
Emmanuel Halgan (Donges, 31 December 1771 - Paris, 20 April 1852) was a French Navy officer and admiral. [1] [2]

Emmanuel Halgan (Donges, 31 December 1771 - Paris, 20 April 1852) was a French Navy officer and admiral. [1] [2]
Born to the family of a bailiff, Halgan joined the French Royal Navy aged 16. He then served as a lieutenant and first officer on merchantmen.
After rejoining the Navy, he served aboard the brig Curieux, captured by a British frigate in 1793. Halgan was taken prisoner. Upon his return to France, he served on the Terrible and on a number of other ships.
In 1798, Halgan received command of Aréthuse. The next year, Aréthuse was dismasted and captured by the 74-gun Excellent, off Portugal. The Royal Navy took Aréthuse into service as HMS Raven.
In 1800, Halgan was tasked with commissioning Clorinde, and then served as first officer on Clorinde as she was sent to Santo Domingo.
Upon his return to France, Halgan received command of the brig Épervier, with ensign Jérôme Bonaparte under his orders.
In Martinique, Halgan took temporary command of the 20-gun Berceau. He sailed to France, and in 1803, sailed to the Indian Ocean to warn of the outbreak of the War of the Third Coalition. At Mauritius, he joined up with Linois' squadron, engaging in commerce raiding. Berceau captured the 1500-ton Countess of Sutherland and on 3 December along with Motard's Sémillante destroyed outposts at Pulo Bay, which was about eight miles from Bencoolen.
Sailing towards the Sea of China, Halgan persuaded Linois to sail through the Gaspar Strait, of which he had studied recent maps. The French squadron then met a 26-ship convoy of the Honourable East India Company, leading to the not quite-Battle of Pulo Aura.
Promoted to capitaine de frégate, Halgan was sent to France and received command of the frigate Cybèle, but was then ordered to embark on the Vétéran instead, under Prince Jérôme Bonaparte.
In 1809, Halgan captained the Heureuse during the Battle of the Basque Roads. Heureuse was amongst the survivors of the battle.
In December 1813, with three companies of sailors and a fraction of the crews of his ships, Halgan defended the fortress of Hellevoetsluis, in Holland, against the attacks of several thousands insurgents. The French-held fortresses were later ordered abandoned due to the advances of the Allies, and the Meuse flotilla was scuttled in Willemstad. Halgan retreated to Anvers. When Anvers was shelled, he defended the harbour and helped preserve the ships and the naval installations.
After the Bourbon Restauration, Helgan was given command of the Superbe, sailing to the Caribbean.
Halgan the supervised the naval divisions of the Levant and of America. In 1819, he was nominated director for personnel at the Ministry of the Navy. He later returned to Levant to command a squadron, before returning to his office at the Ministry in 1824 and serving at the Council of State.
From 1819 to 1830, he sited at the Chamber of Deputies. In 1830, he presided the Commission of Naval Signals.
In 1837, he was made general inspector of the Harbours of the Ocean, and a Peer of France.
After retiring on 24 June 1841, by then a vice-admiral, Halgan was promoted to Grand Cross of the Legion of Honour.
The genus Halgania of small shrubs in the family Boraginaceae, which are native to Australia, was named in his honour.

The Battle of Pulo Aura was a minor naval engagement of the Napoleonic Wars, fought on 14 February 1804, in which a large convoy of Honourable East India Company (HEIC) East Indiamen, well-armed merchant ships, intimidated, drove off and chased away a powerful French naval squadron. Although the French force was much stronger than the British convoy, Commodore Nathaniel Dance's aggressive tactics persuaded Contre-Admiral Charles-Alexandre Durand Linois to retire after only a brief exchange of shot. Dance then chased the French warships until his convoy was out of danger, whereupon he resumed his passage toward British India. Linois later claimed that the unescorted British merchant fleet was defended by eight ships of the line, a claim criticised by contemporary officers and later historians.

Charles-Alexandre Léon Durand, Comte de Linois was a French admiral who served in the French Navy during the reign of Napoleon Bonaparte. He commanded the combined Franco-Spanish fleet during the Algeciras Campaign in 1801, winning the First Battle of Algeciras before losing the Second Battle of Algeciras. He then led an unsuccessful campaign against British trade in the Indian Ocean and South China Sea in 1803, being defeated by a harmless fleet of the East India Company during the Battle of Pulo Aura and ending his cruise and sea-going career being bested in battle by John Warren in the action of 13 March 1806. Following the Bourbon restoration, Linois was appointed Governor of Guadeloupe. He supported Napoleon during the Hundred Days and so, on his return to France, he was forced to resign and was court martialled. Although acquitted, he was placed in retirement and never served again.

The Sémillante was a 32-gun frigate of the French Navy and the lead ship of her class. She was involved in a number of multi-vessel actions against the Royal Navy, particularly in the Indian Ocean. She captured a number of East Indiamen before she became so damaged that the French disarmed her and turned her into a merchant vessel. The British captured her and broke her up in 1809.

