
Maiden Castle is an Iron Age hillfort 1.6 mi (2.6 km) southwest of Dorchester, in the English county of Dorset. Hill forts were fortified hill-top settlements constructed across Britain during the Iron Age.
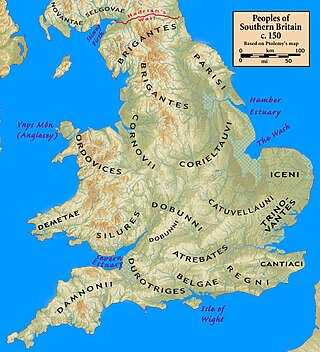
The Durotriges were one of the Celtic tribes living in Britain prior to the Roman invasion. The tribe lived in modern Dorset, south Wiltshire, south Somerset and Devon east of the River Axe and the discovery of an Iron Age hoard in 2009 at Shalfleet, Isle of Wight gives evidence that they may also have lived in the western half of the island. After the Roman conquest, their main civitates, or settlement-centred administrative units, were Durnovaria and Lindinis. Their territory was bordered to the west by the Dumnonii; and to the east by the Belgae.
Combe Hill is a causewayed enclosure, near Eastbourne in East Sussex, on the northern edge of the South Downs. It consists of an inner circuit of ditches and banks, incomplete where it meets a steep slope on its north side, and the remains of an outer circuit. Causewayed enclosures were built in England from shortly before 3700 BC until at least 3500 BC; they are characterized by the full or partial enclosure of an area with ditches that are interrupted by gaps, or causeways. Their purpose is not known; they may have been settlements, meeting places, or ritual sites. The historian Hadrian Allcroft included the site in his 1908 book Earthwork of England, and in 1930 E. Cecil Curwen listed it as a possible Neolithic site in a paper which attempted to provide the first list of all the causewayed enclosures in England.

Badbury Rings is an Iron Age hill fort and Scheduled Monument in east Dorset, England. It was in the territory of the Durotriges. In the Roman era a temple was located immediately west of the fort, and there was a Romano-British town known as Vindocladia a short distance to the south-west.

Yarnbury Castle is the site of a multiphase, multivallate Iron Age hillfort near the village of Steeple Langford, Wiltshire, England. The site covers an area of 28.5 acres (11.5 ha), and was extensively surveyed and investigated by the Royal Commission on the Historical Monuments of England in 1991, with finds of Iron Age and Romano-British pottery, Iron Age and Roman coins, and burials of human remains. There is much evidence of prolonged and extensive settlement of the site, including evidence of around 130 structures of various sizes, most probably representing a mix of round houses, pits, and other features. It was designated as a scheduled monument in 1925.

Vespasian's Camp is an Iron Age hillfort just west of the town of Amesbury, Wiltshire, England. The hillfort is less than 3 kilometres (2 mi) from the Neolithic and Bronze Age site of Stonehenge, and was built on a hill next to the Stonehenge Avenue; it has the River Avon on its southern side and the A303 road on its northern edge. The site is a scheduled monument and lies within the boundaries of the Stonehenge World Heritage Site.

Ringsbury Camp is an Iron Age hill fort, thought to date from approximately the year 50BC, in the civil parish of Purton in Wiltshire, England. The site is a scheduled monument.

Grovely Wood is one of the largest woodlands in southern Wiltshire, England. It stands on a chalk ridge above the River Wylye in Barford St Martin parish, to the south-west of the village of Great Wishford, within the Cranborne Chase and West Wiltshire Downs Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. It is recognised for its nature conservation importance through designation as a County Wildlife Site. Among the species found here is the Purple Emperor butterfly.

Ladle Hill is a 10.5-hectare (26-acre) biological Site of Special Scientific Interest west of Kingsclere in Hampshire. It is also a Scheduled Monument.

