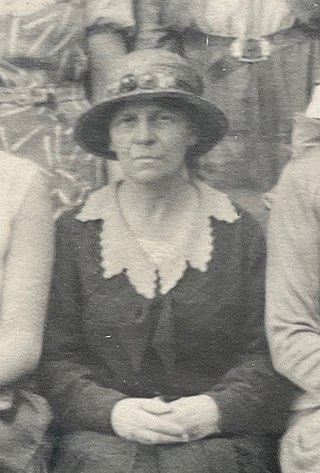The Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain (RPSGB) existed from its founding as the Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain in 1841 until 2010. The word "Royal" was added to its name in 1988. It was the statutory regulatory and professional body for pharmacists and pharmacy technicians in England, Scotland and Wales. In September 2010, the regulatory powers of the Society were transferred to the newly formed General Pharmaceutical Council (GPhC). The RPSGB became the Royal Pharmaceutical Society (RPS) at that time and retained its professional leadership role; the "Great Britain" part of the name was dropped for day-to-day purposes.
The Royal Pharmaceutical Society is the body responsible for the leadership and support of the pharmacy profession (pharmacists) within England, Scotland, and Wales. It was created along with the General Pharmaceutical Council (GPhC) in September 2010 when the previous Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain was split so that representative and regulatory functions of the pharmacy profession could be separated. Membership in the society is not a prerequisite for engaging in practice as a pharmacist within the United Kingdom. Its predecessor the Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain was founded on 15 April 1841.

The Pharmacy Act 1868 was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It was the major 19th-century legislation in the United Kingdom limiting the sale of poisons and dangerous drugs to qualified pharmacists and druggists.
Jean Kennedy Irvine was a pharmacist from Hawick, Scotland and the first woman president of the Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain.
Agnes Borrowman was a Scottish pharmaceutical chemist. In 1924 she became the first woman to serve on the Pharmaceutical Society's Board of Examiners.

Ida Hall Roby was first woman to graduate from the Pharmaceutical Department of the Illinois College of Pharmacy, Northwestern University, and the only woman pharmacist in Illinois at the end of the 19th century.
The National Association of Women Pharmacists was founded in London on 15 June 1905, following discussions between Margaret Elizabeth Buchanan and Isabella Skinner Clarke. Early meetings were held at Clarke's home. Membership was restricted to those who had passed the major or minor examination and 50 women joined immediately. By 1912 Buchanan claimed that practically all women practicing pharmacy were members. Buchanan served as its president at one point.

The Women's Coronation Procession was a suffragette march through London, England, on 17 June 1911, just before the Coronation of George V and Mary, demanding women's suffrage in the coronation year. The march was organised by the Women's Social and Political Union (WSPU). It was "the largest women’s suffrage march ever held in Britain and one of the few to draw together the full range of suffrage organisations".
Margaret Elizabeth Buchanan was a British pharmacist and pioneer of women in pharmacy.
Frances Elizabeth Deacon (1837–1930) was an English chemist and druggist who was the first woman to qualify after the 1868 Pharmacy Act, which made registration with the Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain (PSGB) compulsory in order to work as a pharmacist.
Isabella Skinner Clarke–Keer was a British pharmacist and pioneer of women in pharmacy. In 1875, she became the first woman to qualify as a Pharmaceutical Chemist, and was one of the first two women members of the Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain, admitted in 1879. In 1905, she became the first President of the National Association of Women Pharmacists.
Rose Coombes Minshull (1845–1905) was one of the first two women members of the Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain (PSGB), admitted in 1879.

Hope Constance Monica Winch was an English pharmacist and academic.
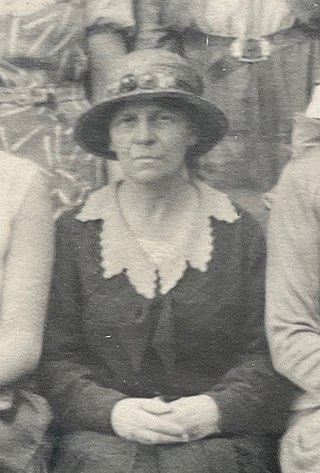
Katherine M King PhC was a pharmacist and joint proprietor of the Gordon Hall School of Pharmacy for Women in Gordon Square.
Ella Corfield was a British pharmacist, achieving pioneering academic work in her early career and later business management. She also held senior ranks in the British Red Cross.
Nora Priscilla Renouf was a British pharmaceutical chemist who was a pioneer for women’s involvement in the profession.
Elizabeth Leech was an English pharmacist known for her struggle to be admitted to the Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain.

Louisa Stammwitz was a British pharmacist whose campaigning contributed to the admission of women to the Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain, along with the efforts of Rose Minshull, Alice Hart, and Isabella Clarke.
Agnes Edith Lothian Short was a British pharmacist and librarian recognised for her expertise in the history of pharmacy, especially on drug jars.
Elsie Kassner was a British pharmacist who co-ran a pharmaceutical analysis company with Ella Corfield.