Pierre-François-Henri-Étienne Bouvet de Maisonneuve was a French Navy officer and privateer.
Clorinde was a 44-gun Uranie-class frigate of the French Navy. The Royal Navy captured her in 1803 and took her into service as HMS Clorinde. She was sold in 1817.

The Atlantic campaign of 1806 was one of the most important and complex naval campaigns of the post-Trafalgar Napoleonic Wars. Seeking to take advantage of the withdrawal of British forces from the Atlantic in the aftermath of the Battle of Trafalgar, Emperor Napoleon ordered two battle squadrons to sea from the fleet stationed at Brest, during December 1805. Escaping deep into the Atlantic, these squadrons succeeded in disrupting British convoys, evading pursuit by British battle squadrons and reinforcing the French garrison at Santo Domingo. The period of French success was brief: on 6 February 1806 one of the squadrons, under Vice-Admiral Corentin Urbain Leissègues, was intercepted by a British squadron at the Battle of San Domingo and destroyed, losing all five of its ships of the line.
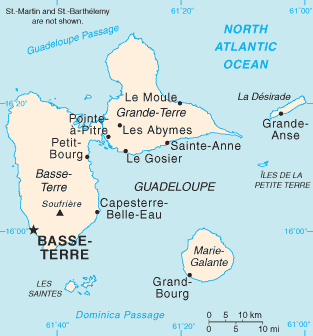
Roquebert's expedition to the Caribbean, was an unsuccessful operation by a French naval squadron to transport supplies to Guadeloupe in December 1809 at the height of the Napoleonic Wars. Over the previous year, British Royal Navy squadrons had isolated and defeated the French Caribbean colonies one by one, until by the autumn Guadeloupe was the only colony remaining in French hands. Cut off from the rest of the world by British blockade squadrons that intercepted all ships coming to or from the island, Guadeloupe was in a desperate situation, facing economic collapse, food shortages and social upheaval, as well as the impending threat of British invasion. In an effort to reinforce and resupply the colony, the French government sent four vessels to the West Indies in November 1809 under Commodore François Roquebert. Two of the ships were 20-gun flûtes carrying supplies and troops. The two others were 40-gun frigates, ordered to protect the storeships on their journey from the British forces operating off both the French and Guadeloupe coasts.
Félicité was a 32-gun frigate of the French Navy, lead ship of her class. Captured by the British Royal Navy and sold to the State of Haiti, she entered Haitian service as Améthyste.

Linois's expedition to the Indian Ocean was a commerce raiding operation launched by the French Navy during the Napoleonic Wars. Contre-Admiral Charles-Alexandre Durand Linois was ordered to the Indian Ocean in his flagship Marengo in March 1803 accompanied by a squadron of three frigates, shortly before the end of the Peace of Amiens. When war between Britain and France broke out in September 1803, Marengo was at Pondicherry with the frigates, but escaped a British squadron sent to intercept it and reached Isle de France. The large distances between naval bases in the Indian Ocean and the limited resources available to the British commanders in the region made it difficult to concentrate sufficient forces to combat a squadron of this size, and Linois was subsequently able to sustain his campaign for three years. From Isle de France, Linois and his frigates began a series of attacks on British commerce across the Eastern Indian Ocean, specifically targeting the large convoys of East Indiamen that were vital to the maintenance of trade within the British Empire and to the British economy. Although he had a number of successes against individual merchant ships and the small British trading post of Bencoolen, the first military test of Linois squadron came at the Battle of Pulo Aura on 15 February 1804. Linois attacked the undefended British China Fleet, consisting of 16 valuable East Indiamen and 14 other vessels, but failed to press his military superiority and withdrew without capturing a single ship.

The Battle of Vizagapatam was a minor naval engagement fought in the approaches to Vizagapatam harbour in the Coastal Andhra region of British India on the Bay of Bengal on 15 September 1804 during the Napoleonic Wars. A French squadron under Contre-Admiral Charles-Alexandre Léon Durand Linois in the ship of the line Marengo attacked the British Royal Navy fourth rate ship HMS Centurion and two East Indiaman merchant ships anchored in the harbour roads. Linois was engaged in an extended raiding campaign, which had already involved operations in the South China Sea, in the Mozambique Channel, off Ceylon and along the Indian coast of the Bay of Bengal. The French squadron had fought one notable engagement, at the Battle of Pulo Aura on 15 February 1804, in which Linois had attacked the Honourable East India Company's (HEIC) China Fleet, a large convoy of well-armed merchant ships carrying cargo worth £8 million. Linois failed to press the attack and withdrew with the convoy at his mercy, invoking the anger of Napoleon when the news reached France.

