A video codec is software or hardware that compresses and decompresses digital video. In the context of video compression, codec is a portmanteau of encoder and decoder, while a device that only compresses is typically called an encoder, and one that only decompresses is a decoder.
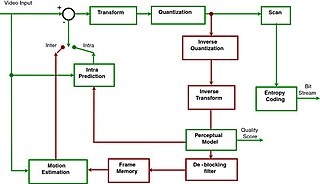
Advanced Video Coding (AVC), also referred to as H.264 or MPEG-4 Part 10, Advanced Video Coding, is a video compression standard based on block-oriented, motion-compensated coding. It is by far the most commonly used format for the recording, compression, and distribution of video content, used by 91% of video industry developers as of September 2019. It supports resolutions up to and including 8K UHD.
Nero Digital is a brand name applied to a suite of MPEG-4-compatible video and audio compression codecs developed by Nero AG of Germany and Ateme of France. The audio codecs are integrated into the Nero Digital Audio+ audio encoding tool for Microsoft Windows, and the audio & video codecs are integrated into Nero's Recode DVD ripping software.
SMPTE 421, informally known as VC-1, is a video coding format. Most of it was initially developed as Microsoft's proprietary video format Windows Media Video 9 in 2003. With some enhancements including the development of a new Advanced Profile, it was officially approved as a SMPTE standard on April 3, 2006. It was primarily marketed as a lower-complexity competitor to the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC standard. After its development, several companies other than Microsoft asserted that they held patents that applied to the technology, including Panasonic, LG Electronics and Samsung Electronics.
x264 is a free and open-source software library and a command-line utility developed by VideoLAN for encoding video streams into the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC video coding format. It is released under the terms of the GNU General Public License.
MPEG-4 Part 2, MPEG-4 Visual is a video compression format developed by the Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG). It belongs to the MPEG-4 ISO/IEC standards. It is uses block-wise motion compensation and a discrete cosine transform (DCT), similar to previous standards such as MPEG-1 Part 2 and H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2.
Α video codec is software or a device that provides encoding and decoding for digital video, and which may or may not include the use of video compression and/or decompression. Most codecs are typically implementations of video coding formats.
The following is a list of H.264/MPEG-4 AVC products and implementations.
H.264 and VC-1 are popular video compression standards gaining use in the industry as of 2007.
AVC-Intra is a type of video coding developed by Panasonic, and then supported in products made by other companies. AVC-Intra is available in Panasonic's high definition broadcast products, such as, for example, their P2 card equipped broadcast cameras.

VP8 is an open and royalty-free video compression format created by On2 Technologies as a successor to VP7 and owned by Google from 2010.
High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is a video compression standard designed as part of the MPEG-H project as a successor to the widely used Advanced Video Coding. In comparison to AVC, HEVC offers from 25% to 50% better data compression at the same level of video quality, or substantially improved video quality at the same bit rate. It supports resolutions up to 8192×4320, including 8K UHD, and unlike the primarily 8-bit AVC, HEVC's higher fidelity Main 10 profile has been incorporated into nearly all supporting hardware.
MainConcept GmbH is a software company founded in Germany by Markus Moenig and Thomas Zabel. They specialize in developing video/audio codecs and also applications and plug-ins related to video/audio encoding. They are a subsidiary of Endeavor Streaming, with employees in Germany, Russia, United States and Japan.
Sorenson Media was an American software company specializing in video encoding technology. Established in December 1995 as Sorenson Vision, the company developed technology which was licensed and ultimately acquired from Utah State University. The company first announced its codec at a developer’s preview at MacWorld Expo in January 1997.
A video coding format is a content representation format for storage or transmission of digital video content. It typically uses a standardized video compression algorithm, most commonly based on discrete cosine transform (DCT) coding and motion compensation. Examples of video coding formats include H.262, MPEG-4 Part 2, H.264, HEVC (H.265), Theora, RealVideo RV40, VP9, and AV1. A specific software or hardware implementation capable of compression or decompression to/from a specific video coding format is called a video codec; an example of a video codec is Xvid, which is one of several different codecs which implements encoding and decoding videos in the MPEG-4 Part 2 video coding format in software.

Thomson Video Networks (TVN) was a technology broadcast company that used to provide video compression, transcoding and processing solutions for media companies, video service providers, and TV broadcasters. The firm has offices in 16 countries and headquarters in Rennes, France. TVN has been acquired by Harmonic Inc. in 2016.
Versatile Video Coding (VVC), also known as H.266, ISO/IEC 23090-3, and MPEG-I Part 3, is a video compression standard finalized on 6 July 2020, by the Joint Video Experts Team (JVET), a joint video expert team of the VCEG working group of ITU-T Study Group 16 and the MPEG working group of ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 29. It is the successor to High Efficiency Video Coding. It was developed with two primary goals – improved compression performance and support for a very broad range of applications.

Low Complexity Enhancement Video Coding (LCEVC) is a ISO/IEC video coding standard developed by the Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) under the project name MPEG-5 Part 2 LCEVC.




