
The Territory of Ashmore and Cartier Islands is an uninhabited external territory of Australia consisting of four low-lying tropical islands in two separate reefs, and the 12-nautical-mile territorial sea generated by the islands. The territory is located in the Indian Ocean situated on the edge of the continental shelf, about 320 km (199 mi) off the northwest coast of Australia and 144 km (89 mi) south of the Indonesian island of Rote.
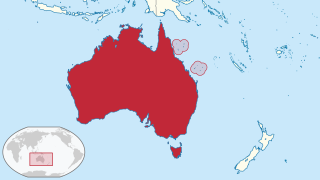
The Coral Sea Islands Territory is an external territory of Australia which comprises a group of small and mostly uninhabited tropical islands and reefs in the Coral Sea, northeast of Queensland, Australia. The only inhabited island is Willis Island. The territory covers 780,000 km2 (301,160 sq mi), most of which is ocean, extending east and south from the outer edge of the Great Barrier Reef and includes Heralds Beacon Island, Osprey Reef, the Willis Group and fifteen other reef/island groups. Cato Island is the highest point in the Territory.
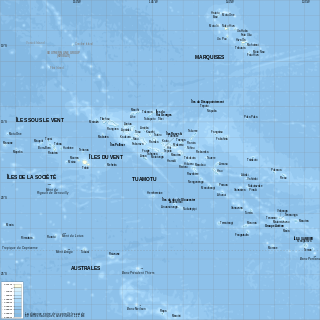
French Polynesia is located in Oceania. It is a group of six archipelagos in the South Pacific Ocean, about halfway between South America and Australia. Its area is about 4,167 km2, of which 3,827 km2 is land and 340 km2 is (inland) water. It has a coastline of 2,525 km but no land borders with other countries.

An atoll, sometimes known as a coral atoll, is a ring-shaped coral reef, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon partially or completely. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical oceans and seas where corals can grow. Most of the approximately 440 atolls in the world are in the Pacific Ocean.

Fiji is a group of volcanic islands in the South Pacific, lying about 4,450 kilometres (2,765 mi) southwest of Honolulu and 1,770 km (1,100 mi) north of New Zealand. Of the 332 islands and 522 smaller islets making up the archipelago, about 106 are permanently inhabited. The total land size is 18,272 km2 (7,055 sq mi). It has the 26th largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 1,282,978 km2 (495,361 sq mi).
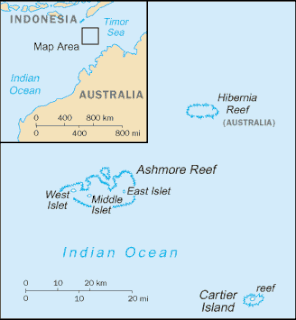
Cartier Island is an uninhabited and unvegetated sand cay in a platform reef in the Timor Sea north of Australia and south of Indonesia. It is within the Territory of Ashmore and Cartier Islands, an external territory of Australia. The land area of Cartier Island is about 0.4 hectares. It is located at 12°31′S123°33′E, on the edge of the Sahul Shelf, about 300 kilometres (190 mi) off the north west coast of Western Australia, 200 kilometres (120 mi) south of the Indonesian island of Roti, and 70 kilometres (43 mi) south-east of Ashmore Reef.

The states and territories are federated administrative divisions in Australia, ruled by regional governments that constitute the second level of governance between the federal government and local governments. States are self-governing polities with incomplete sovereignty and have their own constitutions, legislatures, departments, and certain civil authorities that administer and deliver most public policies and programmes. Territories can be autonomous and administer local policies and programmes much like the states in practice, but are still constitutionally and financially subordinate to the federal government and thus have no true sovereignty.

Scott and Seringapatam Reefs is a group of atoll-like reefs in the Timor Sea more than 300 kilometres (190 mi) northwest of Cape Leveque, Western Australia, on the edge of the continental shelf. There are three or four separate reef structures, depending on whether Scott Reef Central is counted separately.

The Chesterfield Islands are a French archipelago of New Caledonia located in the Coral Sea, 550 km (300 nmi) northwest of Grande Terre, the main island of New Caledonia. The archipelago is 120 km long and 70 km broad, made up of 11 uninhabited islets and many reefs. The land area of the islands is less than 10 km².
Ruxton Island is one of the six islands in the De Courcy Islands group. It is one of the southern Gulf Islands in British Columbia. It is due south-east of DeCourcy Island, being separated by Ruxton Passage.

The geography of Australia encompasses a wide variety of biogeographic regions being the world's smallest continent, while comprising the territory of the sixth-largest country in the world. The population of Australia is concentrated along the eastern and south-eastern coasts. The geography of the continent is extremely diverse, ranging from the snow-capped mountains of the Australian Alps and Tasmania to large deserts, tropical and temperate forests, grasslands, heathlands and woodlands.

Cato Reef, a part of Cato Bank, is an area in the Coral Sea off the central coast of Queensland, Australia.
The following outline is provided as an overview and topical guide to Oceania.
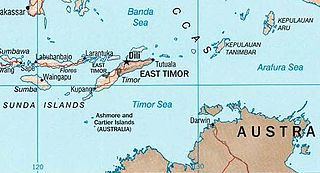
The MOU Box, or sometimes the MOU 74 Box, refers to a rectangular tract of marine waters in the Timor Sea, lying within Australia's Exclusive Economic Zone, that is subject to a 1974 memorandum of understanding (MoU), and subsequent agreements, between Australia and Indonesia. The MOU Box covers an area of about 50,000 km2 (19,000 sq mi) including Scott and Seringapatam Reefs, Browse Island, and Ashmore and Cartier Islands. Australia declared a marine protected area around Ashmore Island in 1983, and around Cartier Island in 2000.

Chinamans Hat Island is an islet located off the south coast of Yorke Peninsula in Investigator Strait in South Australia about 2.4 kilometres south-west of Stenhouse Bay and within 350 metres of the shore. As of 2014, it is located within the Innes National Park.
Aipysurus fuscus, commonly known as the dusky sea snake or Timor Reef snake, is a species of sea snake in the family Elapidae. It is found in the Timor Sea between Australia, Indonesia and East Timor and has been classified as endangered.
The Cartier Island Marine Park is an Australian marine park that covers the Cartier Island and reef surrounds, about 610 km (380 mi) north of Broome, Western Australia. The marine park covers an area of 172 km2 (66 sq mi) and is assigned IUCN category Ia. It is one of the 13 parks managed under the North-west Marine Parks Network.
The Ashmore Reef Marine Park is an Australian marine park that covers the Ashmore Reef, which is located about 630 km (390 mi) north of Broome and 110 km (68 mi) south of the Indonesian island of Rote. The marine park covers an area of 583 km2 (225 sq mi) and is assigned IUCN category Ia. It is one of 13 parks managed under the North-west Marine Parks Network.














