
A convergent boundary is an area on Earth where two or more lithospheric plates collide. One plate eventually slides beneath the other, a process known as subduction. The subduction zone can be defined by a plane where many earthquakes occur, called the Wadati–Benioff zone. These collisions happen on scales of millions to tens of millions of years and can lead to volcanism, earthquakes, orogenesis, destruction of lithosphere, and deformation. Convergent boundaries occur between oceanic-oceanic lithosphere, oceanic-continental lithosphere, and continental-continental lithosphere. The geologic features related to convergent boundaries vary depending on crust types.

Island arcs are long chains of active volcanoes with intense seismic activity found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the mantle along the subduction zone. They are the principal way by which continental growth is achieved.

The Philippine Sea Plate or the Philippine Plate is a tectonic plate comprising oceanic lithosphere that lies beneath the Philippine Sea, to the east of the Philippines. Most segments of the Philippines, including northern Luzon, are part of the Philippine Mobile Belt, which is geologically and tectonically separate from the Philippine Sea Plate.
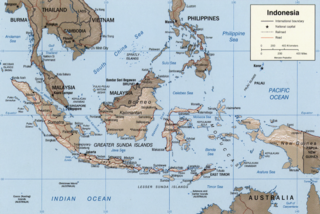
The Sunda Arc is a volcanic arc that produced the volcanoes that form the topographic spine of the islands of Sumatra, Nusa Tenggara, and Java, the Sunda Strait and the Lesser Sunda Islands. The Sunda Arc begins at Sumatra and ends at Flores, and is adjacent to the Banda Arc. The Sunda Arc is formed via the subduction of the Indo-Australian Plate beneath the Sunda and Burma plates at a velocity of 63–70 mm/year.
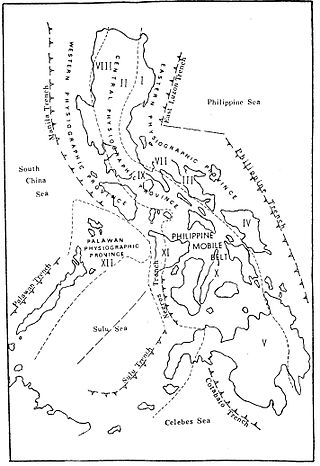
The Manila Trench is an oceanic trench in the Pacific Ocean, located west of the islands of Luzon and Mindoro in the Philippines. The trench reaches a depth of about 5,400 metres (17,700 ft), in contrast with the average depth of the South China Sea of about 1,500 metres (4,900 ft). It is created by subduction, in which the Sunda Plate is subducting under the Philippine Mobile Belt, producing this almost N-S trending trench. The convergent boundary is terminated to the north by the Taiwan collision zone, and to the south by the Mindoro terrane. It is an area pervaded by negative gravity anomalies.

The Philippine Trench is a submarine trench to the east of the Philippines. The trench is located in the Philippine sea of the western North Pacific Ocean and continues NNW-SSE. It has a length of approximately 1,320 kilometres and a width of about 30 km (19 mi) from the center of the Philippine island of Luzon trending southeast to the northern Maluku island of Halmahera in Indonesia. At its deepest point, the trench reaches 10,540 meters.

A back-arc basin is a type of geologic basin, found at some convergent plate boundaries. Presently all back-arc basins are submarine features associated with island arcs and subduction zones, with many found in the western Pacific Ocean. Most of them result from tensional forces, caused by a process known as oceanic trench rollback, where a subduction zone moves towards the subducting plate. Back-arc basins were initially an unexpected phenomenon in plate tectonics, as convergent boundaries were expected to universally be zones of compression. However, in 1970, Dan Karig published a model of back-arc basins consistent with plate tectonics.

The Izu–Bonin–Mariana (IBM) arc system is a tectonic plate convergent boundary in Micronesia. The IBM arc system extends over 2800 km south from Tokyo, Japan, to beyond Guam, and includes the Izu Islands, the Bonin Islands, and the Mariana Islands; much more of the IBM arc system is submerged below sealevel. The IBM arc system lies along the eastern margin of the Philippine Sea Plate in the Western Pacific Ocean. It is the site of the deepest gash in Earth's solid surface, the Challenger Deep in the Mariana Trench.

The Mariana Trough is an active back-arc basin in the western Pacific Ocean. It is an integral part of the Izu–Bonin–Mariana Arc system.
The Solomon Sea Plate is a minor tectonic plate to the northwest of the Solomon Islands archipelago in the south Pacific Ocean. It roughly corresponds with the Solomon Sea east of Papua New Guinea. The plate boundaries are associated with high earthquake activity as part of the New Britain subduction zone.