Scratchbury Camp is the site of an Iron Age univallate hillfort on Scratchbury Hill, overlooking the Wylye valley about 1 km northeast of the village of Norton Bavant in Wiltshire, England. The fort covers an area of 37 acres (15 ha) and occupies the summit of the hill on the edge of Salisbury Plain, with its four-sided shape largely following the natural contours of the hill.

Cholesbury Camp is a large and well-preserved Iron Age hill fort on the northern edge of the village of Cholesbury in Buckinghamshire, England. It is roughly oval-shaped and covers an area, including ramparts, of 15 acres (6.1 ha), and measures approximately 310 m (1,020 ft) north-east to south-west by 230 m (750 ft) north-west to south-east. The interior is a fairly level plateau which has been in agricultural use since the medieval period. The hill fort is now a scheduled ancient monument.

Grovely Castle is the site of an Iron Age univallate hill fort in the parish of Steeple Langford, in Wiltshire, England. The remaining ramparts stand approximately 3.2 m (10 ft) high, with 1.5 m (4.9 ft) deep ditches, although ploughing has damaged the earthworks in some parts of the site. Excavations have uncovered the remains of five human skeletons within the ramparts. Entrances are in the south-west and north-east corners of the hillfort. A circular enclosure of 35 to 40 m is evident in aerial photographs of the hillfort interior. There is also a later bank and ditch which runs through the hill-fort from south-west to north-east, and is probably part of an extensive surrounding Celtic field system.

Knook Castle is the site of an Iron Age univallate hillfort on Knook Down, near the village of Knook in Wiltshire, England, but largely within the civil parish of Upton Lovell. It has also been interpreted as a defensive cattle enclosure associated with nearby Romano-British settlements. It is roughly rectangular in plan with a single entrance on the south/south-east side, but with a later break in the wall on the western side. The site is a scheduled monument.

Castle Rings is a univallate hill fort in the parish of Donhead St Mary in Wiltshire, England. The site is a Scheduled Ancient Monument. Castle Rings has been dated to the Iron Age and is at an altitude of 228 metres (748 ft) upon Upper Greensand sandstone beds. The bulk of the fort enclosure lies within the boundaries of Donhead St Mary parish but some of the outlying earthworks are in the neighbouring Sedgehill and Semley parish. In the mid-1980s a metal detectorist unearthed a hoard of stater coins of the Durotriges tribe within the hill fort.

The Knock of Alves is a small wooded hill that lies 3 miles (4.8 km) to the west of Elgin in Moray, Scotland, rising to 335 feet (102 m) above ordnance datum. Its summit is marked by York Tower, a 3-storey octagonal folly erected in 1827 to commemorate Prince Frederick, the Duke of York; and the Forteath Mausoleum, built in 1850 as the burial place of 7 members of the Forteath family of the nearby house of Newton.

King John's Hill is the site of an Iron Age hillfort located in Hampshire, in southeast England. The hill is situated in the parish of Worldham, in East Hampshire District. It is a Scheduled Ancient Monument with a list entry identification number of 1020314, and a Monument Number of 243207.

Hollingbury Castle, also known as Hollingbury Camp and Hollingbury Hillfort, is an Iron Age hillfort on the northern edge of Brighton, in East Sussex, England. It is adjacent to Hollingbury Park Golf Course.

Margidunum was a Roman settlement on the Fosse Way at Castle Hill near present-day Bingham, in Nottinghamshire, England. The site is a protected Scheduled Monument.

Thundersbarrow Hill is an archaeological site in West Sussex, England. It is on a chalk ridge, aligned north-west to south-east, on the South Downs north of Shoreham-by-Sea.

Woodcutts Settlement is an archaeological site of the late Iron Age and Romano-British period on Cranborne Chase, England. It is situated about 1 mile (1.6 km) north of the hamlet of Woodcutts, and about 1.75 miles (2.8 km) north-west of the village of Sixpenny Handley, in Dorset, near the boundary with Wiltshire. It is a scheduled monument.




















