Related Research Articles

A spermatozoon is a motile sperm cell produced by male animals relying on internal fertilization. A spermatozoon is a moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete that joins with an ovum to form a zygote.

Fertilisation or fertilization, also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a zygote and initiate its development into a new individual organism or offspring. While processes such as insemination or pollination, which happen before the fusion of gametes, are also sometimes informally referred to as fertilisation, these are technically separate processes. The cycle of fertilisation and development of new individuals is called sexual reproduction. During double fertilisation in angiosperms, the haploid male gamete combines with two haploid polar nuclei to form a triploid primary endosperm nucleus by the process of vegetative fertilisation.

For fertilization to happen between a sperm and egg cell, a sperm must first fuse with the plasma membrane and then penetrate the female egg cell to fertilize it. While the fusion of the sperm cell with the egg cell's plasma membrane is relatively straightforward, penetrating the egg's protective layers, such as the zona pellucida, presents a significant challenge. Therefore, sperm cells go through a process known as the acrosome reaction, which is the reaction that occurs in the acrosome of the sperm as it approaches the egg.

Karyogamy is the final step in the process of fusing together two haploid eukaryotic cells, and refers specifically to the fusion of the two nuclei. Before karyogamy, each haploid cell has one complete copy of the organism's genome. In order for karyogamy to occur, the cell membrane and cytoplasm of each cell must fuse with the other in a process known as plasmogamy. Once within the joined cell membrane, the nuclei are referred to as pronuclei. Once the cell membranes, cytoplasm, and pronuclei fuse, the resulting single cell is diploid, containing two copies of the genome. This diploid cell, called a zygote or zygospore can then enter meiosis, or continue to divide by mitosis. Mammalian fertilization uses a comparable process to combine haploid sperm and egg cells (gametes) to create a diploid fertilized egg.

Ascidiacea, commonly known as the ascidians or sea squirts, is a paraphyletic class in the subphylum Tunicata of sac-like marine invertebrate filter feeders. Ascidians are characterized by a tough outer "tunic" made of a polysaccharide.

The zona pellucida is the specialized area surrounding mammalian oocytes (eggs). It is also known as an egg coat. The zona pellucida is essential for oocyte growth and fertilization.
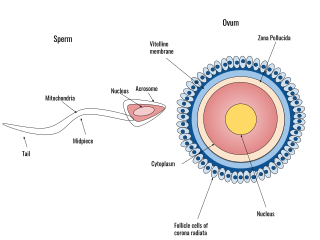
Human fertilization is the union of an egg and sperm, occurring primarily in the ampulla of the fallopian tube. The result of this union leads to the production of a fertilized egg called a zygote, initiating embryonic development. Scientists discovered the dynamics of human fertilization in the 19th century.
In biology, polyspermy describes the fertilization of an egg by more than one sperm. Diploid organisms normally contain two copies of each chromosome, one from each parent. The cell resulting from polyspermy, on the other hand, contains three or more copies of each chromosome—one from the egg and one each from multiple sperm. Usually, the result is an unviable zygote. This may occur because sperm are too efficient at reaching and fertilizing eggs due to the selective pressures of sperm competition. Such a situation is often deleterious to the female: in other words, the male–male competition among sperm spills over to create sexual conflict.

