
Lessoniaceae are a family of kelp. Species of this family have transition zone with intercalary meristem subdivided so that there are a number of secondary stipes in addition to the primary stipe.

Arame, sea oak is a species of kelp, of the brown algae, best known for its use in Japanese cuisine.

Carl Ernst Otto Kuntze was a German botanist.

Brongniartella is a genus of red alga, named after French naturalist Adolphe Brongniart.
Charles Baron Clarke was a British botanist. He was born at Andover, the eldest son of Turner Poulter Clarke. He was educated at King's College School, London, and at Trinity and Queens' Colleges, Cambridge. He began the study of law at Lincoln's Inn in 1856 and was called to the bar in 1860. He lectured in mathematics at Presidency College, Calcutta, from 1857 to 1865. Clarke was Inspector of Schools in Eastern Bengal and later of India, and superintendent of the Calcutta Botanical Garden from 1869 to 1871. He retired from the Indian Civil Service in 1887. He was president of the Linnean Society from 1894 to 1896, and was elected a fellow of the Royal Society in 1882. He worked at Royal Botanic Gardens Kew until his death in 1906.

Paul Friedrich August Ascherson was a German botanist. His author citation is Asch., although Aschers. has been used in the past.

Adolphia is a genus of shrubs in the buckthorn family containing only two species.

Johan Erhard Areschoug was a Swedish botanist who was a native of Göteborg. He was a member of the Arreskow family. His first name is sometimes recorded as "John".
Ludwig Benjamin (1825–48) was a German botanist who contributed to Carl Friedrich Philipp von Martius' Flora Brasiliensis. The genus Benjaminia is named in his honour.

Ecklonia is a genus of kelp belonging to the family Lessoniaceae.
Chicita Frances Culberson is an American lichenologist.
Duboscquella is a genus of dinoflagellates.
Arthur Francis George Kerr (1877–1942) was an Irish medical doctor. He is known particularly now for his botanical work, which was important for the study of the flora of Thailand.
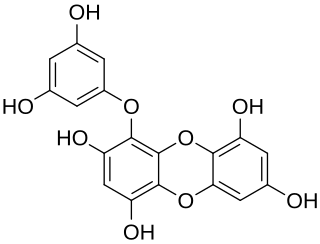
Eckol is a phlorotannin isolated from brown algae in the family Lessoniaceae such as species in the genus Ecklonia such as E. cava or E. kurome or in the genus Eisenia such as Eisenia bicyclis.
Burgella is a genus of fungi in the family Clavulinaceae. The genus is monotypic, containing the single species Burgella flavoparmeliae, described in 2007.
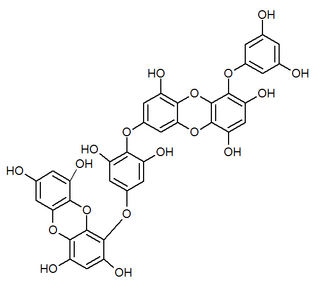
Dieckol is a phlorotannin that can be found in arame, in Ecklonia cava or in Ecklonia stolonifera.

Fucosterol is a sterol isolated from algae such as Ecklonia cava or Ecklonia stolonifera.

William Louis "Bill" Culberson was an American lichenologist.
Georg Carl Wilhelm Vatke was a German botanist who collected spermatophytes during 1868–1876 in Austria, Germany, Madagascar and Angola. He was an assistant at the botanical gardens in Berlin during 1876–1879, and later became a private scholar.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.












