduction of sound signals that are independent of one another.

Surround sound is a technique for enriching the fidelity and depth of sound reproduction by using multiple audio channels from speakers that surround the listener. Its first application was in movie theaters. Prior to surround sound, theater sound systems commonly had three screen channels of sound that played from three loudspeakers located in front of the audience. Surround sound adds one or more channels from loudspeakers to the side or behind the listener that are able to create the sensation of sound coming from any horizontal direction around the listener.
Dolby Pro Logic is a surround sound processing technology developed by Dolby Laboratories, designed to decode soundtracks encoded with Dolby Surround.
Matrix decoding is an audio technology where a small number of discrete audio channels are decoded into a larger number of channels on play back. The channels are generally, but not always, arranged for transmission or recording by an encoder, and decoded for playback by a decoder. The function is to allow multichannel audio, such as quadraphonic sound or surround sound to be encoded in a stereo signal, and thus played back as stereo on stereo equipment, and as surround on surround equipment – this is "compatible" multichannel audio.
Founded by David Hafler and Ed Laurent in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania in 1955, Dynaco was an American hi-fi audio system manufacturer popular in the 1960s and 1970s for its wide range of affordable, yet high quality audio components.. Its best known product was the ST-70 tube stereo amplifier. They also manufactured other tube and solid state amplifiers, preamplifiers, radio tuners and bookshelf loudspeakers. Dynaco was liquidated in 1980, and the trademark is now owned by Radial Engineering Ltd.
Dolby Stereo is a sound format made by Dolby Laboratories. It is a unified brand for two completely different basic systems: the Dolby SVA 1976 system used with optical sound tracks on 35mm film, and Dolby Stereo 70mm noise reduction on 6-channel magnetic soundtracks on 70mm prints.
Multiple electronic amplifiers can be connected such that they drive a single floating load (bridge) or a single common load (parallel), to increase the amount of power available in different situations. This is commonly encountered in audio applications.
David Hafler was an American audio engineer. He was best known for his work on an improved version of the Williamson amplifier using the ultra-linear circuit of Alan Blumlein.

An audio/video receiver (AVR) is a consumer electronics component used in a home theater. Its purpose is to receive audio and video signals from a number of sources, and to process them and provide power amplifiers to drive loudspeakers and route the video to displays such as a television, monitor or video projector. Inputs may come from a satellite receiver, radio, DVD players, Blu-ray Disc players, VCRs or video game consoles, among others. The AVR source selection and settings such as volume, are typically set by a remote controller.

The Fender Twin and Twin Reverb are guitar amplifiers made by Fender Musical Instruments Corporation. The Twin was introduced in 1952, two years before Fender began selling Stratocaster electric guitars. The amps are known for their characteristically clean tone.
Ambisonic UHJ format is a development of the Ambisonic surround sound system designed to be compatible with mono and stereo media. It is a hierarchy of systems in which the recorded soundfield will be reproduced with a degree of accuracy that varies according to the available channels. Although UHJ permits the use of up to four channels, only the 2-channel variant is in current use. In Ambisonics, UHJ is also known as "C-Format".
The Label: The Story of Columbia Records is a 2007 book by Gary Marmorstein, about the rise of Columbia Records. It covers how it made its way from the beginning: from signing its own artists, to making them celebrities.
SQ Quadraphonic was a matrix 4-channel quadraphonic sound system for vinyl LP records. It was introduced by CBS Records in 1971. Many recordings using this technology were released on LP during the 1970s.
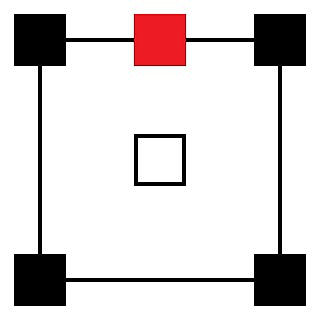
Center channel refers to an audio channel common to many surround sound formats. It is the channel that is mostly, or fully, dedicated to the reproduction of the dialogue of an audiovisual program. The speaker(s) connected to the center channel are placed in the center of and behind the perforated projection screen, to give the effect that sounds from the center channel are coming from the screen. In many home surround sound units, the center channel is positioned above or below the video screen.

The TRM-800 was a high-end solid state integrated stereo amplifier made in Japan, using NEC power transistors, by Nikko. It was the top-of-the-line model in the Nikko amplifier range of TRM's series; housed in a wooden walnut-finished cabinet and a brushed aluminum front panel, was introduced in 1975 the same year as the Marantz 2235. It was a two-channel amp; however, it had three sets of speaker connections; those powered selected by buttons. At 8 ohms, the amp could put out 65 Watts per channel RMS, delivering superb high fidelity sound with exceptional tone quality. Unlike many amps of this time, however, the TRM-800 was stable at lower impedances than 8 ohms; down to 4 ohms. The TRM-800's frequency response ranges 10Hz to 40.000 Hz ±1 dB with T.H.D. less than 0.1% at rated output. Its preamplifier and main amplifier were separable for multi-channel amplifier systems. The amp has internal circuit breakers which prevent it from clipping or overheating. Its power consumption is 250 watts. For equalization it has only a bass and a treble knob; however the frequency of these are selectable; between 250 and 500 Hertz for the bass, and between 2.5 and 5 kHz for the treble. It also has a high, low, and a subsonic filter. There are two phono stages; phono 2 is provided with impedance matching selection, for using different types of cartridges (MC/MM).

Quadraphonic Sound was a phase amplitude matrix 4-channel quadraphonic sound system for phonograph records. The system was based on technology created by Peter Scheiber, but further developed by engineer Ryosuke Ito of Sansui in the early 1970s.

Compatible Discrete 4, also known as Quadradisc or CD-4 was as a discrete four-channel quadraphonic system for phonograph records. The system was created by JVC and RCA in 1971 and introduced in May 1972. Hundreds of recordings using this technology were released on LP during the 1970s.
The Hafler circuit is a passive electronics circuit with the aim of getting derived surround sound or ambiophony from regular stereo recordings without using costly electronics. Such circuits are generally known as matrix decoders. The Dynaquad system works using similar principles.
Stereo-4, also known as EV or EV-4, was a matrix 4-channel quadraphonic sound system developed in 1970 by Leonard Feldman and Jon Fixler.

UD-4 was a discrete four-channel quadraphonic sound system for phonograph records introduced by Nippon Columbia (Denon) in 1974. This system had some similarities with the more successful CD-4 process introduced by JVC and RCA in 1972.











