Related Research Articles

Electorates of the Australian House of Representatives are single member electoral districts for the lower house of the Parliament of the Commonwealth. There are currently 151 electorates.

The Parliament of Tasmania is the bicameral legislature of the Australian state of Tasmania. It follows a Westminster-derived parliamentary system and consists of the governor of Tasmania, the Legislative Council, and the House of Assembly. Since 1841, the Legislative Council has met in Parliament House, Hobart, with the House of Assembly following suit from its establishment in 1856. The Parliament of Tasmania first met in 1856.
The Division of Braddon is an Australian electoral division in the state of Tasmania. The current MP is Gavin Pearce of the Liberal Party, who was elected at the 2019 federal election.

The Division of Denison was an Australian electoral division in Tasmania, before being replaced by the Division of Clark as part of a 2016–17 redistribution.
This is a list of the members of the Australian House of Representatives in the First Australian Parliament, which was elected on 29 and 30 March 1901. There were 75 members, as required by the Constitution, as near as possible to twice the number of Senators which was then 36. South Australia and Tasmania had not been divided into electoral divisions in 1901 which resulted in the particular state voting as a single electorate. There were seven members for South Australia, and five members for Tasmania elected.
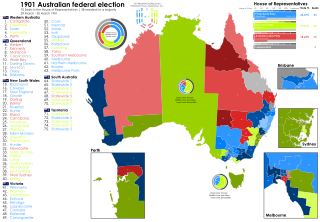
The 1901 Australian federal election for the inaugural Parliament of Australia was held in Australia on Friday 29 March and Saturday 30 March 1901. The elections followed Federation and the establishment of the Commonwealth of Australia on 1 January 1901. All 75 seats in the Australian House of Representatives, six of which were uncontested, as well as all 36 seats in the Australian Senate, were up for election.
In Australia, a redistribution is the process of redrawing the boundaries of electoral divisions for the House of Representatives arising from changes in population and changes in the number of representatives. There is no redistribution for the Senate as each State constitutes a division, though with multiple members. The Australian Electoral Commission (AEC), an independent statutory authority, oversees the apportionment and redistribution process for federal divisions, taking into account a number of factors. Politicians, political parties and the public may make submissions to the AEC on proposed new boundaries, but any interference with their deliberations is considered a serious offence.
The lower houses of the parliaments of the states and territories of Australia are divided into electoral districts. Most electoral districts send a single member to a state or territory's parliament using the preferential method of voting. The area of a state electoral district is dependent upon the Electoral Acts in the various states and vary in area between them. At present, there are 409 state electoral districts in Australia.
The voting rights of Indigenous Australians became an issue from the mid-19th century, when responsible government was being granted to Britain's Australian colonies, and suffrage qualifications were being debated. The resolution of universal rights progressed into the mid-20th century.

The 1909 Tasmanian state election was held on Friday, 30 April 1909 in the Australian state of Tasmania to elect 30 members of the Tasmanian House of Assembly. This was the first general election in the British Empire to elect all members through a form of proportional representation, the single transferable vote.
This is a list of electoral results for the Division of Bass in Australian federal elections from the division's creation in 1903 until the present.
This is a list of electoral results for the Division of Braddon in Australian federal elections from the division's creation in 1955 until the present.
This is a list of electoral results for the Division of Lyons in Australian federal elections from the division's creation in 1984 until the present.
This is a list of electoral results for the Division of Franklin in Australian federal elections from the division's creation in 1903 until the present.
This is a list of electoral results for the Division of Darwin in Australian federal elections from the division's creation in 1903 until its abolition in 1955.
This is a list of electoral results for the Division of Wilmot in Australian federal elections from the division's creation in 1903 until its abolition in 1984.

Women's suffrage in Australia was one of the early achievements of Australian democracy. Following the progressive establishment of male suffrage in the Australian colonies from the 1840s to the 1890s, an organised push for women's enfranchisement gathered momentum from the 1880s, and began to be legislated from the 1890s, decades in advance of Europe and North America. South Australian women achieved the right to vote in 1894, and to stand for office in 1895 following the world first Constitutional Amendment Act 1894. This preceded even male suffrage in Tasmania. Western Australia granted women the right to vote from 1899, although with some racial restrictions. In 1902, the newly established Australian Parliament passed the Commonwealth Franchise Act 1902, which set a uniform law enabling women to vote at federal elections and to stand for the federal parliament. By 1908, the remaining Australian states had legislated for women's suffrage for state elections. Grace Benny was elected as the first councillor in 1919, Edith Cowan the first state Parliamentarian in 1921, Dorothy Tangney the first Senator and Enid Lyons the first Member of the House of Representatives in 1943.
Suffrage in Australia is the voting rights in the Commonwealth of Australia, its six component states and territories, and local governments. The colonies of Australia began to grant universal male suffrage from 1856, with women's suffrage following between the 1890s and 1900s. Some jurisdictions introduced racial restrictions on voting from 1885. Such restrictions had been eradicated by the 1960s. Today, the right to vote at all levels of government is held by citizens of Australia over the age of 18 years.
References
- ↑ Commonwealth By-elections 1901–82. Canberra: Australian Electoral Commission. 1983.
- ↑ "1901 House of Representatives: Tasmania". Psephos Adam Carr's Election Archive. Retrieved 29 May 2022.