
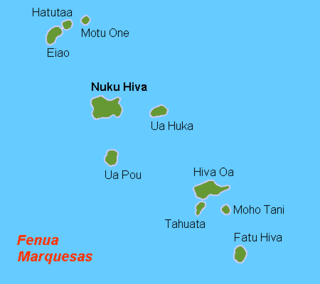
The Marquesas Islands are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in the southern Pacific Ocean. Their highest point is the peak of Mount Oave on Ua Pou island, at 1,230 m (4,035 ft) above sea level.
Marquesan is a collection of East-Central Polynesian dialects, of the Marquesic group, spoken in the Marquesas Islands of French Polynesia. They are usually classified into two groups, North Marquesan and South Marquesan, roughly along geographic lines.

Motu One is the name of a small sandbank with no vegetation, located on the western edge of a coral reef; the only atoll in the Marquesas Islands.

Hatutu is a small island approximately 3 km (2 mi.) northeast of Eiao in the northern Marquesas Islands. It is approximately 3 km from Eiao by a channel 50 meters deep. It was also known by the names Hancock, Chanal, Langdon, and Nexsen

Eiao is the largest of the extreme northwestern Marquesas Islands. The island is uninhabited, but is administratively part of the commune (municipality) of Nuku-Hiva, itself in the administrative subdivision of the Marquesas Islands.
The Motu One Reserve is a nature reserve encompassing the whole of the island and reef system of Motu One in the northern Marquesas Islands. The reserve was declared in 1992 in combination with several other reserves were declared as a part of the Marquesan Nature Reserves. This includes the Hatutu Nature Reserve, the Motane Nature Reserve, and the Eiao Island Nature Reserve.
The Marquesan Nature Reserves are a network of small nature reserves in the Marquesas Islands. The reserves were declared by the government of French Polynesia in 1992, as a first step toward preserving the native flora and fauna of some of the smaller islands of the group.
The Motane One Reserve is a nature reserve containing the whole of the islands of Moho Tani and Terihi, as well as the surrounding rocks, in the southern Marquesas Islands. It was declared in 1992, as the first step toward protecting the ecosystem, much of which, on Moho Tani, has been destroyed by over-grazing by feral sheep, pigs and goats. Terihi and the smaller rocks are home to large seabird rookeries. The island and its ecological disaster is mentioned by Thor Heyerdahl in his book Green Was the Earth on the Seventh Day.
The Hatutu Nature Reserve is a nature reserve encompassing the whole of the island of Hatutu in the northern Marquesas Islands. The reserve was declared in 1971, and is the primary nesting site of several endangered species, several of which are endemic, including the Hatutu Marquesan warbler and the Marquesas ground dove. The Hatutu Nature Reserve is home to one of the most important nesting grounds for the blue-footed booby.
The Hatutu Marquesan warbler, also called the Hatutu Polynesian warbler or the long-billed Polynesian warbler, is a subspecies of the northern Marquesan reed warbler. The subspecies is endemic to the island of Hatutu, and one of the primary breeding species in the Hatutu Nature Reserve.
The Eiao Marquesan warbler is a subspecies of the northern Marquesan reed warbler found only in the dry upland forest on Eiao in the northern Marquesas Islands.

Vaituha is a small valley in northwestern Eiao in which a small watersource empties into a small bay of the same name. This bay is one of two reliable anchorages on Eiao. The depth of the bay is 27 meters.

Ua Huka is one of the Marquesas Islands, in French Polynesia, an overseas territory of France in the Pacific Ocean. It is situated in the northern group of the archipelago, approximately 25 mi (40 km) to the east of Nuku Hiva, at 8°54′S139°33′W.
Mangareva, Mangarevan is a Polynesian language spoken by about 600 people in the Gambier Islands of French Polynesia and by Mangarevians emigrants on the islands of Tahiti and Moorea, located 1,650 kilometres (1,030 mi) to the North-West of the Gambier Islands.
The Eiao monarch is an extinct species of bird in the family Monarchidae. The species is sometimes considered to have been conspecific with the Iphis monarch. It was endemic to French Polynesia. Its natural habitats were subtropical or tropical dry forests, subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, and subtropical or tropical moist shrubland.

Pomarea is a genus of birds in the monarch flycatcher family Monarchidae. The genus is restricted to the islands of Polynesia. The monarchs of this genus are around 15–19 cm long and most have sexually dimorphic plumage.
The Iphis monarch, or Ua Huka flycatcher, is a species of bird in the family Monarchidae. It is endemic to French Polynesia. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forests, subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, subtropical or tropical moist shrubland, and plantations.

This page list topics related to French Polynesia.








