
Imaging radar is an application of radar which is used to create two-dimensional images, typically of landscapes. Imaging radar provides its light to illuminate an area on the ground and take a picture at radio wavelengths. It uses an antenna and digital computer storage to record its images. In a radar image, one can see only the energy that was reflected back towards the radar antenna. The radar moves along a flight path and the area illuminated by the radar, or footprint, is moved along the surface in a swath, building the image as it does so.

The SCR-268 was the United States Army's first radar system. Introduced in 1940, it was developed to provide accurate aiming information for antiaircraft artillery and was also used for gun laying systems and directing searchlights against aircraft. The radar was widely utilized by both Army and Marine Corps air defense and early warning units during World War II. By the end of World War II the system was already considered out of date, having been replaced by the much smaller and more accurate SCR-584 microwave-based system.

SMART-L is a long-range naval search radar introduced in 2002 by Thales Nederland, formerly Hollandse Signaalapparaten (Signaal).

An airport surveillance radar (ASR) is a radar system used at airports to detect and display the presence and position of aircraft in the terminal area, the airspace around airports. It is the main air traffic control system for the airspace around airports. At large airports it typically controls traffic within a radius of 60 miles (96 km) of the airport below an elevation of 25,000 feet. The sophisticated systems at large airports consist of two different radar systems, the primary and secondary surveillance radar. The primary radar typically consists of a large rotating parabolic antenna dish that sweeps a vertical fan-shaped beam of microwaves around the airspace surrounding the airport. It detects the position and range of aircraft by microwaves reflected back to the antenna from the aircraft's surface. The secondary surveillance radar consists of a second rotating antenna, often mounted on the primary antenna, which interrogates the transponders of aircraft, which transmits a radio signal back containing the aircraft's identification, barometric altitude, and an emergency status code, which is displayed on the radar screen next to the return from the primary radar.

A wind profiler is a type of weather observing equipment that uses radar or sound waves (SODAR) to detect the wind speed and direction at various elevations above the ground. Readings are made at each kilometer above sea level, up to the extent of the troposphere. Above this level there is inadequate water vapor present to produce a radar "bounce." The data synthesized from wind direction and speed is very useful to meteorological forecasting and timely reporting for flight planning. A twelve-hour history of data is available through NOAA websites.
The JY-8 is a mobile 3D air surveillance, target acquisition and interception control radar system operating in the C-band. It can be employed as the main radar sensor for an automated tactical defence system, or can be used as an independent radar. The system uses advanced signal/data processor techniques and is fully solid state with the exception of the magnetrons and thyratrons of the transmitters. The general designer of JY-9 is the head of 38th Research Institute, academician of Chinese Academy of Sciences Mr. Wu Manqing, who is also the general designer of JY-9 and the general designer of the radar systems for KJ-2000 and KJ-200.
The JY-9 Radar is a mobile S band low altitude search radar intended for use in air defense, gap filling, airport surveillance, and coastal defense. It is designed for effective detection of targets at low altitude in both ECM and natural clutter environments. The general designer of the JY-9 is academician of Chinese Academy of Sciences Mr. Wu Manqing, the head of 38th Research Institute, who is also the general designer of the JY-8 Radar and of the radar systems for the KJ-2000 and KJ-200 early warning aircraft.

The AN/SPS-48 is a US naval electronically scanned array, air search three-dimensional radar system manufactured by ITT Exelis and deployed in the 1960s as the primary air search sensor for anti-aircraft warships. The deployment of the AN/SPY-1 and the end of the Cold War led to the decommissioning of many such ships, and many of these vessel's AN/SPS-48 sets were reused on aircraft carriers and amphibious ships where it is used to direct targets for air defense systems such as the Sea Sparrow and RIM-116 SAM missiles. Existing sets are being modernized under the ROAR program to AN/SPS-48G standard for better reliability and usability.

A radar display is an electronic device that presents radar data to the operator. The radar system transmits pulses or continuous waves of electromagnetic radiation, a small portion of which backscatter off targets and return to the radar system. The receiver converts all received electromagnetic radiation into a continuous electronic analog signal of varying voltage that can be converted then to a screen display.

The AN/SPS-67 is a short-range, two-dimensional, surface-search/navigation radar system that provides highly accurate surface and limited low-flyer detection and tracking capabilities.
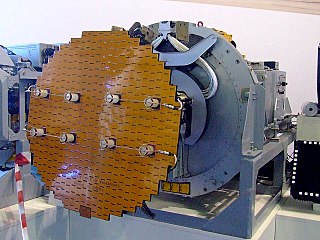
The Zhuk are a family of Russian all-weather multimode airborne radars developed by NIIR Phazotron for multi-role combat aircraft such as the MiG-29 and the Su-27. The PESA versions were also known as the Sokol.
Moving target indication (MTI) is a mode of operation of a radar to discriminate a target against the clutter. It describes a variety of techniques used for finding moving objects, like an aircraft, and filter out unmoving ones, like hills or trees. It contrasts with the modern stationary target indication (STI) technique, which uses details of the signal to directly determine the mechanical properties of the reflecting objects and thereby find targets whether they are moving or not.

The P-14 is a 2D VHF radar that was developed and operated by the Soviet Union.
The AN/MPN is a mobile Ground-controlled approach radar first used during World War II. "MPN" is Joint Electronics Type Designation System nomenclature for (Ground) Mobile (M), Pulsed (P), Navigation aid (N).

The Wasserman radar was an early-warning radar built by Germany during World War II. The radar was a development of FuMG 80 Freya and was operated during World War II for long range detection. It was developed under the direction of Theodor Schultes, beginning in 1942. Wasserman was based on largely unchanged Freya electronics, but used an entirely new antenna array in order to improve range, height-finding and bearing precision.

Curtain arrays are a class of large multielement directional radio transmitting wire antennas, used in the short-wave radio bands. They constitute a type of reflective array antenna, consisting of multiple wire dipole antennas, suspended in a vertical plane, often positioned in front of a "curtain" reflector made of a flat vertical screen of many long parallel wires. These are suspended by support wires strung between pairs of tall steel towers, reaching heights of up to 90 m high. Primarily employed for long-distance skywave transmission, they emit a beam of radio waves at a shallow angle into the sky just above the horizon, which is then reflected by the ionosphere back to Earth beyond the horizon. Curtain arrays are extensively used by international short-wave radio stations for broadcasting to large areas at transcontinental distances.
The 2023–2024 Egyptian financial crisis is an ongoing economic crisis that hit Egypt beginning in 2023 that led to the Egyptian government and the Central Bank of Egypt devaluing the Egyptian pound. Due to a continued shortage of foreign exchange in the face of increasing external public debt service payments and the absence of measures to boost foreign exchange reserves, the country's debt capacity significantly declined during the crisis.
ESR-32A is an Egyptian two-dimensional L band aerial scanning and early-warning radar. It was unveiled during EDEX 2018.
 Egypt: The Egyptian Air Force plans to use it as a gap filler in areas where the coverage provided by long-range fixed radars may be insufficient in a stressed situation; the sensor can be easily linked to a battalion-level command post, also operating in autonomous mode, or providing signals to higher-level air defense decision centers, when operating in networked mode.
Egypt: The Egyptian Air Force plans to use it as a gap filler in areas where the coverage provided by long-range fixed radars may be insufficient in a stressed situation; the sensor can be easily linked to a battalion-level command post, also operating in autonomous mode, or providing signals to higher-level air defense decision centers, when operating in networked mode.










