Related Research Articles

In atomic physics, the Bohr model or Rutherford–Bohr model of the atom, presented by Niels Bohr and Ernest Rutherford in 1913, consists of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons. It is analogous to the structure of the Solar System, but with attraction provided by electrostatic force rather than gravity, and with the electron energies quantized.

Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses computer simulations to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses methods of theoretical chemistry incorporated into computer programs to calculate the structures and properties of molecules, groups of molecules, and solids. The importance of this subject stems from the fact that, with the exception of some relatively recent findings related to the hydrogen molecular ion, achieving an accurate quantum mechanical depiction of chemical systems analytically, or in a closed form, is not feasible. The complexity inherent in the many-body problem exacerbates the challenge of providing detailed descriptions of quantum mechanical systems. While computational results normally complement information obtained by chemical experiments, it can occasionally predict unobserved chemical phenomena.

Henry Gwyn Jeffreys Moseley was an English physicist, whose contribution to the science of physics was the justification from physical laws of the previous empirical and chemical concept of the atomic number. This stemmed from his development of Moseley's law in X-ray spectra.
Quantum chemistry, also called molecular quantum mechanics, is a branch of physical chemistry focused on the application of quantum mechanics to chemical systems, particularly towards the quantum-mechanical calculation of electronic contributions to physical and chemical properties of molecules, materials, and solutions at the atomic level. These calculations include systematically applied approximations intended to make calculations computationally feasible while still capturing as much information about important contributions to the computed wave functions as well as to observable properties such as structures, spectra, and thermodynamic properties. Quantum chemistry is also concerned with the computation of quantum effects on molecular dynamics and chemical kinetics.

The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the size of its atom, usually the mean or typical distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost isolated electron. Since the boundary is not a well-defined physical entity, there are various non-equivalent definitions of atomic radius. Four widely used definitions of atomic radius are: Van der Waals radius, ionic radius, metallic radius and covalent radius. Typically, because of the difficulty to isolate atoms in order to measure their radii separately, atomic radius is measured in a chemically bonded state; however theoretical calculations are simpler when considering atoms in isolation. The dependencies on environment, probe, and state lead to a multiplicity of definitions.
In physics, a correspondence principle is any one of several premises or assertions about the relationship between classical and quantum mechanics. The physicist Niels Bohr coined the term in 1920 during the early development of quantum theory;he used it to explain how quantized classical orbitals connect to quantum radiation. Modern sources often use the term for the idea that the behavior of systems described by quantum theory reproduces classical physics in the limit of large quantum numbers: for large orbits and for large energies, quantum calculations must agree with classical calculations. A "generalized" correspondence principle refers to the requirement for a broad set of connections between any old and new theory.
An operational definition specifies concrete, replicable procedures designed to represent a construct. In the words of American psychologist S.S. Stevens (1935), "An operation is the performance which we execute in order to make known a concept." For example, an operational definition of "fear" often includes measurable physiologic responses that occur in response to a perceived threat. Thus, "fear" might be operationally defined as specified changes in heart rate, galvanic skin response, pupil dilation, and blood pressure.

In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6, meaning that the 1s, 2s, and 2p subshells are occupied by two, two, and six electrons, respectively.
A scientific theory is an explanation of an aspect of the natural world and universe that can be repeatedly tested and corroborated in accordance with the scientific method, using accepted protocols of observation, measurement, and evaluation of results. Where possible, some theories are tested under controlled conditions in an experiment. In circumstances not amenable to experimental testing, theories are evaluated through principles of abductive reasoning. Established scientific theories have withstood rigorous scrutiny and embody scientific knowledge.
In spectroscopy, the Rydberg constant, symbol for heavy atoms or for hydrogen, named after the Swedish physicist Johannes Rydberg, is a physical constant relating to the electromagnetic spectra of an atom. The constant first arose as an empirical fitting parameter in the Rydberg formula for the hydrogen spectral series, but Niels Bohr later showed that its value could be calculated from more fundamental constants according to his model of the atom.
Scientific laws or laws of science are statements, based on repeated experiments or observations, that describe or predict a range of natural phenomena. The term law has diverse usage in many cases across all fields of natural science. Laws are developed from data and can be further developed through mathematics; in all cases they are directly or indirectly based on empirical evidence. It is generally understood that they implicitly reflect, though they do not explicitly assert, causal relationships fundamental to reality, and are discovered rather than invented.
Scientific realism is the view that the universe described by science is real regardless of how it may be interpreted. A believer of scientific realism takes the universe as described by science to be true, because of their assertion that science can be used to find the truth about both the physical and metaphysical in the Universe.