The action of 13 March 1806 was a naval engagement of the Napoleonic Wars, fought when a British and a French squadron met unexpectedly in the mid-Atlantic. Neither force was aware of the presence of the other prior to the encounter and were participating in separate campaigns. The British squadron consisted of seven ships of the line accompanied by associated frigates, led by Rear-Admiral Sir John Borlase Warren, were tasked with hunting down and destroying the French squadron of Contre-Admiral Jean-Baptiste Willaumez, which had departed Brest for raiding operations in the South Atlantic in December 1805, at the start of the Atlantic campaign of 1806. The French force consisted of one ship of the line and one frigate, all that remained of Contre-Admiral Charles-Alexandre Durand Linois' squadron that had sailed for the Indian Ocean in March 1803 during the Peace of Amiens. Linois raided British shipping lanes and harbours across the region, achieving limited success against undefended merchant ships but repeatedly withdrawing in the face of determined opposition, most notably at the Battle of Pulo Aura in February 1804. With his stores almost exhausted and the French ports east of the Cape of Good Hope that could have offered him replenishment eliminated, Linois decided to return to France in January 1806, and by March was inadvertently sailing across the cruising ground of Warren's squadron.

Berceau was a 22-gun corvette of the French Navy, built to a design by Jacques-Noël Sané, and launched in 1794. The Americans captured her in 1800 but restored her to France the next year. She then served in the Indian Ocean before returning to Spain, where she was broken up in 1804.

The Atalante was a 40-gun Virginie-class frigate of the French Navy, launched in 1802.

The Atlantic campaign of 1806 was a complicated series of manoeuvres and counter-manoeuvres conducted by squadrons of the French Navy and the British Royal Navy across the Atlantic Ocean during the spring and summer of 1806, as part of the Napoleonic Wars. The campaign followed directly from the Trafalgar campaign of the year before, in which the French Mediterranean fleet had crossed the Atlantic, returned to Europe and joined with the Spanish fleet. On 21 October 1805, this combined force was destroyed by a British fleet under Lord Nelson at the Battle of Trafalgar, although the campaign did not end until the Battle of Cape Ortegal on 4 November 1805. Believing that the French Navy would not be capable of organised resistance at sea during the winter, the First Lord of the Admiralty Lord Barham withdrew the British blockade squadrons to harbour. Barham had miscalculated – the French Atlantic fleet, based at Brest, had not been involved in the Trafalgar campaign and was therefore at full strength. Taking advantage of the reduction in the British forces off the port, Napoleon ordered two heavy squadrons to sea, under instructions to raid British trade routes while avoiding contact with equivalent Royal Navy forces.

The Java campaign of 1806–1807 was a minor campaign during the Napoleonic Wars by British Royal Navy forces against a naval squadron of the Kingdom of Holland, a client state of the French Empire, based on the island of Java in the Dutch East Indies. Seeking to eliminate any threat to valuable British merchant convoys passing through the Malacca Straits, Rear-Admiral Sir Edward Pellew determined in early 1806 that the Dutch naval forces based at Java, which included several ships of the line and three frigates, had to be defeated to ensure British dominance in the region. Lacking the forces to effect an invasion of the Dutch colony, Pellew instead sought to isolate and blockade the Dutch squadron based at Batavia in preparation for raids specifically targeting the Dutch ships with his main force.

The Raid on Batavia of 27 November 1806 was a successful attempt by a large British naval force to destroy the Dutch squadron based on Java in the Dutch East Indies that posed a threat to British shipping in the Straits of Malacca. The British admiral in command of the eastern Indian Ocean, Rear-Admiral Sir Edward Pellew, led a force of four ships of the line, two frigates and brig to the capital of Java at Batavia, in search of the squadron, which was reported to consist of a number of Dutch ships of the line and several smaller vessels. However the largest Dutch ships had already sailed eastwards towards Griessie over a month earlier, and Pellew only discovered the frigate Phoenix and a number of smaller warships in the bay, all of which were driven ashore by their crews rather than engage Pellew's force. The wrecks were subsequently burnt and Pellew, unaware of the whereabouts of the main Dutch squadron, returned to his base at Madras for the winter.
Pierre-Marie Le Bozec was a French Navy officer.

The Algeciras campaign was an attempt by a French naval squadron from Toulon under Contre-Admiral Charles Linois to join a French and Spanish fleet at Cadiz during June and July 1801 during the French Revolutionary Wars prior to a planned operation against either Egypt or Portugal. To reach Cadiz, the French squadron had to pass the British naval base at Gibraltar, which housed the squadron tasked with blockading Cadiz. The British squadron was commanded by Rear-Admiral Sir James Saumarez. After a successful voyage between Toulon and Gibraltar, in which a number of British vessels were captured, the squadron anchored at Algeciras, a fortified port city within sight of Gibraltar across Gibraltar Bay. On 6 July 1801, Saumarez attacked the anchored squadron, in the First Battle of Algeciras. Although severe damage was inflicted on all three French ships of the line, none could be successfully captured and the British were forced to withdraw without HMS Hannibal, which had grounded and was subsequently seized by the French.

Ange René Armand, Baron de Mackau was a French naval officer and politician. In 1825, he led 14 brigs of war to Haiti in one of the earliest instances of gunboat diplomacy, forcing the recently emancipated people of Haiti to pay 150 million francs to their former enslavers. The Mackau Law that he later instigated as Minister of the Navy and of Colonies paved the way for the abolition of slavery.

The Invasion of Guadeloupe was the last conflict between French and British forces during the Napoleonic Wars, and took place after Napoleon's defeat at Waterloo.