The cortical reaction is a process initiated during fertilization that prevents polyspermy, the fusion of multiple sperm with one egg. In contrast to the fast block of polyspermy which immediately but temporarily blocks additional sperm from fertilizing the egg, the cortical reaction gradually establishes a permanent barrier to sperm entry and functions as the main part of the slow block of polyspermy in many animals.
Hyalin is a protein released from the cortical granules of a fertilized animal egg. The released hyalin modifies the extracellular matrix of the fertilized egg to block other sperm from binding to the egg, and is known as the slow-block to polyspermy. All animals have this slow-block mechanism.
The vitelline membrane or vitelline envelope is a structure surrounding the outer surface of the plasma membrane of an ovum or, in some animals, the extracellular yolk and the oolemma. It is composed mostly of protein fibers, with protein receptors needed for sperm binding which, in turn, are bound to sperm plasma membrane receptors. The species-specificity between these receptors contributes to prevention of breeding between different species. It is called zona pellucida in mammals. Between the vitelline membrane and the oolemma is a fluid-filled perivitelline space.
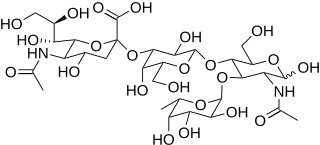
Sialyl LewisX (sLeX), also known as cluster of differentiation 15s (CD15s) or stage-specific embryonic antigen 1 (SSEA-1), is a tetrasaccharide carbohydrate which is usually attached to O-glycans on the surface of cells. It is known to play a vital role in cell-to-cell recognition processes. It is also the means by which an egg attracts sperm; first, to stick to it, then bond with it and eventually form a zygote.
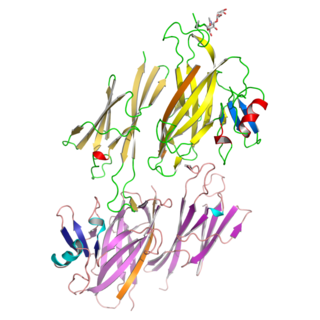
Zona pellucida sperm-binding protein 3, also known as zona pellucida glycoprotein 3 (Zp-3) or the sperm receptor, is a ZP module-containing protein that in humans is encoded by the ZP3 gene. ZP3 is the glycoprotein in the zona pellucida most important for inducting the acrosome reaction of sperm cells at the beginning of fertilization.

Zona pellucida sperm-binding protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZP2 gene.
Vitellin is a protein found in the egg yolk. It is a phosphoprotein. Vitellin is a generic name for major of many yolk proteins.
Sperm chemotaxis is a form of sperm guidance, in which sperm cells (spermatozoa) follow a concentration gradient of a chemoattractant secreted from the oocyte and thereby reach the oocyte.
The zona pellucida-like domain is a large protein region of about 260 amino acids. It has been recognised in a variety of receptor-like eukaryotic glycoproteins. All of these molecules are mosaic proteins with a large extracellular region composed of various domains, often followed by either a transmembrane domain and a short cytoplasmic region or by a GPI-anchor.
Oocyteactivation is a series of processes that occur in the oocyte during fertilization.

Juno also known as folate receptor 4, folate receptor delta or IZUMO1R is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOLR4 gene. Juno is a member of the folate receptor family and is GPI-anchored to the plasmalemma of the mammalian egg cell that recognizes its sperm-riding counterpart, IZUMO1, and facilitates fertilization. The protein was named after Juno, the Roman goddess of fertility and marriage.
Egg jelly is a gelatinous layer that surrounds the oocytes of many organisms and releases species-specific chemoattractants that activate and guide sperm to the oocyte. The release of chemoattractants is species dependent. For example, sperm in Lytechinus variegatus, the green sea urchin, are not chemotactically attracted to the jelly or the egg. The egg jelly is located immediately surrounding the vitelline envelope and consists primarily of a network of short peptides and sulfated fucan glycoproteins. These short peptides diffuse into the surrounding area and stimulate respiration and movement of the sperm to the egg. An example of such a peptide is resact, which has been studied as the primary means of attracting and orientating sperm to the eggs in sea urchins. The sulfated fucan glycoproteins play an important role in binding to sperm receptors and triggering the acrosomal reaction.
References
- ↑ Stout CD, Vacquier VD, Kresge N (2000). "1.35 and 2.07 A resolution structures of the red abalone sperm lysin monomer and dimer reveal features involved in receptor binding". Acta Crystallogr. D. 56 (Pt 1): 34–41. doi:10.1107/s0907444999014626. PMID 10666624.
- ↑ Stout CD, Vacquier VD, Kresge N (2000). "The high resolution crystal structure of green abalone sperm lysin: implications for species-specific binding of the egg receptor". J. Mol. Biol. 296 (5): 1225–1234. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2000.3533. PMID 10698629.
- ↑ Stout CD, Vacquier VD, Kresge N (2001). "The crystal structure of a fusagenic sperm protein reveals extreme surface properties". Biochemistry. 40 (18): 5407–5413. doi:10.1021/bi002779v. PMID 11331004.
- ↑ Raj I, Sadat Al Hosseini H, Dioguardi E, Nishimura K, Han L, Villa A, de Sanctis D, Jovine L (2017). "Structural Basis of Egg Coat-Sperm Recognition at Fertilization". Cell. 169 (7): 1315–1326. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.033. PMC 5480393 . PMID 28622512. PDB: 5MR3, 5IIA, 5IIB