The Caroline Plate is a minor tectonic plate that straddles the Equator in the eastern hemisphere located north of New Guinea. It forms a subduction zone along the border with the Bird's Head Plate and other minor plates of the New Guinea region to the south. A transform boundary forms the northern border with the Pacific Plate. Along the border with the Philippine Sea Plate is a convergent boundary that transitions into a rift.

The Mariana Plate is a micro tectonic plate located west of the Mariana Trench which forms the basement of the Mariana Islands which form part of the Izu–Bonin–Mariana Arc. It is separated from the Philippine Sea Plate to the west by a divergent boundary with numerous transform fault offsets. The boundary between the Mariana and the Pacific Plate to the east is a subduction zone with the Pacific Plate subducting beneath the Mariana. This eastern subduction is divided into the Mariana Trench, which forms the southeastern boundary, and the Izu–Ogasawara Trench the northeastern boundary. The subduction plate motion is responsible for the shape of the Mariana plate and back arc.

In the geology of the Philippines, the Philippine Mobile Belt is a complex portion of the tectonic boundary between the Eurasian Plate and the Philippine Sea Plate, comprising most of the country of the Philippines. It includes two subduction zones, the Manila Trench to the west and the Philippine Trench to the east, as well as the Philippine Fault System. Within the Belt, a number of crustal blocks or microplates which have been shorn off the adjoining major plates are undergoing massive deformation.

The Luzon Volcanic Arc is a chain of volcanoes in a north–south line across the Luzon Strait from Taiwan to Luzon. The name "Luzon Volcanic Arc" was first proposed by Carl Bowin et al. to describe a series of Miocene to recent volcanoes due to eastward subduction along the Manila Trench for approximately 1,200 km from the Coastal Range in Taiwan south to southern Mindoro in the Philippines. Islands that form part of the arc are the Eastern Coastal Range of Taiwan, Green Island, Taiwan, Orchid Island, Kaotai Rock, Mavudis or Y'ami Island, Mabudis, Siayan Island, Itbayat Island, Diogo Island, Batan Island, Unnamed volcano Ibuhos, Sabtang Island, Babuyan, Didicas, Camiguin Island. At the south end it terminates on Luzon. The geochemistry of a number of volcanoes along the arc have been measured. There are five distinct geochemical domains within the arc. The geochemistry of the segments verified that the volcanoes are all subduction related. Isotopes and trace elements show unique geochemical characteristics in the north. Geochemical variations northward were due to the subduction of sediments derived from the erosion of continental crust from China and Taiwan.

The West Melanesian Trench is an oceanic trench in the Bismarck Sea north of Papua New Guinea delineating the plate tectonic boundary between the Caroline and North Bismarck plates.

Subduction polarity reversal is a geologic process in which two converging plates switch roles: The over-lying plate becomes the down-going plate, and vice versa. There are two basic units which make up a subduction zone. This consists of an overriding plate and the subduction plate. Two plates move towards each other due to tectonic forces. The overriding plate will be on the top of the subducting plate. This type of tectonic interaction is found at many plate boundaries.

The subduction tectonics of the Philippines is the control of geology over the Philippine archipelago. The Philippine region is seismically active and has been progressively constructed by plates converging towards each other in multiple directions. The region is also known as the Philippine Mobile Belt due to its complex tectonic setting.

Oblique subduction is a form of subduction for which the convergence direction differs from 90° to the plate boundary. Most convergent boundaries involve oblique subduction, particularly in the Ring of Fire including the Ryukyu, Aleutian, Central America and Chile subduction zones. In general, the obliquity angle is between 15° and 30°. Subduction zones with high obliquity angles include Sunda trench and Ryukyu arc.
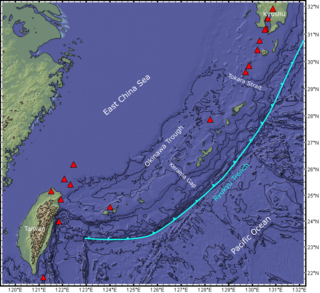
The Ryukyu Arc is an island arc which extends from the south of Kyushu along the Ryukyu Islands to the northeast of Taiwan, spanning about 1,200 kilometres (750 mi). It is located along a section of the convergent plate boundary where the Philippine Sea Plate is subducting northwestward beneath the Eurasian Plate along the Ryukyu Trench. The arc has an overall northeast to southwest trend and is located northwest of the Pacific Ocean and southeast of the East China Sea. It runs parallel to the Okinawa Trough, an active volcanic arc, and the Ryukyu Trench. The Ryukyu Arc, based on its geomorphology, can be segmented from north to south into Northern Ryukyu, Central Ryukyu, and Southern Ryukyu; the Tokara Strait separates Northern Ryukyu and Central Ryukyu at about 130˚E while the Kerama Gap separates Central Ryukyu and Southern Ryukyu at about 127 ˚E. The geological units of the arc include igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, ranging from the Paleozoic to Cenozoic in age.


















