Cupronickel or copper-nickel (CuNi) is an alloy of copper that contains nickel and strengthening elements, such as iron and manganese. The copper content typically varies from 60 to 90 percent.
Nondestructive testing (NDT) is a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage. The terms nondestructive examination (NDE), nondestructive inspection (NDI), and nondestructive evaluation (NDE) are also commonly used to describe this technology. Because NDT does not permanently alter the article being inspected, it is a highly valuable technique that can save both money and time in product evaluation, troubleshooting, and research. The six most frequently used NDT methods are eddy-current, magnetic-particle, liquid penetrant, radiographic, ultrasonic, and visual testing. NDT is commonly used in forensic engineering, mechanical engineering, petroleum engineering, electrical engineering, civil engineering, systems engineering, aeronautical engineering, medicine, and art. Innovations in the field of nondestructive testing have had a profound impact on medical imaging, including on echocardiography, medical ultrasonography, and digital radiography.

Brazing is a metal-joining process in which two or more metal items are joined together by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint, the filler metal having a lower melting point than the adjoining metal.

A diving cylinder, scuba tank or diving tank is a gas cylinder used to store and transport the high pressure breathing gas required by a scuba set. It may also be used for surface-supplied diving or as decompression gas or an emergency gas supply for surface supplied diving or scuba. Cylinders provide gas to the diver through the demand valve of a diving regulator or the breathing loop of a diving rebreather.

The Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive 2002/95/EC, (RoHS 1), short for Directive on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, was adopted in February 2003 by the European Union.

A pressure vessel is a container designed to hold gases or liquids at a pressure substantially different from the ambient pressure.

Within industry, piping is a system of pipes used to convey fluids from one location to another. The engineering discipline of piping design studies the efficient transport of fluid.

CE marking is a certification mark that indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA). The CE marking is also found on products sold outside the EEA that have been manufactured to EEA standards. This makes the CE marking recognizable worldwide even to people who are not familiar with the European Economic Area. It is in that sense similar to the FCC Declaration of Conformity used on certain electronic devices sold in the United States.
Friction welding (FRW) is a solid-state welding process that generates heat through mechanical friction between workpieces in relative motion to one another, with the addition of a lateral force called "upset" to plastically displace and fuse the materials. Because no melting occurs, friction welding is not a fusion welding process in the traditional sense, but more of a forge welding technique. Friction welding is used with metals and thermoplastics in a wide variety of aviation and automotive applications.
Titanium alloys are alloys that contain a mixture of titanium and other chemical elements. Such alloys have very high tensile strength and toughness. They are light in weight, have extraordinary corrosion resistance and the ability to withstand extreme temperatures. However, the high cost of both raw materials and processing limit their use to military applications, aircraft, spacecraft, bicycles, medical devices, jewelry, highly stressed components such as connecting rods on expensive sports cars and some premium sports equipment and consumer electronics.
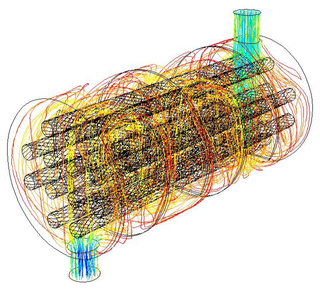
A shell and tube heat exchanger is a class of heat exchanger designs. It is the most common type of heat exchanger in oil refineries and other large chemical processes, and is suited for higher-pressure applications. As its name implies, this type of heat exchanger consists of a shell with a bundle of tubes inside it. One fluid runs through the tubes, and another fluid flows over the tubes to transfer heat between the two fluids. The set of tubes is called a tube bundle, and may be composed of several types of tubes: plain, longitudinally finned, etc.
The Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) 2014/68/EU of the EU sets out the standards for the design and fabrication of pressure equipment generally over one litre in volume and having a maximum pressure more than 0.5 bar gauge. It also sets the administrative procedures requirements for the "conformity assessment" of pressure equipment, for the free placing on the European market without local legislative barriers. It has been mandatory throughout the EU since 30 May 2002, with 2014 revision fully effective as of 19 July 2016. This is enacted in the UK as the Pressure Equipment Regulations (PER). The set out standards and regulations regarding pressure vessels and boilers safety is also very close to the US standards defined by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). This enables most international inspection agencies to provide both verification and certification services to assess compliance to the different pressure equipment directives.
Welder certification, is a process which examines and documents a welder's capability to create welds of acceptable quality following a well defined welding procedure.
Austenitic stainless steel is a specific type of stainless steel alloy. Stainless steels may be classified by their crystalline structure into four main types: austenitic, ferritic, martensitic and duplex. Austenitic stainless steels possess austenite as their primary crystalline structure. This austenite crystalline structure is achieved by sufficient additions of the austenite stabilizing elements nickel, manganese and nitrogen. Due to their crystalline structure, austenitic steels are not hardenable by heat treatment and are essentially non-magnetic.

Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) are the standards used for industrial activities in Japan, coordinated by the Japanese Industrial Standards Committee (JISC) and published by the Japanese Standards Association (JSA). The JISC is composed of many nationwide committees and plays a vital role in standardizing activities across Japan.
BS EN 13121-3 is European Standard adopted by UK, titled "GRP tanks and vessels for use above ground. Design and workmanship". Design and workmanship is the final part within a four parts standard series which specifies the necessary requirements for design, fabrication, inspection and testing by manufacturers and specifiers within the area of chemical storage.
PD 5500 "Specification for unfired, fusion welded pressure vessels" is a code of practice that provides rules for the design, fabrication, and inspection of pressure vessels.
The ASME Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC) is an American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) standard that regulates the design and construction of boilers and pressure vessels. The document is written and maintained by volunteers chosen for their technical expertise. The ASME works as an accreditation body and entitles independent third parties to inspect and ensure compliance to the BPVC.

Transportable pressure vessels for high-pressure gases are routinely inspected and tested as part of the manufacturing process. They are generally marked as evidence of passing the tests, either individually or as part of a batch, and certified as meeting the standard of manufacture by the authorised testing agency, making them legal for import and sale. When a cylinder is manufactured, its specification, including manufacturer, working pressure, test pressure, date of manufacture, capacity and weight are stamped on the cylinder.









