
Nova Scotia is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".

The Nova Scotia House of Assembly, or Legislative Assembly, is the deliberative assembly of the General Assembly of Nova Scotia of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada. The assembly is the oldest in Canada, having first sat in 1758, and in 1848 was the site of the first responsible government in the British Empire. Bills passed by the House of Assembly are given royal assent by the Lieutenant Governor of Nova Scotia in the name of the King.
The Executive Council of Nova Scotia is the cabinet of the Canadian province of Nova Scotia.

The lieutenant governor of Nova Scotia is the viceregal representative in Nova Scotia of the Canadian monarch, King Charles III, who operates distinctly within the province but is also shared equally with the ten other jurisdictions of Canada, as well as the other Commonwealth realms and any subdivisions thereof, and resides predominantly in his oldest realm, the United Kingdom. The lieutenant governor of Nova Scotia is appointed in the same manner as the other provincial viceroys in Canada and is similarly tasked with carrying out most of the monarch's constitutional and ceremonial duties. The present, and 33rd lieutenant governor of Nova Scotia is Arthur Joseph LeBlanc, who has served in the role since 28 June 2017.

Province House in Halifax is where the Nova Scotia legislative assembly, known officially as the Nova Scotia House of Assembly, has met every year since 1819, making it the longest serving legislative building in Canada. The building is Canada's oldest house of government. Standing three storeys tall, the structure is considered one of the finest examples of Palladian architecture in North America.
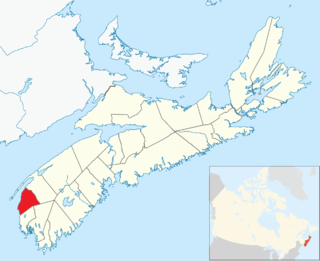
Clare, officially named the Municipality of the District of Clare, is a district municipality in western Nova Scotia, Canada. Statistics Canada classifies the district municipality as a municipal district.

Barrington, officially named the Municipality of the District of Barrington, is a district municipality in western Shelburne County, Nova Scotia, Canada. Statistics Canada classifies the district municipality as a municipal district.

The Diocese of Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island is a diocese of the Ecclesiastical Province of Canada of the Anglican Church of Canada. It encompasses the provinces of Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island and has two cathedrals: All Saints' in Halifax and St. Peter's in Charlottetown. Its de facto see city is Halifax, and its roughly 24 400 Anglicans distributed in 239 congregations are served by approximately 153 clergy and 330 lay readers according to the last available data. According to the 2001 census, 120,315 Nova Scotians identified themselves as Anglicans, while 6525 Prince Edward Islanders did the same.

Mulgrave is a town on the Strait of Canso in Guysborough County, Nova Scotia, Canada. Located along the Marine Drive, Route 344 traverses the community. The town's current name was adopted in 1859 to honour the colonial Lieutenant Governor, the Earl of Mulgrave. Lying opposite to the town of Port Hawkesbury, the community is located along the western shore of the Canso Strait. It was established as McNair's Cove in the early 19th century, and the name Port Mulgrave was adopted in 1859, later shortening to its current form. The early industry of the community relied on ferry service between the Nova Scotia mainland and Cape Breton Island. Ferry service began in the 1810s and rail service reached the area in the 1880s. The ferry services lasted until the opening of the Canso Causeway in 1955, dealing a major blow to the local economy. As of 2016, Mulgrave has a population of 722 and a population density of 40.5/km2 (104.9/sq mi), within an area of 17.83 km2 (6.88 sq mi).
Port Williams is a Canadian village in Kings County, Nova Scotia. It is located on the north bank of the Cornwallis River, named after Edward Cornwallis, first governor of Nova Scotia. As of 2021, the population was 1,110.

Route 333 is a collector road in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia.
Upper Tantallon is a suburban community that extends from the Hammonds Plains Road to the crossroads of Trunk 3 and Route 333 within the Halifax Regional Municipality of Nova Scotia Canada, 28.5 km (17.7 mi) west from Downtown Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada. The community is likely named for Tantallon Castle in Scotland.

Tiverton is a small village located on the northeast tip of Long Island, Nova Scotia. Tiverton has a population of about 300 people. It was named for Tiverton, Devon.

Black Nova Scotians are Black Canadians whose ancestors primarily date back to the Colonial United States as slaves or freemen, later arriving in Nova Scotia, Canada, during the 18th and early 19th centuries. As of the 2021 Census of Canada, 28,220 Black people live in Nova Scotia, most in Halifax. Since the 1950s, numerous Black Nova Scotians have migrated to Toronto for its larger range of opportunities. Before the immigration reforms of 1967, Black Nova Scotians formed 37% of the total Black Canadian population.

Apple River is a community in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia, located in Cumberland County.
Little Dover is a small community in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia, founded in 1860 and located in The Municipality of the District of Guysborough in Guysborough County.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Nova Scotia:
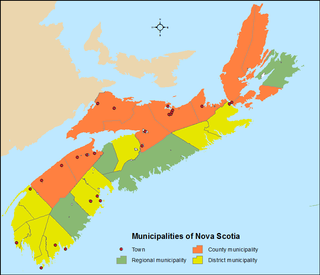
The Canadian province of Nova Scotia is divided into 49 municipalities, of which there are three types: regional (4), town (25), and county or district municipality (20).















