
The Wank is a mountain in southern Germany, situated in the Loisach valley close to the Austrian border in the southwestern Ester Mountains range near Garmisch-Partenkirchen. It rises from about 700 metres (2,300 ft) above mean sea level up to 1,780 metres (5,840 ft) at the summit. The mountain is crowned by a grassy summit which has views over Garmisch-Partenkirchen and the surrounding region. The summit can be reached via the eponymous Wankbahn, a cable car system that runs during the summer months, or by a network of footpaths that criss-cross the area. A mountain hut on the summit, the Wank-Haus, provides food and accommodation, and a nearby scientific observatory plays a role in monitoring atmospheric and climatic conditions. The Wank is a destination for hikers, day-trippers from Garmisch-Partenkirchen and paragliders.

The Altai Mountains, also spelled Altay Mountains, are a mountain range in Central Asia and Eastern Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan converge, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob have their headwaters. The massif merges with the Sayan Mountains in the northeast, and gradually becomes lower in the southeast, where it merges into the high plateau of the Gobi Desert. It spans from about 45° to 52° N and from about 84° to 99° E.

The Sayan Mountains are a mountain range in southern Siberia spanning southeastern Russia and northern Mongolia. Before the rapid expansion of Tsardom of Russia, the mountain range served as the border between Mongolian and Russian cultures and cultural influences.

Austria is a predominantly mountainous country in Central Europe, approximately between Germany, Italy and Hungary. It has a total area of 83,871 square kilometres (32,383 sq mi).

Dassel is a town in southern Lower Saxony, Germany, located in the district Northeim. It is located near the hills of the Solling mountains.

The Weser Uplands is a hill region in Germany, between Hannoversch Münden and Porta Westfalica, along the river Weser. The area reaches into three states, Lower Saxony, Hesse, and North Rhine-Westphalia. Important towns of this region include Bad Karlshafen, Holzminden, Höxter, Bodenwerder, Hameln, Rinteln, and Vlotho.

The Holzberg is a small range of hills up to 444.5 m above sea level (NHN) in south Lower Saxony, Germany.

The Hoher Meißner is a mountain massif with a height of 753.6 m and is located in the Meißner-Kaufunger Wald nature park in Hesse, Germany.

The Kaufungen Forest is a range of steep, wooded hills straddling the border between the states of Hesse and Lower Saxony in central Germany. It takes its name from the town Kaufungen.
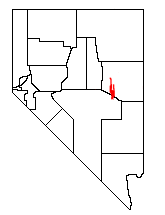
The White Pine Range is a group of mountains in southern White Pine County, in eastern Nevada. The range runs for approximately 51 miles (82 km) from Beck Pass in the north to Currant Pass in the south. To the west of the range are the Duckwater (Shoshone) tribal lands and the northern arm of large Railroad Valley. To the east are Jakes Valley and the northern part of the long White River Valley. To the south are the Horse and Grant Ranges.
Germany is a country in Central and Western Europe that stretches from the Alps, across the North European Plain to the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. It is the second-most populous country in Europe after Russia, and is seventh-largest country by area in the continent. The area of Germany ranked 63rd and covers 357,021 km2 (137,847 sq mi), consisting of 349,223 km2 (134,836 sq mi) of land and 7,798 km2 (3,011 sq mi) of waters, smaller than Japan but larger than Republic of the Congo.
The WeltWald Harz up to 2009 Arboretum Bad Grund, also known as Exotenwald and sometimes called the Arboretum des Forstamtes Grund or the Forstaboretum der Niedersächsischen Landesforstverwaltung, is an arboretum located along the B 242 federal highway near the Hübichenstein, northwest of Bad Grund, Lower Saxony, Germany. It is open daily without charge.
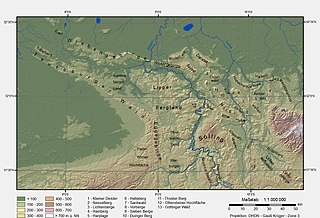
The Lower Saxon Hills are one of the 73 natural regions in Germany defined by the Federal Agency for Nature Conservation (BfN). Geographically it covers roughly the same area as the Weser Uplands in its wider sense.

The Leine Uplands is a region in Germany's Central Uplands which forms a part of the Lower Saxon Hills and lies along the River Leine between Göttingen and Hanover. It borders on the Weser Uplands in the west, the Innerste Uplands in the northeast, the Harz in the east and Untereichsfeld in the southeast.

The Ahlsburg is a range of bunter sandstone hills, relatively small in area and up to 411.4 m above sea level (NN), in the southern part of Lower Saxony, Germany. It lies within the Solling foreland and is part of the Weser-Leine Uplands.

At 527.8 m (1,732 ft) above sea level, the Große Blöße is the highest hill in the Solling-Vogler Nature Park, the Solling and the Weser Uplands.

The Solling-Vogler Nature Park is a nature park in South Lower Saxony in Germany. It has an area of 52,000 hectares (200 sq mi) and was established in 1966.

Mackensen is a village of about 450 inhabitants which is incorporated into the city of Dassel since 1974.

The Amtsberge are a small ridge of hills, up to 392.2 m above sea level (NN), near Dassel in southern Lower Saxony in Germany.
The Dehnenkopf in the Harz Mountains of central Germany is a summit about 775 m above sea level (NN) near Torfhaus in the unincorporated area of Harz in the county of Goslar in Lower Saxony.



















