Related Research Articles

Lake Champlain is a natural freshwater lake in North America mainly within the borders of the United States but also across the Canada–U.S. border into the Canadian province of Quebec.

North Hero is a town in and the shire town of Grand Isle County, Vermont, United States. The population was 803 at the 2010 census.

Swanton is a town in Franklin County, Vermont. The population was 6,427 at the 2010 census. The town includes the village of Swanton.

Alburgh is a village within the town of the same name in Grand Isle County, Vermont, United States. The population was 497 at the 2010 census. The town's name came from the person primarily responsible for chartering the community, Ira Allen.

Alburgh is a town in Grand Isle County, Vermont, United States, founded in 1781 by Ira Allen. The population was 1,998 at the 2010 United States Census. Alburgh is on the Alburgh Tongue, a peninsula extending from Canada into Lake Champlain, and lies on the only road-based route across Lake Champlain to New York state north of Addison, Vermont.
The Rutland Railroad was a railroad in the northeastern United States, located primarily in the state of Vermont but extending into the state of New York at both its northernmost and southernmost ends. After its closure in 1963, parts of the railroad were taken over by the State of Vermont and are now operated by the Vermont Railway.
The Central Vermont Railway was a railroad that operated in the U.S. states of Connecticut, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New York, and Vermont, as well as the Canadian province of Quebec.
The New London Northern Railroad was a part of the Central Vermont Railway from New London, Connecticut, north to Brattleboro, Vermont. After a long period with the Canadian National Railway, it is now operated by the New England Central Railroad. The New London Northern was the only through railroad in Connecticut not to come under the control of the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad.

The New England Central Railroad began operations in 1995. It is a subsidiary of Genesee & Wyoming and runs from New London, Connecticut, to Alburgh, Vermont at the Canada–US border, a distance of 366 miles (589 km). The railroad interchanges with the CN, CSX, MCER, PAS, P&W, GMRC, WACR, and VTR.
U.S. Route 2 (US 2) is a part of the U.S. Highway System that is split into two segments. Its eastern segment runs from Rouses Point, New York, to Houlton, Maine. In Vermont, US 2 extends 151.604 miles (243.983 km) from the New York state line in Alburgh to the New Hampshire state line in Guildhall. West of Vermont, US 2 continues into New York for another 0.87 miles (1.40 km) to an intersection with US 11 in Rouses Point. US 2 passes through the cities of Burlington and Montpelier as it traverses the state. The Burlington to Montpelier route was first laid out as a toll road in the early 19th century. It was later incorporated into the transcontinental auto trail known as the Theodore Roosevelt International Highway in 1919 before being designated as part of US 2 in 1926.
Vermont Route 30 (VT 30) is a 111.870-mile-long (180.037 km) north–south state highway in the U.S. state of Vermont. VT 30 runs from U.S. Route 5 and VT 9 in Brattleboro to US 7 and VT 125 in Middlebury. The northern portion, from Poultney to Middlebury, was part of the New England road marking system's Route 30, from which VT 30 got its number. The route passes through many historic small towns, and travel writers such as those at Southern Vermont have described the route as "idyllic" and "picturesque".

Essex Junction, also known as Essex Junction–Burlington, is an Amtrak train station in the village of Essex Junction, Vermont, United States. The station was originally built by the Central Vermont Railway in 1959. It serves Amtrak's Vermonter train, which runs from St. Albans, near the Canada–U.S. border and Washington, D.C. to the south. Prior to bridge trouble at Alburg north of St. Albans, train service continued to Montreal. Until the early 1960s, the Boston and Maine railroad operated Montreal to Boston service on The Ambassador through the station.
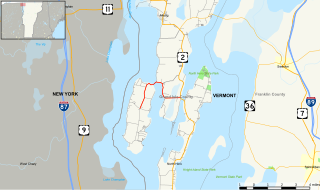
Vermont Route 129 (VT 129) is a short, 5.415-mile-long (8.715 km) connector route for Isle La Motte and Alburgh in the state of Vermont in the United States. VT 129 begins at an intersection in the centre of Isle La Motte, heads northward and terminates at an intersection with U.S. Route 2 in Alburgh. The route originated as Vermont Route F-2 in 1926, and was the name of the road that approached a ferry to Chazy. Route F-2 followed the same routing as the current VT 129, to which it was renumbered in 1944.
Vermont Route 78 (VT 78) is a 21.126-mile-long (33.999 km) east–west state highway in northwestern Vermont, United States. It begins at U.S. Route 2 (US 2) in Alburgh near the New York and Canada–US borders, and runs southeast to VT 105 in Sheldon. It is one of two routes connecting the Vermont mainland to the Grand Isle area of Lake Champlain, the other being US 2 north of Burlington.
Vermont Route 225 (VT 225) is a short 1.59-mile-long (2.56 km) state highway in Grand Isle County, Vermont, United States. It runs from U.S. Route 2 north of Alburgh and runs due north to the Canada–US border, where it becomes Quebec Route 225, from which it derives its number. The route is entirely within Alburgh in Grand Isle County. The entirety of VT 225 is maintained by the town of Alburgh.

The Montrealer was an overnight passenger train between Washington, D.C., United States, and Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The train was operated from 1924 to 1966, and again under Amtrak from 1972 to 1995, excepting two years in the 1980s. The train was discontinued in 1995 and replaced by the Vermonter, which provides daytime service as far north as St. Albans, Vermont. Current Amtrak service to Montreal is provided by the daytime Adirondack from New York City via Albany.

The Alburgh–Noyan Border Crossing connects the villages of Noyan, Quebec with Alburgh, Vermont on the Canada–US border. It is reached by Vermont Route 225 on the American side and by Quebec Route 225 on the Canadian side.
Alburg Dunes State Park is a state park in Alburgh, Vermont. The park lies on the shore of Lake Champlain and features one of the lake's largest beaches. It is named for the sand dunes near the center and western end of the south-facing natural sand beach.

The Rutland Railroad Pumping Station is a historic water pumping facility at 43 Lake Street in the town of Alburgh, Vermont. Built in 1903, it is a rare example in Vermont of an early railroad-related water pumping facility. In use until the 1940s, it provided water needed for steam engines at rail facilities elsewhere in Alburgh. It is now owned by the town, and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1999.

The Rouses Point Bridge carries U.S. Route 2 (US 2) across Lake Champlain at the point where the Richelieu River begins its trek north to the St. Lawrence Seaway. Also known as the Korean War Veterans Memorial Bridge, it connects Rouses Point, New York in the extreme northeast corner of New York to Alburgh, Vermont. It is the northernmost of three bridge crossings over the approximately 130 miles (210 km)-long Lake Champlain border between New York and Vermont.
References
- ↑ U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: East Alburg
- ↑ "New England Central Railroad (NECR)". RailAmerica. Retrieved July 15, 2011.