Soot is a mass of impure carbon particles resulting from the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons. It is more properly restricted to the product of the gas-phase combustion process but is commonly extended to include the residual pyrolysed fuel particles such as coal, cenospheres, charred wood, and petroleum coke that may become airborne during pyrolysis and that are more properly identified as cokes or char.

The emission spectrum of atomic hydrogen has been divided into a number of spectral series, with wavelengths given by the Rydberg formula. These observed spectral lines are due to the electron making transitions between two energy levels in an atom. The classification of the series by the Rydberg formula was important in the development of quantum mechanics. The spectral series are important in astronomical spectroscopy for detecting the presence of hydrogen and calculating red shifts.
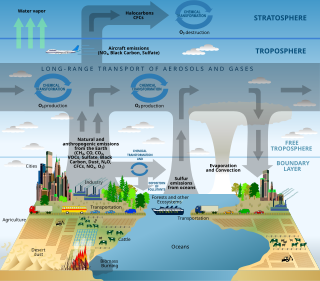
Scientific modelling is an activity that produces models representing empirical objects, phenomena, and physical processes, to make a particular part or feature of the world easier to understand, define, quantify, visualize, or simulate. It requires selecting and identifying relevant aspects of a situation in the real world and then developing a model to replicate a system with those features. Different types of models may be used for different purposes, such as conceptual models to better understand, operational models to operationalize, mathematical models to quantify, computational models to simulate, and graphical models to visualize the subject.
The history of quantum mechanics is a fundamental part of the history of modern physics. The major chapters of this history begin with the emergence of quantum ideas to explain individual phenomena—blackbody radiation, the photoelectric effect, solar emission spectra—an era called the Old or Older quantum theories. Building on the technology developed in classical mechanics, the invention of wave mechanics by Erwin Schrödinger and expansion by many others triggers the "modern" era beginning around 1925. Paul Dirac's relativistic quantum theory work lead him to explore quantum theories of radiation, culminating in quantum electrodynamics, the first quantum field theory. The history of quantum mechanics continues in the history of quantum field theory. The history of quantum chemistry, theoretical basis of chemical structure, reactivity, and bonding, interlaces with the events discussed in this article.
Theoretical physics is a branch of physics that employs mathematical models and abstractions of physical objects and systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena. This is in contrast to experimental physics, which uses experimental tools to probe these phenomena.
The Planck constant, or Planck's constant, denoted by , is a fundamental physical constant of foundational importance in quantum mechanics: a photon's energy is equal to its frequency multiplied by the Planck constant, and the wavelength of a matter wave equals the Planck constant divided by the associated particle momentum.

Semiconductor lasers or laser diodes play an important part in our everyday lives by providing cheap and compact-size lasers. They consist of complex multi-layer structures requiring nanometer scale accuracy and an elaborate design. Their theoretical description is important not only from a fundamental point of view, but also in order to generate new and improved designs. It is common to all systems that the laser is an inverted carrier density system. The carrier inversion results in an electromagnetic polarization which drives an electric field . In most cases, the electric field is confined in a resonator, the properties of which are also important factors for laser performance.
All models are wrong is a common aphorism and anapodoton in statistics; it is often expanded as "All models are wrong, but some are useful". The aphorism acknowledges that statistical models always fall short of the complexities of reality but can still be useful nonetheless. The aphorism originally referred just to statistical models, but it is now sometimes used for scientific models in general.
References
- ↑ Hall, Carl W.; Hinman, George W. (1983), Dictionary of Energy, CRC Press, p. 84, ISBN 0824717937
- 1 2 McMullin, Ernan (1968), “What Do Physical Models Tell Us?”, in B. van Rootselaar and J. F. Staal (eds.), Logic, Methodology and Science III. Amsterdam: North Holland, 385–396.
- ↑ Roman, Frigg; Hartmann, Stephan (27 February 2006). "Models in Science". In Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2012 ed.). Retrieved 24 July 2015.